![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
77 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
1. Aspirin, also known as acetylsalicylic acid, is a salicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication since the nineteenth century (Bayer 1899). However, the biochemical mechanism as an anti-inflammatory agent was not discovered until 1971 when biochemist John Vane showed the inhibitory effect of aspirin to PGH2 synthase, or called cyclooxygenase. The molecular mechanism of aspirin action is that ______________ will covalently link to ______________ of PGH2 synthase, or called cyclooxygenase and decrease its enzyme activity, which leads to much reduced production of prostaglandins, mediators of inflammation. |
a) acetyl group of aspirin; arachidonic acid portion b) acetyl group of aspirin; serine c) aspirin; arachidonic acid portion d) aspirin; serine |
B |
|
|
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. It has four irreversible stages: G1 (Gap 1), S (DNA synthesis), G2 (Gap 2) and M (mitosis). Two key classes of regulatory molecules, _________________, determine a cell's progress through the cell cycle. Leland H. Hartwell, R. Timothy Hunt, and Paul M. Nurse won the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their discovery of these central molecules. Active RNA and protein biosyntheses occur in ________ |
a) cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases; G1, S and G2 stages b) cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases; S and G2 stages, but not in G1 stages c) cyclins and tyrosine kinases; G1, S and G2 stages d) cyclins and tyrosine kinases; S and G2 stages, but not in G1 stages |
A |
|
|
Intracellular buffer system takes place inside the cell and extracellular buffers take place outside the cell. The body's acid–base balance is normally tightly regulated, keeping the arterial blood pH of around 7.40 and keeping intracellular pH around 6.80. Acid-base balance within cells is very important because many cellular functions are exquisitely sensitive to pH changes. Extracellular buffer is the system using the following dissociation process of No. 1 and intracellular buffer is the system using the following dissociation process of No. 4. Number of Dissociation Processes pKa Values H2CO3 ↔ H+ 6.45 + HCO3 H2PO4 - ↔ H+ 7.21 + HPO4 Which of the following statement on extracellular and intracellular buffers is correct? |
a) Intracellular: [H2PO4 - ]/[HPO4 2-] < 1 and extracellular buffer: [H2CO3]/[HCO3 - ] < 1 b) Intracellular: [H2PO4 - ]/[HPO4 2-] < 1 and extracellular buffer: [H2CO3]/[HCO3 - ] > 1 c) Intracellular: [H2PO4 - ]/[HPO4 2-] > 1 and extracellular buffer: [H2CO3]/[HCO3 - ] < 1 d) Intracellular: [H2PO4 - ]/[HPO4 2-] > 1 and extracellular buffer: [H2CO3]/[HCO3 - ] > 1 |
C |
|
|
Gene translocation results in an oncogenic BCR-ABL protein that causes human leukemia. Depending on the precise location of fusion, the molecular weight of this protein can range from 185 to 210 kDa. In the late 1990s, imatinib, a drug, was identified by the pharmaceutical company Novartis. Imatinib is used in treatment of leukemia patients caused by BCR-ABL through the mechanism of its significantly inhibiting BCR-ABL activity. BCR-ABL is a_____________ . If you would like to perform affinity chromatography to purify BCR-ABL from leukemia cells, which of the following molecules can be used? A. Imatinib B. Substrate of BCR-ABL C. Antibody against BCR-ABL D. Antigen of BCR-ABL |
a) serine kinase; A, B, and C, but not D b) serine kinase; B and C, but not A and D c) tyrosine kinase; A, B, and C, but not D d) tyrosine kinase; B and C, but not A and D |
C |
|
|
Amino acids are biologically important organic compounds composed of amine and carboxylic acid functional groups, along with a side-chain specific to each amino acid. All amino acids except _____________ have D- and L-forms. All amino acids in proteins are |
a) glycine; D-forms b) glycine; L-forms c) proline; D-forms d) proline; L-forms |
B |
|
|
