![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
How is evolution supported by biological molecules? |
• There is a huge variety of different organisms but they share the same biochemical base. • For example, they use the same nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) • Means that plants and animals are more likely to have the same common ancestor. |
|
|
What are polymers? Examples? |
• They are complex molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together by undergoing the process of polymerisation. • Natural examples: polysaccharides, polypeptides and polynucleotides. • Unnatural examples: polythene and polyester. |
|
|
What are monomers? Examples? |
• They are smaller units from which larger molecules are made. • Examples: monosaccharides, amino acids and nucleotides. |
|
|
How does a condensation reaction work? |
Joins two molecules together with the formation of a chemical bond and the elimination of a molecule of water. |
|
|
How does a hydrolysis reaction work? |
It breaks a chemical bond between two molecules and involves a molecule of water. |
|
|
What is a mole? |
It is the SI unit for measuring amount of substance. |
|
|
What is a molar solution? |
It is a solution that contains one mole of solute in each litre of solution. |
|
|
What is metabolism? |
Chemical processes that take place in living organisms. |
|
|
What are monosaccharides? General formula? Examples? |
• They are monomers from which larger carbohydrates are made of. (Contains C, H, O) • (CH2O)n • Glucose, fructose, galactose. |
|
|
What are maltose, sucrose and lactose made of? |
• Maltose - Two alpha glucose. • Sucrose - glucose and fructose. • Lactose - glucose and galactose. |
|
|
Test for reducing sugar? |
1) Take a 2cm^3 sample of the food sample (if not in liquid form then grind up in water). 2) Add equal volume of benedict's reagent (blue) 3) Place in hot water bath that has been brought to the boil for about 5 minutes. 4) Should form a precipitate in this order: green -> yellow -> orange -> brick red. |
|
|
Test for non-reducing sugar? |
1) Take a 2cm^3 sample of the food sample (if not in liquid form then grind up in water). 2) Add 2cm^3 of dilute hydrochloric acid and add too hot water bath brought to the boil (hydrolyse any dissacharide to a monosaccharide). 3) Neutralise by adding sodium hydrogencarbonate (test with pH paper to check if it's still alkaline or the benedict's won't work). 4) Add benedict's reagent and do what you'd do for a reducing sugar test. 5) Should form a precipitate in this order: green -> yellow -> orange -> brick red. |
|
|
How can you compare the amounts of reducing sugars? |
• Filter and weigh the precipitate • Remove precipitate and use colorimeter to see how much of the benedict's had been absorbed. |
|
|
How does the benedict's reagent form a precipitate in the presence of a reducing sugar? |
Benedict's reagent is an alkaline solution of copper (ll) sulfate. When it is heated with a benedict's reagent the it turns into an insoluble red precipitate of copper (l) oxide. |
|
|
How are polysaccharides formed? |
By a condensation reaction between many glucose units. |
|
|
Give a few basic facts about starch. |
• Plants use it to store excess glucose. • Amylose - long, unbranched chains of alpha glucose. Angles of glycosidic bonds give it a coiled structure, OH groups inwards form hydrogen bonds to hold the helix in place. Makes it compact so it fits more. • Amylopectin - long, branched chains of alpha glucose. Side branches allows enzymes to nreak the molecule to get at the glycosidic bonds easily, so glucose is released quicker. • It is in insoluble (good for storage) in water and doesn't affect the water potential. This means water can'take enter by osmosis (which would make them swell). |
|
|
Give some facts about glycogen. |
• Animals store excess glucose as glycogen. • It is similar to amylopectin except it has loads more side chains, meaning that glucose can be released even more quickly with the help of enzymes. • Very compact, which makes them good storage molecules. • Need it for animals as they have a higher metabolic rate as animals are more active than plants. • It is in insoluble (good for storage) in water and doesn't affect the water potential. This means water can'take enter by osmosis (which would make them swell). |
|
|
Give a few facts about cellulose |
• They are long unbranched chains of beta glucose. • The straight cellulose chains are linked together by hydrogen bonds to form strong fibres called microfibrils. • Gives structural support to plant cells. • Cell wall prevents cells from bursting by exerting an inward pressure that stops any further influx of water. This provides it with a maximum surface area. |
|
|
Test for starch? |
• Add a few drops of potassium iodide solution to your solution and shake/stir. • Positive - blue/black • Negative - orange/brown |
|
|
How triglycerides made? |
By a condensation reaction of one molecule of glycerol and three fatty acid molecules. |
|
|
What does fatty acids look like? |
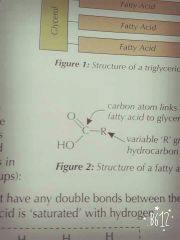
|
|
|
Why are lipids polar? |
Because the head and the tail do different things. |
|
|
What does a phospholipid consist of? |
A phosphate group, glycerol and two fatty acids. |
|
|
Name the properties of triglycerides. |
• They are energy storage molecules. • Lots of chemical energy is released because of the hydrocarbon tails, twice as much energy per gram compared to carbohydrates. • Bundle together to make insoluble droplets when in water. • It is in insoluble (good for storage) in water and doesn't affect the water potential. This means water can'take enter by osmosis (which would make them swell). |
|
|
Low mass to energy ratio |
. |
|
|
Name some properties of phospholipids. |
• Make up a bilayer of cell membranes. • Controls what enter and exits the leaf. • Form a double-layer so water-soluble substances can't pass through easily. |
|
|
Test for lipids |
• Shake the 2cm^3 substance with 5cm^3 of ethanol for a minute. • The pour into 5cm^3 of water. • Any lipid will show a milky-white emulsion. |
|
|
The role of lipids? |
• Source of energy - when oxidised provides twice as much energy per gram compared to carbohydrates. • Waterproofing - It is insoluble so waxy layers of insects/plants could conserve water. Mammals can produce oily secretion from glands). • Insulation - Slow conductors of heat to retain body heat. • Protection - around delicate organs like the kidney. |
|
|
What are amino acids? |
Monomers from which proteins are made. |
|
|
What does a functional group consist of? |
One or many polypeptides. |
|
|
What does an amino acid look like? |

