![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
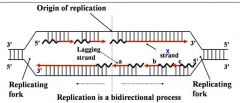
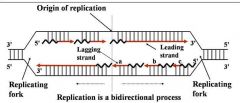
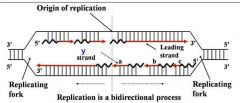
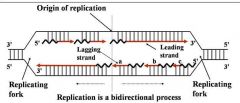
1. Semiconservative process
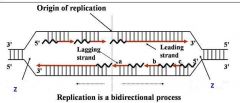
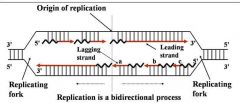
2. DNA polymerase(s) Components required for DNA synthesis 3. Origin of replication 4. Bi-directional 5. Replicating forks 6. Leading strand 7. Lagging strand (Okazaki fragments) |
General concepts of DNA replication
|
|
|
These proteins need the following for DNA synthesis:
a. Substrates: dATP, dTTP, dCTP & dGTP b. Mg2+ c. Template d. Primer chain with free 3' hydroxyl group |
DNA polymerases
DNA polymerases can only carry out the process of elongation; they can not carry out the process of initiation. |
|
|
The addition of a deoxyribonucleotide to the __' end of a polynucleotide chain
|
3' end
The fundamental reaction by which DNA is synthesized |
|
|
DNA synthesis occurs in the ____' to 3' direction.
|
5'
|
|
|
Site of unwinding of parental duplex and DNA synthesis
|
Replication forks (two)
|
|
|
Function:
DNA repair Replication (minor) Exonuclease activity: - 3' to 5' - 5' to 3' (exonuclease removes RNA primer.) |
Pol I
Replication is assisted by removal of RNA primers in conjunction with RNase H Fills in gaps after removal of RNA primers |
|
|
Function:
DNA repair (Damage bypass) Exonuclease activity: - 3' to 5' |
Pol II
|
|
|
Function:
DNA repair Replication (major) Exonuclease activity: - 3' to 5' |
Pol III
|
|
|
Pol III holoenzyme core complex:
Polymerase |
Alpha subunit
Synthesizes DNA |
|
|
Pol III holoenzyme core complex:
3' -> 5'exonuclease |
Epsilon subunit
Proofreads DNA |
|
|
Pol III holoenzyme core complex:
Stimulates 3' -> 5' exonuclease |
Theta subunit
Regulates activity of epsilon |
|
|
Pol III holoenzyme core complex:
Forms sliding clamp |
Beta subunit
|
|
|
Pol III holoenzyme core complex:
Enhances dimerization of core; ATPase |
Tau subunit
Forces core to form a dimer Protein will have two active sites. |
|
|
The number of nucleotides added before dissociation
A measure of efficiency. Pol III holoenzyme complex processivity = >500,000 nucleotides added before dissociation |
Processivity
The high processivity of Pol III is due to the Beta subunit and Gamma complex. |
|
|
Action of helicases at the replicating fork introduces positive supercoiling ahead of the fork.
Removed through the action of DNA gyrase. |
If the positive supercoiling ahead of the fork is not removed through the action of DNA gyrase, then replication will cease.
|
|
|
In the final steps of replication, the RNA primers are removed and the resulting gaps in the DNA fragments are filled in by the action of Pol ____.
|
I
- Synthesizes DNA 5'-3' - Fragments not joined together Next the DNA fragments are joined together by DNA ligase |
|
|
- Requires NAD+ in prokaryotes
- ATP in eukaryotes |
DNA ligase
|
|
|
Hydrophobic interactions
Phe, Ile interact with Ile and Leu Ionic interaction Glutamate and arginine |
Forces that hold the subunits together
Gamma subunit can disrupt these bond |
|
|
First step of DNA replication
|
Binding of a DNA-A tetramer
Adds 20-40 DnaA monomers |
|
|
Dna-___ protein regulates activity of DNA-b protein.
Cannot bind |
C
|
|
|
DNA-__
Allows DNA-b to add to each end of the open complex |
T
|
|
|
Unwinds ds- DNA at the forks
Requires ATP Displaces Dna-A proteins as it moves to the right. |
Dna-B protein = helicase
|
|
|
Composed of three different proteins
DNA-b Primase PriA |
Primosome
- Forms at each end of open complex |
|
|
Action of Pri __ and ___ loads Primase and PriA onto DNA complex
Forms Primosome |
B and C
|
|
|
1. Substrates: ATP, GTP, CTP, UTP
2. Mg2+ 3. Template to direct process 4. No primer required. 5. Primer synthesized in 5'-3' direction |
Primase synthesizes RNA primers
|
|
|
Need the RNA primer _____ time for the leading strand.
|
one
|
|
|
After synthesizing the primer for leading strand, the _______ strand primers will be formed.
|
lagging
|
|
|
Synthesizing DNA in 5'-3' direction
Need template to run 3'-5' direction Have parallel orientation of both strands can synthesize two strands at one time. |
Loop converts antiparallel orientation to parallel
|
|
|
Top B subunit remains attached throughout the entire process.
What about the lower B subunit? . |
Lower B subunit has to cycle on and off as it runs out of template
|
|
|
If positive supercoiling is not removed, replication wil l cease
DNA gyrase binds to this region and removes positive supercoiling. |
Major target for treating bacterial infections
Block DNA gyrase |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
This protein is used as a diagnostic marker for proliferating cells
|
Proliferating cell nuclear antigen
|