There are two peptides: Peptide A: Ala-Tyr-Trp-Leu-Thr Peptide B: Ala-Val-Met-Phe-Ser Which of the peptides would absorb UV light at 280 nm, and which of the peptides could migrate faster in SDS-PAGE? |
a) Only peptide A; Peptide A b) Only peptide A; Peptide B c) Peptide A and B; Peptide A d) Peptide A and B; Peptide B |
D |
|
|
___________ determines phi (Φ) and psi (Ψ) angles of a polypeptide. The main weak chemical force to maintain an α-helix is through ___________ hydrogen bonds and the main noncovalent interaction to hold a β pleated sheet is through ___________ hydrogen bonds. |
a) The entire path of the main chain; inter chain; intra molecular b) The entire path of the main chain; intra molecular; inter chain c) Amino acid sequence; inter chain; intra molecular d) Amino acid sequence; intra molecular; inter chain |
D |
|
|
Lys has three dissociable H+ with three pK values shown below. pKa = 2.2 (-COOH of Lys main chain) pKb = 9.2 (-NH3 + of Lys main chain) pKR = 10.8 (-NH3 + of Lys side chain) pI of Lys is ______________. The form of Lys predominating in a solution at pH 12.0 is |
6.5; Lys0 b) 6.5; Lys- c) 10; Lys0 d) 10; Lys- |
D |
|
|
Keratin is the key structural material making up the outer layer of human skin. It is also the key structural component of hair and nails. α-keratin is an example of fibrous proteins. The folding process for α-keratin can be summarized as ___________ . The interaction between α helices are mainly mediated by ___________ . |
a) helix Æ triple helix Æ fibril Æ fiber; hydrogen bonds b) helix Æ triple helix Æ fibril Æ fiber; hydrophobic interactions c) helix Æ coiled coil Æ protofilament Æ filament; hydrogen bonds d) helix Æ coiled coil Æ protofilament Æ filament; hydrophobic interactions |
D |
|
|
A peptide bond is a covalent chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, causing the release of a molecule of water, hence the process is a dehydration synthesis reaction (also known as a condensation reaction). The peptide bond has a partial double bond character due to a ___________ structure. Due to the ___________, six atoms of the peptide bond group are always planar. |
a) resonance; partial double character of a peptide bond b) resonance; trans position of the carbonyl oxygen and the amide hydrogen c) stereochemical; partial double character of a peptide bond d) stereochemical; trans position of the carbonyl oxygen and the amide hydrog |
A |
|
|
You are given the following types of bonds or interactions: A. Hydrogen bonds B. Electrostatic bonds C. Hydrophobic interactions D. Disulfide bonds E. Ester bonds Which of the bonds or interactions above are least likely to be involved in stabilizing the three- dimensional folding of most proteins? Which of the bonds or interactions above are most likely to be involved in stabilizing the three-dimensional folding of membrane portion of a membrane protein? |
a) C; A b) C; C c) E; A d) E; C |
D |
|
|
A human protein A can be phosphorylated inside human cells. If you want to isolate the kinase that phosphorylates protein A, with high purity from cell extracts containing a protein mixture by affinity chromatography, most likely, you will need _____________ . If the phosphorylated protein A has lost its function, the reason is that _____________ . |
a) phosphorylated protein A; phosphorylation introduces the phosphate functional group necessary for protein A activity. b) unphosphorylated protein A; phosphorylation introduces the phosphate functional group necessary for protein A activity c) phosphorylated protein A; phosphoryaltion causes conformational changes that can alter protein A function d) unphosphorylated protein A; phosphoryaltion causes conformational changes that can alter protein A function |
D |
|
|
You are given the following amino acids: A. Serine B. Histidine C. Isoleucine D. Glutamate E. Lysine A water-soluble globular protein is most likely to have the highest proportion of which of the amino acids above buried within its core? Which of the amino acids in protein above most likely can be posttranslationally methylated? |
a) A; Only B and E b) A; Only E c) C; Only B and E d) C; Only E |
C |
|