|
|
|
Define primary structure. |
The number and sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. |
|
|
Define secondary structure. |
• Not flat/straight. • Hydrogen bonds form. • Coil into alpha helix or fold into beta pleated sheet. |
|
|
All living things consist of 20 amino acids. What is the difference between these? |
What makes up the carbon containing R group. |
|
|
Define tertiary structure. |
• Coiled or folded even more. • Consists of: hydrogen bonds (easily broken), ionic bonds (attractions between positive and negative charges on different parts of the molecule, broken by changes in pH) and disulfide bridges (two molecules of cysteine come close together and the sulfur there bonds, strongest bond). • Forms final 3D structure. |
|
|
Define quaternary structure. |
More than one polypeptide chain, is assembled together (protein). |
|
|
Give four proteins and how they are adapted and their jobs. |
• Enzymes - Spherical (due to tight folding sliding in polypeptide chains). It is soluble. It also has roles in metabolism or synthesis large molecules. • Antibodies - Involved in immune response, made of 2 light (short) and 2 heavy (long) polypeptide chains. They have variable regions (amino acids vary greatly). • Transport proteins - for example channel proteins in the cell membranes contain hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acids, causes protein to fold up. Transports molecules and ions. • Structural proteins - they are strong. Long polypeptide chains that lay parallel to each other with cross-lines. Supportive tissue in animals i.e. hair. |
|
|
Test for proteins? |
• The solution needs to be alkaline so you'd have to add sodium hydroxide solution. • Then add a few drops of copper (ll) sulfate solution. • Should go from blue to purple. • Could use biuret's reagent. |
|
|
What are fibrous and globular proteins? |
• Fibrous - such as collagen have structural functions. • Globular - such as enzymes and haemoglobin carry out metabolic functions. |
|
|
What are enzymes? |
They are biological catalysts that speed up metabolic reactions. They can affect structures in organisms. |
|
|
Enzyme activity can be intracellular or extracellular. |
. |
|
|
What do enzymes do to the activation energy? How? |
They lower the activation energy because: • It holds two substrates close together and reduces any repulsion between molecules so they bond easily. • When the enzyme fits in the active site it puts a strain on the bond in the substrate. So the substrate molecule breaks up more easily. |
|
|
How does lock and key work? |
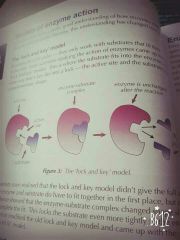
|
|
|
How does induced fit work? |
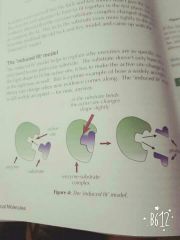
|
|
|
Give some properties of enzymes. |
• Catalyse one reaction (due to complementary substrates). • If the tertiary structure is altered, the active site would be altered preventing the enzyme-substrate complex from functioning. • Primary sequence is determined by gene, if that gene has a mutation it could affect the tertiary structure. |
|
|
How can you measure enzyme activity? |
• How fast the product is made (measuring the amount of end product there is present at different times). • How fast the substrate is broken down (measuring substrate levels at different times. • Plot on graph, calculate the percentage change and look at the correlation. And work out the gradient. |
|
|
How does temperature affect enzyme activity? |
• More heat means that there's more kinetic energy so molecules move faster. But too much heat means that bond can be broken, so the active site becomes denatured. • At low temperatures, the substrate fits. |
|
|
How does pH affect enzyme activity? |
• Optimum for most parts of the human is pH 7. • Above or below means that the H+ or the OH- ions can disrupt the ionic bonds and the hydrogen bonds. Which leads to the tertiary structure being denatured. |
|
|
How does substrate and enzyme concentration affect enzyme activity? |
It would increase the rate of reaction but then it would level off, when there's an excess. When it levels off that means the rate isn't increasing. It hasn't stopped. |
|
|
How does a competitive and non-competitive inhibitor work? |

• Competitive inhibitor - Similar shape to substrate. Takes up the active site but doesn't react. A high concentration of substrate may increase chances of the substrate getting a space. • Non-competitive inhibitor - Bind away from the active site. Denaturing and changes the active site so no substrate can fit. Increasing the substrate concentration won't make a difference. |
|
|
How does end product inhibition work? Is it competitive or non-competitive. |

If the concentration of the end product is high, then there will be greater inhibition to enzyme A, returns to normal. Non-competitive. |
|
|
How can you measure how fast the product of a reaction appears under different conditions. |

|
|
|
How can you measure how fast the substrate is broken down? |

|
|

Answer 1a. |

|
|
|
Sucrose is a non-reducing sugar. Describe a biochemical test you could use to identify the presence of a non-reducing sugar. |
• Heat in hot water bath with benedict's reagent to ensure it's not a reducing sugar. • Add dilute hydrochloric acid • Neutralise with sodium hydrogencarbonate. • Heat with benedict's reagent. • Coloured precipitate should form. |
|
|
Describe the process by which pepsin breaks down a protein. |
• Forms an enzyme-substrate complex. • Lowers the activation energy (by putting a strain on the polypeptide chains). • Reaction is catalysed and the products are released. |

