![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
135 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hydrolysis |
Cleavage of covalent bond by water; Brekdown of bonds |
|
|
Lactate Dehydrogenase |
Most widely distributed enzymes in the body |
|
|
Hydrocarbons |
Simplest type of organic molecules; Are C and H containing molecules that are hydrophobic |
|
|
Amino Acid |
Polymer: Protein Function: Catalysis, structural elements, energy source |
|
|
Sugars |
Polymer: CarbohydratesFunctions: Energy source, structural elements |
|
|
Fatty Acid |
Polymer: Lipids Functions: Energy source, structural elements of complex lipid molecules |
|
|
Nucleotides |
Polymer: DNA and RNA Functions: Genetic information, protein synthesis |
|
|
Amino Acid |
Biomolecule that contain an amino group and carboxy group |
|
|
Sugar/Carbohydrates |
Biomolecules that contain both alcohol and carbonyl function groups; Described in terms of both carbon number and type of carbonyl |
|
|
Fatty Acid |
Monocarboxylic acid that contain an even number |
|
|
Saturated |
Fatty acid that has no double bond |
|
|
Unsaturated |
Fatty acid that have double bond |
|
|
Polyunsaturated |
Fatty Acid that have more than 2 bonds |
|
|
Hydroxyl |

Properties: Polar |
|
|
Methyl |
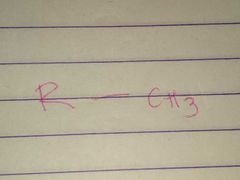
Properties: Nonpolar |
|
|
Carbonyl |

Properties: Polar |
|
|
Carboxyl |
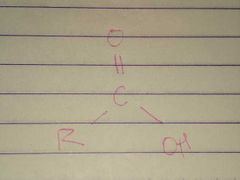
Properties: Charged, ionizes to release H+ since carboxyl groups can release H+ ions into solution, they are considered acidic |
|
|
Amino |

Properties: Charged, accepts H+ to form NH3+. Since amino groups can remove H+ from solution, they are considered basic |
|
|
Phosphate |
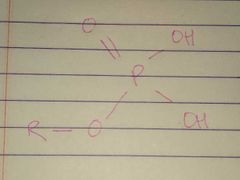
Properties: Charged, ionizes to release H+. Since phosphate groups can release H+ ions into solution, they are considered acidic |
|
|
1. Stable environment 2. Greater complexity in form nd function 3. Exploit environment resources |
Advantages of multicellular organisms over unicellular |
|
|
1. Complex and Dynamic 2. Organized and Self-sustainable/Self-sustaining 3. Cellular 4. Information base 5. Adapts and Evolves |
What is Life? |
|
|
Viruses |
Biologically inert; Composed of DNA or RNA |
|
|
Bacteriophages |
Reproduce themselves by inserting their genetic information into susceptible host cells |
|
|
Water |
Predominant chemical component of living organisms; Able to solvate organic and inorganic molecules; excellent nucleophile |
|
|
• Hypothalamic mechanism that control • ADH • H2O retention or excretion by tbe kidney • Evaporative loss |
Water Regulation dependent on: |
|
|
Water/H2O |
Has a slight tendency to dissociate into hydroxise ions and protons |
|
|
Bicarbonate and Buffer |
Maintain pH and ECF between 7.35 and 7.45 |
|
|
• pH of arterial blood • CO2 content of venous blood |
Acid-Base balance disturbances verified through: |
|
|
Alcohol; Hydroxyl |
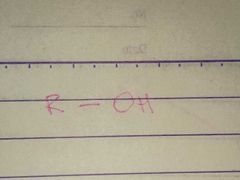
Family; Group Name |
|
|
Aldehyde; Carbonyl |
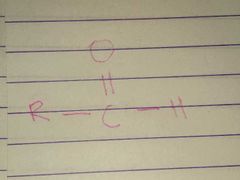
Family; Group Name |
|
|
Ketone; Carbonyl |
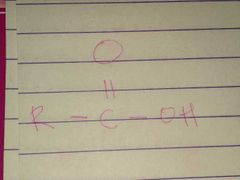
Family; Group Name |
|
|
Amines; Amino |
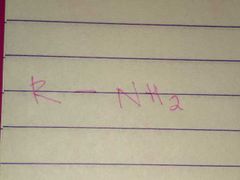
Family; Group Name |
|
|
Amides; Amido |
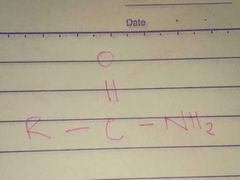
Family; Group Name |
|
|
Thiols; Sulfhydryl |
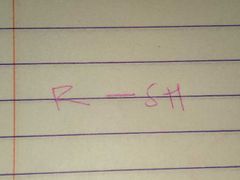
Family; Group Name |
|
|
Esters; Ester |
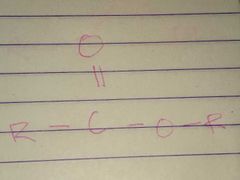
Family; Group Name |
|
|
Phenylalanine Valine Tryptophan Threonine Isoleucine Methionine Histidine Arginine Lysine Leucine |
Essential Amino Acid |
|
|
Leucine Isoleucine Valine |
Branched-Chain Amino Acid |
|
|
Histidine Arginine Lysine |
Basic Amino Acid |
|
|
Enzyme |
Catatyze chemical reactions of all living organism |
|
|
Metabolism |
The reaction in a living organism |
|
|
Metabolism |
Acquisition and utilization of energy; Synthesis of molecules needed for cell structure and functioning; Removal of wastes products |
|
|