|
a) The protein X has two polypeptide chains. The protein X contains one disulfide bond between two polypeptides. b) The protein X has four polypeptide chains. The protein X contains two disulfide bonds between two polypeptide chains. c) The protein X has three polypeptide chains. The protein X contains one disulfide bond between two of the three polypeptides. d) The protein X has three polypeptide chains. The protein X contains two disulfide bonds. |
D |
|
|
Increase in temperature can induce protein denaturation: a process from native proteins to denatured proteins. What will happen to DNase and RNase if they are heated to 100ºC and then cooled down to 36ºC? Protein folding is a process in which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional 3-D structure from newly synthesized polypeptide chain. The folding process (fast or slow) of a protein is determined by its _____________ . |
a) DNase will remain denatured while RNase will return to its native form; amino acid sequence b) DNase will remain denatured while RNase will return to its native form; function c) RNase will remain denatured while DNase will return to its native form; amino acid sequence d) RNase will remain denatured while DNase will return to its native form; function |
A |
|
|
Determine the correct amino acid sequence of a heptapeptide (a small peptide containing seven amino acids) on the basis of the following data. Note: when the amino acid sequence is not given, a comma separates the amino acids. (i) Amino acid composition: (Ala, Arg, Leu, Lys, Phe and 2Val). It means that this heptapeptide contains one Ala, one Arg, one Leu, one Lys, one Phe and two Val. (ii) N-terminal analysis of the heptapeptide: Leu (iii)Trypsin digestion (cleavage) of the heptapeptide yielded two fragments: (Lys, Phe, Val, Val) and (Ala, Arg, Leu) (iv) Carboxypeptidase A digestion of the heptapeptide: no digestion (v) Chymotrypsin digestion of the heptapeptide produced two fragments: (Ala, Arg, Leu, Phe) and (Lys, Val, Val) The correct amino acid sequence of this heptapeptide from N-terminal to C-terminal is |
a) Leu-Ala-Phe-Arg-Val-Val-Lys b) Leu-Ala-Arg-Phe-Val-Val-Lys c) Leu-Ala-Arg-Val-Phe-Val-Lys d) Leu-Ala-Lys-Val-Phe-Val-Arg |
B |
|
|
A sequence of amino acids in a certain part of protein is -S-G-P-G-. The sequence is most probably part of a(n): |
a) helix b) β-pleated sheet c) β strand d) β turn e) random loop |
D |
|
|
All the possible interactions to maintain protein tertiary structure are _____________ |
a) hydrogen bonds, van der Waals interactions, electrostatic interactions, hydrophobic interactions and disulfide bonds b) hydrogen bonds, van der Waals interactions, electrostatic interactions and hydrophobic interactions, but not disulfide bonds that are specifically to maintain quaternary structure c) hydrogen bonds, van der Waals and electrostatic interactions, but not hydrophobic interactions and disulfide bonds d) only hydrogen bonds, and van der Waals interactions e) only hydrogen bonds |
A |
|
|
Keratin is the key structural material making up the outer layer of human skin. It is also the key structural component of hair and nails. keratin is an example of fibrous proteins. The folding process for α-keratin can be summarized as ___________ . The interaction between α helices are mainly mediated by ___________ |
a) helix triple helix fibril fiber; hydrogen bonds b) helix triple helix fibril fiber; hydrophobic interactions c) helix coiled coil protofilament filament; hydrogen bonds d) helix coiled coil protofilament filament; hydrophobic interactions e) helix coiled coil protofilament filament; neither hydrogen bonds nor hydrophobic interactions |
D |
|
|
Six atoms of the peptide bond group are always planar due to the ____________. Dipole of amide linkage of a peptide bond is due to partially ___________charged carbonyl oxygen and partially ___________ charged amide nitrogen. |
a) resonance structure; negatively; positively b) resonance structure; positively; negatively c) trans position between amide hydrogen and carbonyl oxygen; negatively; positively d) trans position between amide hydrogen and carbonyl oxygen; positively; negatively e) and angles; negatively; positively |
A |
|
|
Ion exchange chromatography (or ion chromatography) is a process that allows the separation of proteins based on their charges. Commonly used matrixes in ion exchange chromatography include carboxymethyl-celllulose (CM-cellulose) and diethylaminoethyl-celllulose (DEAEcellulose). CM-cellulose is used in __________ exchange chromatography while DEAE- cellulose is used in __________ exchange chromatography. You are given three types of oligopeptides, A: E-D-D-D-A-D; B: A-L-V-I-I-L; C: K-L-A-K-K-R. Which oligopeptide will come out first from CM-cellulose column? |
a) anion; cation; A b) anion; cation; C c) cation; anion; A d) cation; anion; C e) either anion or cation; either anion or cation; B |
C |
|
|
Protein 3D structures can be experimentally solved by X-ray crystallography or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). _____________ can solve small to large proteins and protein complexes and _____________ currently cannot solve structures of large proteins or large protein complexes. It is challenging to solve structures of membrane proteins due to high hydrophobicity of _____________ in transmembrane domains. |
a) NMR; X-ray crystallography; nonpolar amino acids b) NMR; X-ray crystallography; polar amino acids c) X-ray crystallography; NMR; nonpolar amino acids d) X-ray crystallography; NMR; polar amino acids e) Either X-ray crystallography or NMR; both X-ray crystallography and NMR; either polar or nonpolar amino acids |
C |
|
|
A hormone receptor is a protein that has one transmembrane domain composed entirely of helical secondary structure. Which one of the following amino acids would you expect to find in the transmembrane domain? A Glu residue of this hormone receptor is altered to an Ala residue in a human disease. The binding assay showed that binding of the hormone to its hormone receptor with Glu → Ala mutation decreased 100-fold. The force to hold the hormone and its hormone receptor together in normal people is mainly mediated by ____________ interaction. |
a) Leucine; electrostatic b) Leucine; hydrophobic c) Lysine; electrostatic d) Lysine; hydrophobic e) Either Leucine or Lysine; either electrostatic or hydrophobic |
A |
|

