![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
95 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
FA degradation is a __ process |
oxidative |
|
|
FA is cleaved to yield what two products? |
FA (n-2) and acetyl CoA |
|
|
Monosaccharides are joined to ___ and ____ through what types of bonds? |
alcohols and amines through glycosidic bonds |
|
|
Oligosaccharides and polysaccharides are created through ____ bonds |
O-glycosidic linkages` |
|
|
How is glucose stored? |
as a long polymer |
|
|
Polymers of glucose have what type of linkages? |
AGlycogen: Alpha 1,4
Starch: linear form only has alpha 1-4 |
|
|
Linkages in cellulose |
beta 1,4 |
|
|
Cellulose: branched or unbranched? H bonding? |
unbranched, h bonded |
|
|
Glycoprotein |
mostly carb with a protein group |
|
|
Where are glycoproteins found? |
surface of membrane |
|
|
Carbohydrates can be linked to proteins through ___ or ____ |
N or O linked |
|
|
All ___ have a common ___ |
N linked oligosaccharides have a common pentasaccharide core |
|
|
How are FA stored? |
as trigylcerols (neutral fats) |
|
|
"Stored as___" |
uncharged esters of FA with glycerol |
|
|
FA are building blocks for |
phosholipids and glycolipids |
|
|
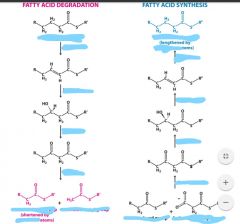
What involves reduction reactions? |
FA synthesis |
|
|
|
|
|
Which is more reduced carbs or lipids? |
Lipids (more C-H bonds compared to C=O of C-OH bonds) |
|
|
Which is more oxidized? Pasta or butter? |
Pasta |
|
|
Celery has what type of linkages? |
beta 1,4 |
|
|
TAG are highly concentrated stores of ____ energy |
metabolic |
|
|
TAG are ____ and ____ |
reduced and anhydrous |
|
|
Yield of oxidation from FA vs carb or proein? |
2x as high |
|
|
Glycogen more or less oxidized than fats? |
more oxidized |
|
|
Controls mobilization of TAG in adiopose tissue |
catabolic hormones |
|
|
Glucagon signals |
low energy |
|
|
Epinephrine signals |
immediate energy need |
|
|
At destination, FA are |
activated and transported to mitochondia for degredation |
|
|
FA broken down to |
acetyl CoA |
|
|
Liver converts glycerol to |
pyruvate or glucose |
|
|
Various tissues can use FA to produce ___? after what process? |
ATP after converting it to Acetyl CoA |
|
|
Creation of activated FA. First, use ____ to create |
ATP to create FA-AMP |
|
|
Next, transfer ___ to ___ |
FA to CoA molecule |
|
|
What drives the activation of FA? |
pyrophoshatase degrading pyrophosphate |
|
|
Precursor for virtually all FA |
Acetyl CoA |
|
|
Link 2C units together to produce what? |
16C FA (palmite) which is the precursor for other FA |
|
|
Selecting and condensing compartment binds ____ and ____ to form what? |
substrates (acyl CoA and malonyl CoA) and condenses them to form the growing chain |
|
|
Modification compartment catalyzes |
Reduction and dehydration |
|
|
FA synthesis requires a ___? |
an activated malonyl group (2C) |
|
|
FA synthesis highest when ___ are plentiful and ____ are scarce |
carbs and energy are plentiful and FA are scarce |
|
|
Key regulator in synthesis and degredation |
acetyl CoA carboxylase |
|
|
Committed step in FA synthesis? Accompanied by? |
production of activated 2C donor malonyl CoA. ATP hydrolysis |
|
|
Acetyl CoA carboxylase inhibited by high ATP or low ATP? |
Low ATP (high AMP) |
|
|
Acetyl CoA carboxylase: High ATP? |
activated |
|
|
Acetyl CoA carboxylase: High citrate? |
activated |
|
|
Acetyl CoA carboxylase: high AMP? |
inhibited |
|
|
Acetyl CoA carboxylase : High insulin? |
activated |
|
