![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the sensory nerves? |
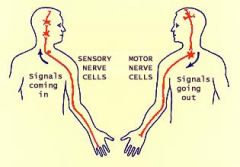
The ones that perceive sensations |
|
|
What are the motor nerves? |
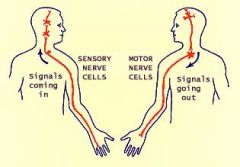
The ones that react towards the sensantion perceived (reaction to the perception) |
|
|
What is the function of the CNS? |
It interprets and stores information. Issues orders to muscles and glands. |
|
|
What is the CNS made up of? |
Brain and spinal cord |
|
|
Function of the Peripheral NS |
Indicates you how to act and it takes the inforation received to the CNS |
|
|
What is the PNS Somatic? |
is the voluntaty movements that you do. [If you want to open a can, then the pns somatic will realize the action] |
|
|
What is the PNS Autonomic? |
Is the involuntary action done by our body such as blinking, breathing, pumping blood, etc. |
|
|
Divisions of the Autonomic PNS |
Sympathetic NS and Parasympathetic NS |
|
|
What is the sympathetic NS? |
The ns that increases the output of energy during stress and emotion [arouses the body] [fight or flight] |
|
|
What is the parasympathetic NS? |
The ns that relaxes the body and conserves energy [calms after arousal] |
|
|
Parts of a neuron |
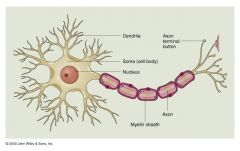
-dendrites -axon -myelin sheath -synaptic cleft -axon terminal -cell body |
|
|
Function of the Dendrites |
Receives information from other neurons and transmits it to the cell body |
|
|
Function of the axon |
Transmits neural signals from the cell body to the terminal endings |
|
|
What is the myelin sheath? |
Is a protein that surrounds the axon and facilitates conduction of electrical impulses. |
|
|
What is the cell body (neurons) ame up of? |
Is made up of synaptic information that is then transmitted to other cells. |
|
|
What is the nucleus (neurons)? |
The one that contains genetic material in chromosomes |
|
|
What are the axon terminals? |
Where the chemical from one neuron is converted into another chemical that is transmitted to a dif. neuron |
|
|
What can the axon terminal lie near? |
Dendrites of neighboring neurons |
|
|
What are neurotransmitters? |
Chem. subtance released from one neuron that alters the activity of the receiving neuron. |
|
|
How do neurotransmitters function? |
They allow signals to pass across the synapse from axon to dendrite. |
|
|
What is a synapse? |
Junction between two neurons where transmission of a nerve impulse take place. |
|
|
In how many parts is the brain divided and what are their names? |
In two: left and right hemisphere. |
|
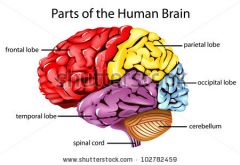
Cerebral cortex's lobes' names
|
Frontal lobe
Temporal Lobe
Parietal Lobe
Occipital Lobe |
|
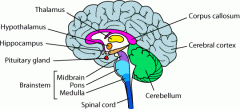
What is the function of the brain stem? and its parts
|
It helps with basic life functions such as heartbeat, breathing blood pressuting etc.
[Made up of medulla, midbrain and pons] |
|
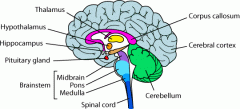
Function of the Cerebellum |
Helps with balance, posture and coordination. |
|
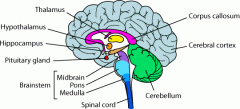
Thalamus's function |
Controls incoming and outgoing signals |
|
|
Whta is the function of the Hypothalamus? |
Set of glands that control hormonal processes.
[Regulates mood, thirst, hunger, temp, etc] |
|
|
Function of the Pituitary gland |
Endrocine gland that regulates other endrocine glands and releases hormones |
|
|
What is the cerebrum for? |
Is the largest part of the brain and in charge of most cognitive processes |
|
|
What is the Hypocampus for? |
Used for learning memory, helps analyzaze. [converts temp. memories into permanent ones] |
|
|
Function of the Amygdala |
Involved in arousal and stimulation of emotion. [Helps to store memory in dif. senses] |
|
|
What is the cerebral cortex? |
Thin layers of cell covering the cerebrum; responsible for thinking metal functions. [sensing, thinking, learning, emotion, consciueness, etc] |
|
|
What is the corpus callosum? |
Bridge of nerve fibers that connect the two hemispheres. |
|
|
What is the medulla? |
Structure in the brain stem responsible for certain autonomic pns function such as heart beating, breathinf, circulation, etc. |
|
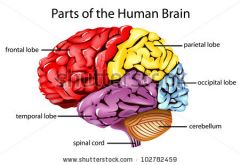
Function fo the FRONTAL LOBE |
Controls creative thought, problem solving, behavior, attention, smell, personality among others. |
|
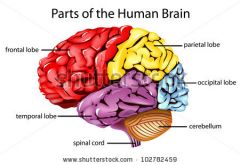
Function of the TEMPORAL LOBE |
Controls visual and auditory memories. |
|
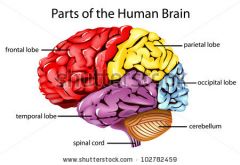
Funtion of the PARIETAL LOBE |
Focuses on comprehension, language, reading. |
|
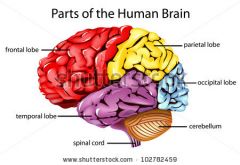
Function of the OCCIPITAL LOBE |
Helps to control vision. |
|
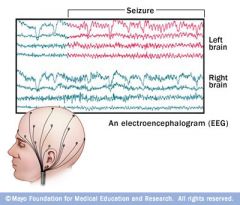
What is the Electroencephalogram for (EEC)? |
To record neural activity detected by electrodes |
|
|
What is lateralization? |
Specialization of the two hemispheres for part. operations [left hand/right leg; right hand/left leg (crawling)] |
|
|
What is MELATONIN? |
Hormone involved in regulation of daily biological rythyms. |
|
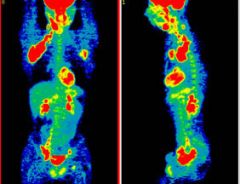
What is the PET SCAN? |
Method for analyzing biochem activity by injecting a radioactive element. |
|
|
What is the cerebral hemisphere? |
The two halves of the cerebrum |
|
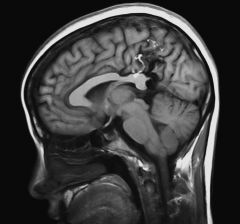
What is a MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGE (MRI) ? |
Method for studying body and brain using ganteic fields and special radio receivers. |
|
|
What are endorhins? |
Chem. subtances released for pain reduction, pleasure and memory. |
|
|
What are hormones? |
Chem sub secreted by glands that affect other glands |
|
|
What are adrenal hormones? |
Hormones produced byt he adrenal glands, involved in stress and emotion |
|
|
What is Neuropsychology? |
Field of psych concerced with the neural and biochem bases of behavior and mental health |
|
|
What are endocrine glands? |
Internal organs that produce hormones and release them into the bloodstream |