IEF separates proteins based on their ____________ and SDS-PAGE separates based on their ____________ . |
a) charges; charges b) charges; sizes c) sizes; charges d) sizes; sizes e) both charges and sizes; both charges and sizes |
B |
|

What is the order of low to high molecular weight for spots A, B, C, D, and E? What is the order of pI from small to large for spots A, B, C, D, and E? |
a) A < E < D < B < C; A = B < C = E < D b) A < E < D < B < C; D < C = E < A =B c) C < B < D < E < A; A = B < C = E < D d) C < B < D < E < A; D < C = E < A =B e) A = B =C = D = E; A = B =C = D = E |
C |
|

If the native polypeptides of A, C and D are purified by anion exchange chromatography, what is the order of first to last coming out of from the column? |
a) A < C < D b) A < D < C c) C < D < A d) D < C < A e) A, C and D come out at almost same time from the column. |
D |
|
|
Assume that A, B, C and D are human proteins. You are interested in protein C. What method(s) can you use to determine amino acid sequence of protein C? If C is phosphorylated, phosphorylated C will shift to ___________ side of the original spot C in the 2-D gel. |
a) Amino acid sequencing by Edman method but not mass spectrometry; left b) Amino acid sequencing by Edman method but not mass spectrometry; right c) Either amino acid sequencing by Edman method or mass spectrometry; left d) Either amino acid sequencing by Edman method or mass spectrometry; right e) Amino acid sequence of protein C cannot be determined; either left or right |
C |
|
|
Increase in temperature can induce protein denaturation: a process from native proteins to denatured proteins. What will happen to DNase and RNase if they are heated to 100ºC and then cool down to 36ºC? Which protein most likely will be synthesized in response to the increase of body temperature from 36ºC to 38ºC? |
a) DNase will remain denatured while RNase will return to its native form; Proteases b) DNase will remain denatured while RNase will return to its native form; HSP70 c) RNase will remain denatured while DNase will return to its native form; Proteases d) RNase will remain denatured while DNase will return to its native form; HSP70 e) Both DNase and RNase will remain denatured; neither proteases and HSP70 |
B |
|
|
There are two peptides: Peptide A: Ala-Tyr-Trp-Trp-Leu-Pro-Trp Peptide B: Ala-Val-Phe-Ser-Leu-Ile-Thr Which of the peptides would absorb(s) UV light at 280 nm, and which of the peptides can be phosphorylated? |
a) Only peptide A; Only peptide B b) Only peptide A; Peptides A and B c) Peptides A and B; Only peptide B d) Peptides A and B; Peptides A and B e) Neither A nor B; Neither A nor B |
D |
|
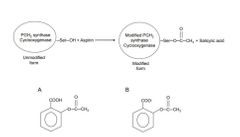
PGH2 synthase or cyclooxygenase (COX) is a homodimer, composed of two 70 kDa monomers. It can be covalently modified in presence of aspirin demonstrated by John Vane’s group in 1971. Please see the following reaction. Prostaglandins are hormone-like 20 carbon lipid compounds that mediate inflammatory responses. pKa of aspirin is 2.97. Arachidonic acid and prostaglandin H2 are substrate and product of ____________PGH2 synthase/cycloxoygenase respectively. If assuming pH inside cells is 7.2, the majority of the form of aspirin is ____________ . |
a) modified; A b) modified; B c) unmodified; A d) unmodified; B e) neither modified nor unmodified; either A or B |
D |
|
|
CDKs and cyclins are the key regulators of cell cycle. Which of the following proteins or protein complexes can add a phosphate group to other proteins? Binding of Cyclin E to CDK2 ___________ cell cycle progression, and binding of p21 to CDK2-Cyclin E complex___________ cell cycle progression |
A. Cyclin E alone B. CDK2 alone C. CDK2-Cyclin E complex D. CDK2-Cyclin E-p21 complex a) B or C or D; inhibits; facilitates b) B or C or D; facilitates; inhibits c) Only C; inhibits; facilitates d) Only C; facilitates; inhibits e) Only A; has no effect on; has no effect on |
D |
|
|
Determine the correct amino acid sequence of a heptapeptide (a small peptide containing seven amino acids) on the basis of the following data. Note: when the amino acid sequence is not given, a comma separates the amino acids. (i) Amino acid composition: (Ala, Arg, Leu, Lys, Phe and 2Val). It means that this heptapeptide contains one Ala, one Arg, one Leu, one Lys, one Phe and two Val. (ii) N-terminal analysis of the heptapeptide: Leu (iii)Trypsin digestion (cleavage) of the heptapeptide yielded two fragments: (Lys, Phe, Val, Val) and (Ala, Arg, Leu) (iv) Carboxypeptidase A digestion of the heptapeptide: no digestion (v) Chymotrypsin digestion of the heptapeptide produced two fragments: (Ala, Arg, Leu, Phe) and (Lys, Val, Val) The correct amino acid sequence of this heptapeptide from N-terminal to C-terminal is |
a) Leu-Ala-Arg-Phe-Val-Val-Lys b) Leu-Ala-Arg-Val-Phe-Val-Lys c) Leu-Ala-Phe-Arg-Val-Val-Lys d) Leu-Ala-Lys-Val-Phe-Val-Arg e) Leu-Arg-Ala -Val-Phe-Val-Lys |
A |
|
|
A polypeptide is subjected to the following degradative techniques resulting in polypeptide fragments with the indicated amino acid sequences. What is the amino acid sequence of the original entire polypeptide? (i) Chymotrypsin cleavage: K-Y A-M-K G-M-D-I-K-Q-W R-F (ii) Trypsin cleavage: Q-W-K G-M-D-I-K F-A-M-K Y-R |
a) A-M-K-G-M-D-I-K-Q-W-K-Y-R-F b) A-M-K-G-M-D-I-K-R-F-Q-W-K-Y c) G-M-D-I-K-Q-W-K-Y-R-F-A-M-K d) G-M-D-I-K-R-Q-W-F-K-Y-A-M-K e) Q-W-K-F-A-M-K- G-M-D-I-K-Y-R |
C |
|
|
The following polypeptide has 20 amino acids (using 1-letter codes) that is folded into an helix: AVLLRNSIWKADVTVEVCQF What is maximal number of intra-chain hydrogen bonds in the main chain of this helix? What is maximal number of electrostatic interaction in this helix including main chain and side chain? |
a) 16; 3 b) 16; 6 c) 20; 3 d) 20; 6 e) 40; 6 |
A |
|