Nucleophilic Substitution Elimination Addition Isomerization Oxidation-Reduction Hydrolysis |
Biochemical Reaction |
|
|
Nucleophile |
The element rich species that will react with an electron poor species |
|
|
Substitution |
Implies that one group replaces another |
|
|
Electrophile |
Atoms or group that are transferred from the nucleophile to another |
|
|
Elimination |
A double bond is formed with two atoms in a molecule are removed |
|
|
Addition |
Two molecules combine to form a single product |
|
|
Hydration |
The most common addition reaction |
|
|
Isomerization |
Involves intramolecular shift of atoms of groups |
|
|
Oxidation-Reduction |
Also known as redox reaction |
|
|
Oxidation-Reaction |
Occurs when there is a transfer of electrons from a donor to a electron acceptor |
|
|
Oxidizing Agent |
Electron acceptor |
|
|
Reducing Agent |
Electron Donor |
|
|
Oxidized Agent |
When reducing agent donate they become? |
|
|
Reduced Agent |
When oxidizing agent accept electrons they become? |
|
|
Oxidation |
Occurs if a molecules gains oxygen or loss hydrogen |
|
|
Reduction |
Occurs if a molecules loss oxygen or gains hydrogen |
|
|
Tetrahedral Geometry of H2O |
It is the irregular slightly skewed tetrahedron with O2 at its center; Two H+ and unshared electrons of the remaining two sp3 hybridized orbitals occupy the corners |
|
|
104.5° |
Degree of bandage of tetrahedral geometry of H2O |
|
|
Ionic/Polar molecules |
Dissolves readily |
|
|
Non-polar |
Dissolves poorly |
|
|
Hydrophilic |
Interact well with H2O and dissolves; It is polar; Soluble |
|
|
Hydrophobic |
Do not dissolves in water; It is non-polar; Insoluble |
|
|
Amphipathic |
Both hydrophilic and hydrophobic |
|
|
1. Water molecules form dipole 2. Water molecules form H+ bond |
Potent Properties of Water |
|
|
1. Increase its dielectric constant 2. Greatly decreass the force of attraction between charged and polar species relative to H2O free environmemt 3. Allows H2O to solvate large quantities of charged compounds |
Water's strong dipole..... |
|
|
Viscosity Surface Tension |
H+ bonding influences the physical properties of H2O including its high? |
|
|
4 H+ bonds |
How many bonds H2O molecule can form? |
|
|
Hydrogen bonded |
H2O forms ______ bonded clusters with itself and with other proton donors or acceptors |
|
|
[H+][OH-] K= ----------------- H2O |
Ionization of water in formula |
|
|
pH |
Small concentrations of H+ |
|
|
7 |
pOH of water |
|
|
5.55 M |
M of pure water |
|
|
1.8x10^-16 |
Equilibrium constant of water |
|
|
Acid |
Has protons tht can dissociate (came off) when dissolved in H2O |
|
|
Base |
Can absorb protons when dissolved in H2O |
|
|
Increase |
Addition of base, _____ the pH |
|
|
Decrease |
Addition of acid, ______ pH |
|
|
Buffers |
H+ or HO+ added to solution to resist pH changes; Essential to maintain pH |
|
|
Henderson-Hasselbalch Regulation |
Predicts the response of the H2SO3 system to changes in H+ concentration; Defines the relationship between the pH and the ratio of HCO and H2CO4 |
|
|
Ka |
It is the acid dissociation constant and in a measure of the strength of an acid |
|
|
Stronger |
The _____ the acid, the more protons will dissociates from it when added to H2O and the larger the value its Ka will have |
|
|
Lower values |
Large values of Ka translate to lower values of pKa |
|
|
pKa values |
The lower the _____ of a given acid, the stronger the weak acid is |
|
|
Primary Protein |
Amount order and sequence of amino acid; Has peptide bond |
|
|
Secondary Protein |
Alpha helix and beta-pleated sheets; Hydrogen bond |
|
|
Tertiary Protein |
Structure of protein that are composed of polypeptide bonds |
|
|
Quaternary Protein |
Structure of protein that have multiple body peptide |
|
|
Sickle Cell Anemia |
Interchange of valine and glutamic acid |
|
|
COOH- | +HN3 ----- alpha ----- H | R GROUP |
Structure of Amino acid |
|
|
• Ampholytes: Contain an amino and carboxyl • H and -COOH groups bond toalpha carbon are both acidic • Basic characteristic ia due to the lone pair of electrons of the amino group • Naturally occuring amino acid belong to the a- configuration |
