![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Atom |
The basic unit of matter |
|
|
|
Bohr Model |
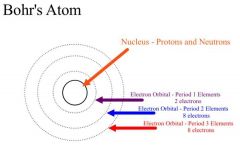
|
Atomic Model: Allows us to see the amount of electrons for each ring |
|
|
Electron Cloud |
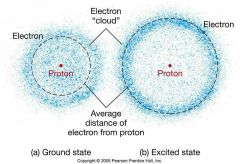
|
Atomic Model |
|
|
Ball & Stick |
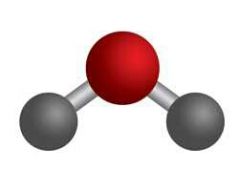
|
Atomic Model |
|
|
Molecule |
Smallest unit of most compounds that displays all the properties of that compound |
|
|
|
Compound |
Substance formed by the chemical combination of two or more elements in definite proportions |
|
|
|
Electron |
Negatively charged particles; located in the space surrounding the nucleus |
(-) |
|
|
Proton |
Positively charged particles |
(+) |
|
|
Neutron |
Particles that carry no charge at all |
(+/-) 0 Neutral |
|
|
Ion |
Atom that has a positive or negative charge |
|
|
|
Ionic Bond |
Chemical bond formed when one or more electrons are transferred from one atom to another |
|
|
|
Covalent Bond |
Type of bond between atoms in which the electrons are shared |
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bond |
Weak attraction between a hydrogen atom and another atom |
|
|
|
Acid |
Compound that forms hydrogen ions (H+) in solution; a solution with a pH of less than 7 |
|
|
|
Base |
Compound that produce hydroxide ions (OH-) in solution; solution with a pH of more than 7 |
|
|
|
pH Scale |
Scale with values from 0-14, used to measure the concentration of H+ ions in a solution; a pH of 0-7 is acidic, a pH of 7 is neutral, and a pH of 7-14 is basic |
|
|
|
Buffer |
Compound that prevents sharp, sudden changes in pH |
|
|
|
Polar Covalent Bond |
Bonds that are partly ionic |
|
|
|
Adhesion |
Force of attraction between different kinds of molecules |
|
|
|
Cohesion |
Attraction between molecules of the same substance |
|
|
|
Polar Molecule |
A molecule in which the charges are evenly distributed |
|
|
|
Organic Compound |
any member of a large class of gaseous, liquid, or solid chemical compounds whose molecules contain carbon |
|
|
|
Monomer |
Small chemical unit that makes up a polymer |
|
|
|
Dimer |
a molecule or molecular complex consisting of two identical molecules linked together |
|
|
|
Polymer |
Molecules composed of many monomers; makes up macromolecules |
Makes up macromolecules |
|
|
Glycogen |
a substance deposited in bodily tissues as a store of carbohydrates. It is a polysaccharide that forms glucose on hydrolysis |
|
|
|
Cellulose |
an insoluble substance that is the main constituent of plant cell walls and of vegetable fibers such as cotton. It is a polysaccharide consisting of chains of glucose monomers |
The major component of both wood and paper |
|
|
Starch |
It is a polysaccharide that functions as a carbohydrate store and is an important constituent of the human diet |
|
|
|
Lipid |
Macromolecule made mostly from carbon and hydrogen atoms; includes fats, oils, and waxes |
|
|
|
Hydrophobic |
Tending to repel or fail to mix with water |
|
|
|
Hydrophilic |
having a tendency to mix with, dissolve in, or be wetted by water |
|
|
|
Fatty Acid |
a carboxylic acid consisting of a hydrocarbon chain and a terminal carboxyl group, especially any of those occurring as esters in fats and oils |
|
|
|
Triglyceride |
an ester formed from glycerol and three fatty acid groups. |
|
|
|
Unsaturated |
having carbon–carbon double or triple bonds and therefore not containing the greatest possible number of hydrogen atoms for the number of carbons |
|
|
|
Saturated |
containing the greatest possible number of hydrogen atoms, and so having no carbon–carbon double or triple bonds |
|
|
|
Amino Acid |
Compound with an amino group on one end and a carboxyl group on the other end |
|
|
|
Peptide Bond |
a chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, releasing a molecule of water (H2O) |
|
|
|
Polypeptide |
Long chain of amino acids that makes proteins |
|
|
|
Protein |
Macromolecule that contains carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen; needed by the body for growth and repair |
Needed by the body for growth and repair |
|
|
Levels of Protein Structure |
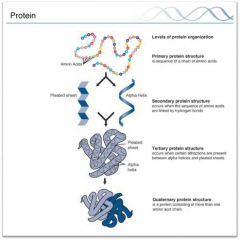
|
|
|
|
Nucleic Acid |
Macromolecules containing hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, and phosphorus |
|
|
|
RNA (ribonucleic acid) |
Single-stranded nucleic acid that contains the sugar ribose |
|
|
|
DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) |
a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information |
|
|
|
Nucleotide |
Subunit of which nucleic acids are composed; made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenois base |
|
|
|
Chemical Reaction |
Process that changes, or transforms, one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals |
|
|
|
Reactant |
Elements or compounds that enter into a chemical reaction |
|
|
|
Product |
Element or compounds produced by a chemical reaction |
|
|
|
Enzyme |
Protein catalyst that speeds up the rate of specific biological reactions |
|
|
|
Activation Energy |
Energy that is needed to get a reaction started |
|
|
|
Substrate |
Reactant of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction |
|
|
|
Enzyme-Substrate Complex |
A non-covalent complex composed of a substrate bound to the active site of the enzyme |
|
|
|
Induced Fit Model |
A model for enzyme-substrate interaction to describe that only the proper substrate is capable of inducing the proper alignment of the active site that will enable the enzyme to perform its catalytic function. It suggests that the active site continues to change until the substrate is completely bound to it, at which point the final shape and charge is determined |
|
|
|
Dehydration Synthesis |
A chemical reaction that builds up molecules by losing water molecules |
|
|
|
Polymerization |
A process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks |
|
|
|
Condensation Reaction |
a chemical reaction in which two molecules or moieties, often functional groups, combine to form a larger molecule, together with the loss of a small molecule |
|
|
|
Hydrolysis Reaction |
A chemical reaction in which the interaction of a compound with water results in the decomposition of that compound |
|
|
|
Catalyst |
A substance that speeds up the rate of a chemical reaction |
|