|
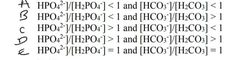
|
B |
|

|
a) 2; Both molecule A and molecule B b) 2; Only molecule A c) 2; Only molecule B d) 4; Both molecule A and molecule B e) 4; Only molecule B |
D |
|

|
a) Ala; Arg b) Arg; Ala c) Ala; Glu d) Glu; Ala e) Either Ala or Arg or Glu; Either Ala or Arg or Glu |
A |
|

|
a) Asp and Phe; 5.23 b) Asp and Phe; 6.63 c) Asp and Trp; cannot be determined based on the available information d) Glu and Trp; 5.37 e) Glu and Trp; 6.92 |
B |
|
|
Treatment of a protein by β-mercaptoethanol yields two smaller polypeptides that have the following amino acid sequences: I. A-F-C-M-Y-C-L-W-C-N II. V-C-W-V-I-F-G-C-K Chymotrypsin-catalyzed hydrolysis of the intact polypeptide yields smaller polypeptide fragments with the following amino acid compositions: III. (A, F) IV. (N, C, M, Y) V. (C, G, K) VI. (C, L, W, V) VII. (I, F, V) How many disulfide bond(s) is(are) there in the original protein? Which one(s) is(are) the correct disulfide bond(s) in the original protein? |
a) 1; There is one disulfide bond between polypeptides I and II, but there is no disulfide bond in polypeptide I and in polypeptide II. b) 2; There is one disulfide bond in polypeptide I and there is a second disulfide bond between polypeptides I and II. c) 2; There is one disulfide bond in polypeptide II and there is a second disulfide bond between polypeptides I and II. d) 2; There are two disulfide bonds between polypeptides I and II, but there is no disulfide bond in polypeptide I and in polypeptide II. e) 2; There are one disulfide bond in polypeptide I and another one in polypeptide II, but there is no disulfide bond between polypeptides I and II. |
B |
|
|
You are given the following amino acids: A. Phenylalanine B. Aspartate C. Leucine D. Glutamate E. Lysine A water-soluble globular protein is most likely to have the highest proportion of which of the amino acids above buried within its core? Which of the amino acids in protein above most likely can be posttranslationally phosphorylated? |
a) A; Only B and D b) A; None c) A and C; Only B and D d) A and C; None e) A, C and E; Only B and D |
D |
|