Characteristic of Amino Acid |
|
|
Nonpolar Ala A |
Alanine: Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Polar; Postively Charged Group Arg R |
Arginine: Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Polar; Neutral Uncharged R Group Asn N |
Aspargine: Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Acidic Amino Acid Asp D |
Aspartic Acid: Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Polar; Neutral R charged 4 Groups Cys C |
Cysteine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Eukaryotic Prokaryotic |
2 Types of Cell |
|
|
Polar; Uncharged Glu E |
Glutamic Acid Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Polar; Uncharged Gln Q |
Glutamine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Nonpolar; Aliphatic Gly G |
Glycine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Polar; Positively Charged His H |
Histidine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Nonpolar; Aliphatic Ile I |
Isoleucine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Nonpolar; Aliphatic Leu L |
Leucine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Polar; Positively Charged Lys K |
Lysine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Nonpolar; Aliphatic Met M |
Methionine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Aromatic Phe F |
Phenylalanine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Polar; Uncharged Pro P |
Proline Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Polar; Uncharged Ser S |
Serine Class3-letter code1-letter code |
|
|
Polar; Uncharged Thr T |
Threonine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Aromatic Trp W |
Tryptophan Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Aromatic Tyr Y |
Tyrosine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Nonpolar; Aliphatic Val V |
Valine Class 3-letter code 1-letter code |
|
|
Neutral |
The amino acid is ______ unless there is an extra acid or base on the side chain |
|
|
Neutral Side Chain |
No side chains |
|
|
L-absolute Configuration |
A-NH3+ groups are projected to the left |
|
|
D-absolute Configuration |
A-NH3+ is projected to the left |
|
|
L Configuration |
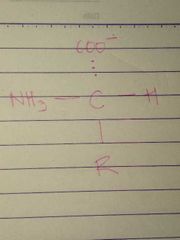
|
|
|
D Configuration |
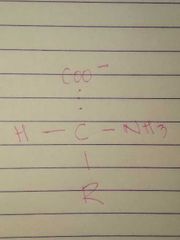
|
|
|
Peptide Bond Formation |
This polymerization is a dehydration reaction |
|
|
Peptide Bond |
It is rigid and polar; Must have 1 amino terminal and carboxyl terminal |
|
|
Amino Terminal |
N - terminal |
|
|
Carboxyl Terminal |
C - terminal |
|
|
Trans Configuration |
Most stable configuration for the peptide bond with 2 side chains also in trans; Always found in proteins except where they are proline residues |
|
|
Cis Configuration |
Brings two side chain groups to the same side of the c¢=N bond where unfavorable repulsive steric forces occur between between the two side chain groups |
|
|
Amino Acid Reaction |
Its is a disulfide bridge reaction |
|
|
Non-essential |
Human produce _______ amino acids |
|
|
Arginine |
An amino acid that can make in urea cycle |
|
|
PTT - FYW Phenylalanine - F Tyrosine - Y Tryptophan -W |
Aromatic AA |
|
|
LAH - KRH Lysine - K Arginine - R Histidine - H |
Negative AA |
|
|
GAVLIM Glycine - G Alanine - A Valine - V Leucine - L Isoleucine - I Metheonine - M |
Nonpolar AA |
|
|
SPAGCyTh - SPNQCT Serine - S Proline - P Asparagine- N Glutamine - Q Cysteine - C Threonine - T |
Polar AA |
|
|
AAA GGG CPST Alanine Asparagine Aspartate Glutamate Glutamine Glycine Cysteine Proline Serine Tyrosine |
Non-essential AA |
|
|
PVT TIM HALL Phenylalanine Valine Threonine Tryptophan Isoleucine Metheonine Histidine Arginine Leucine Lysine |
Essential AA |
|
|
Arginine |
Synthesized by mammalian cells but at a rate that is insufficient to meet the growth needs of the body and the majority that is synthesized is cleared to form urea |
|
|
Methionine |
Required in large amount to produce cysteine if the latter amino acid is not adequately supplied in the diet |