|
Acetyl CoA carboxylase: energy need conditions? |
inhibted |
|
|
Acetyl CoA carboxylase: energy abundance |
activated |
|
|
Acetyl CoA carboxylase : high palmatoyl CoA? |
inhibited |
|
|
Acetyl CoA carboxylase : catabolic hormones? |
inhibited |
|
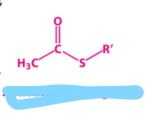
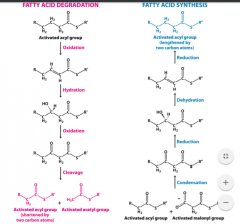
|
activated acetyl group |
|
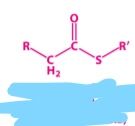
|
activated acyl group |
|
|
Lipid bilayers rarely form or form spontaneously? |
spontaneously |
|
|
Major driving force or of lipid bilayer formation |
hydrophobic interactions |
|
|
favor close packing in lipid bilayers |
vderwals |
|
|
occur between polar heads and H20 |
electrostatic and h bonding |
|
|
Buildup of activated palmite inhibits or activates Acetyl CoA carboxylase |
activated |
|
|
FA normally branched or unbranched? |
unbranched |
|
|
More unsaturated FA--butter or oil? |
oil |
|
|
Four components to phosholipids |
1 or more FA, a platform (glycerol), phosphate, alcohol |
|
|
Type of linkage in phosphoglycerides |
esterification between carboxyl group and phosphoric acid |
|
|
Key intermediate in synthesis of phoshoglycerides |
phosphatidate |
|
|
How to make phosphoglycerides? |
phosphatidate + alcohol |
|
|
Alcohol attached using what type of linkage? |
ester |
|
|
Do all phospholipids have a glycerol backbone? |
no, some have a sphingomyelin backbone |
|
|
sphingosine is a ___ ____ |
amino alcohol |
|
|
Glycolipids: 4 aspects |
glycerol or sphingosine bacjbone, no phosphate, sugar group, sugar faces extracellular side of membrane |
|
|
Cholesterol structure |
4 HC rings (3 hex, 1 pent) |
|
|
Amphipathic molecules arrange as |
micelles (polar heads out), lipid bilayers (favored) |
|
|
Lipid bilayers often enclose |
aqueous environments |
|
|
Lipid bilayers highly impermeable to |
polar molecules and ions |
|
|
Permeability units |
cm s ^-1 |
|
|
Membrane protein types |
pumps, receptors, channels, enzymes |
|
|
Interact with FA tails |
integral membrane proteins |
|
|
associated with polar head groups or membrane surface |
peripheral membrane proteins |
|
|
Facilitated by hydrophobic rsidues in protein |
integral membrane proteins |
|
|
anchored to lipid bilayer by covalently attached HC |
peripheral membrane protein |
|
|
How to remove integral membrane proteins? |
detergent |
|
|
How to remove peripheral membrane protein? |
salt of pH change |
|
|
Membrane anchored proteins use |
membrane lipids as substrates |
|
|
Proteins span membrane with what structure? |
alpha helices |
|
|
Many residues in the alpha helices are polar or non polar? charged or uncharged? |
nonpolar, uncharged |
|
|
bacteria regulate fluidity by? |
varying FA chain length and unsaturation helps with low temps |
|
|
Animals regulate fluidity through |
cholesterol (disrupts packing) |
|
|
Metabolic pathways allow for __ and __? |
fuel consumption and large molecule synthesis |
|
|
currency of all life forms |
ATP |
|
|
powers ATP formation |
carbon fuel oxidation |
|
|
Useful energy employed for what types of reactions? |
anabolic |
|
|
three things that require input of free energy |
mechanical work, active transport, synthesis of complex biomolecules |
|
|
ATP hydrolysis is |
exergonic |
|
|
ATP is ___ to become what two products? |
hydrolyzed to become ADP and Pi |
|
|
energy released or gain from bonds breaking? |
released MAJOR amount ATP--->ADP |
|
|
delta G ATP--->ADP |
-50kj/mol |
|
|
ions associate with ATP hydrolyzation |
Mn2+ and Mg2+ |