The following figure show a β-pleated sheet with two β strands. This is an example of ____________ β-pleated sheets. How many hydrogen bonds can be formed between two strands showed in the figure? |
a) anti-parallel; 2 b) anti-parallel; 3 c) parallel; 2 d) parallel; 3 e) either anti-parallel or parallel; 2 or 3 |
A |
|
|
An increase in pH from 7.0 to 13 usually results in protein denaturation due to which one of the followings? |
a) Loss of primary structure caused by base-induced cleavage of the peptide bonds. b) Loss of secondary strcuture caused by prontonation of basic groups. c) Loss of tertiary strcuture caused by deprontonation of basic groups. d) Loss of tertiary strcuture caused by prontonation of carboxylic acid groups. e) Loss of quaternary strcuture caused by deprontonation of carboxylic acid groups. |
C |
|
|
The protein allergen from peanuts called Arah8 was recently purified and characterized. The investigators initially had difficulty separating Arah8 from a similar protein in peanuts called Arah6 because the two proteins were of similar size and had nearly identical pI values. Separation of the two proteins was finally achieved when it was noted that Arah6 protein contained 10 cysteine residues involved in disulfide bridges where Arah8 contained no cysteine. The protein mixture extracted from peanuts was treated with dithiolthreitol (DTT) and then treated with iodoacetic acid ICH2COOH. CH2COOH will covalently link to SH group and release free iodine, I. The mixture was then loaded onto an anion exchange column and two proteins were successfully separated. Which protein, Arah8 or Arah6 treated with DTT and iodoacetic acid, elutes first from the anion exchange column? Which protein Arah8 or Arah6 treated with DTT and iodoacetic acid will stay at lower pH spot if the mixture was loaded on an IEF chamber? |
a) Arah6 treated with DTT and iodoacetic acid; Arah6 treated with DTT and iodoacetic acid b) Arah6 treated with DTT and iodoacetic acid; Arah8 c) Arah8; Arah6 treated with DTT and iodoacetic acid d) Arah8; Arah8 e) It cannot be determined since no enough information is available; It cannot be determined since no enough information is available. |
C |
|

A polypeptide of collagen folds into left handed helical structure. Most common secondary structure is helix that is right handed. How many left handed helices are there in one collagen molecule? What is the possible reason why left handed helical structure was found in collagen? |
a) ~100; because of unique amino acid composition and hydroxylation of glycine b) ~100; because of unique amino acid composition and hydroxylation of proline c) ~300; because of unique amino acid composition and hydroxylation of glycine d) ~300; because of unique amino acid composition and hydroxylation of proline e) It cannot be determined since no enough information is available; beacuse collagen is a fibrous protein. |
D |
|

Collagen biosynthesis requires an enzyme and a vitamin? What are the enzyme X and vitamin Y respectively in the following figure? |

a) glylyl hydroxylase; vitamin C b) glylyl hydroxylase; vitamin E c) prolyl hydroxylase; vitamin C d) prolyl hydroxylase; vitamin E e) It is unknown; It is unknown. |
C |
|

The collagen has unique amino acid composition: -(G-X-Y)n- . What is the correct structure of the product, Edman reagent-Gly, after the peptide bond of Edman reagent-G-X-Y is broken? The amino acid covalently linked to Edman can be identified by ____________ . |
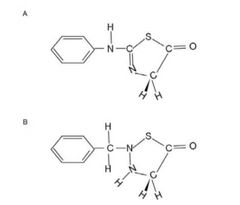
a) A; affinity chromatography b) A; ion exchange chromatography c) B; affinity chromatography d) B; ion exchange chromatography e) Both A and B; either affinity chromatography or ion exchange chromatography |
B |
|
|
Which of the following statement is true about two separate solutions: trypsin solution and chymotrypsin solution? |
a) Both trypsin and chymotrypsin solutions will lose their activities over time because trypsin can cleave other trypsin molecules in the solution and it is also true for chymotrypsin. b) Trypsin solution will lose its activities over time while chymotrypsin solution would not lose its activity over time. c) Chymotrypsin solution will lose its activities over time while trypsin solution would not lose its activity over time. d) Neither trypsin nor chymotrypsin solution will lose their activities over time because they are stable enzymes. e) Both trypsin and chymotrypsin solutions will lose their activities over time. However, chymotrypsin solution will lose its activities faster than trypsin solution. |
A |
|
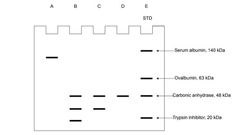
A student obtained mouse antibody anti-cyclin E against human antigen cyclin E. The student isolated total protein mixture X from the cells at G0 stage, protein mixture Y from the cells under cell cycle, and protein mixture Z from the cells with DNA damages during the cell cycle. And then the student performed three independent affinity chromatography purifications: mixture X was loaded onto one affinity column with anti-cyclin E, mixture Y was loaded onto second affinity column with anti-cyclin E, and mixture Z was loaded onto third affinity column with anti-cyclin E. After affinity purification, the final elutions (solutions pass through the columns) were further studied by SDS-PAGE. Lane E contains standards of molecular weight (STD) indicated on the right side of the gel. Size of human cyclin E is ~49 kDa, size of human CDK2 is ~34 kDa and human p21 is ~18 kDa. Which lane was from mixture X? Which lane was from mixture Y? Which lane was from mixture Z? |
a) A; B; C b) B; C; D c) C; D; A d) D; B; A e) D; C; B |
E |
|

A student obtained mouse antibody anti-cyclin E against human antigen cyclin E. The student isolated total protein mixture X from the cells at G0 stage, protein mixture Y from the cells under cell cycle, and protein mixture Z from the cells with DNA damages during the cell cycle. And then the student performed three independent affinity chromatography purifications: mixture X was loaded onto one affinity column with anti-cyclin E, mixture Y was loaded onto second affinity column with anti-cyclin E, and mixture Z was loaded onto third affinity column with anti-cyclin E. After affinity purification, the final elutions (solutions pass through the columns) were further studied by SDS-PAGE. Lane E contains standards of molecular weight (STD) indicated on the right side of the gel. Size of human cyclin E is ~49 kDa, size of human CDK2 is ~34 kDa and human p21 is ~18 kDa. If a student wants to purify human CDK2 by affinity chromatography, which of the following molecules can be used? |
A. An antibody against human CDK2 B. Substrate of CDK2 C. Cyclin E D. p21 E. An antibody against human p21 a) Only A b) Only A and B c) Only A, B and C d) Only A, B, C and D e) A, B, C, D, and E |
E |
|
|
______________, ______________, is the buffer system to maintain appropriate pH in the human blood vessel whereas ______________, ______________, is the buffer system to maintain appropriate pH inside human cells. |
a) Carbonate buffer; extracellular buffer; phosphate buffer; intracellular buffer b) Carbonate buffer; intracellular buffer; phosphate buffer; extracellular buffer c) Phosphate buffer; extracellular buffer; carbonate buffer; intracellular buffer d) Phosphate buffer; intracellular buffer; carbonate buffer; extracellular buffer |
A |
|
|
You are examining the thermodynamically stable structures of proteins. In particular, you are studying the α-helix and β-sheet conformations that form in the study protein. These conformations correspond to which of the followings? The quaternary structure of a given protein is defined by which of the followings? |
a) Native conformation; Overall structure resulting from the association of different portions of a polypeptide b) Native conformation; Structure resulting from the interactions between multiple polypeptide chains c) Secondary structure; Overall structure resulting from the association of different portions of a polypeptide d) Secondary structure; Structure resulting from the interactions between multiple polypeptide chains |
D |
|
|
Amino acids are biologically important organic compounds composed of amino and carboxylic acid functional groups, along with a side-chain specific to each amino acid. All amino acids except glycine have D- and L-forms. All amino acids in proteins are _____________ . What charged group(s) are present in glycine at a pH of 7? |
a) D-forms; Only carboxylic group b) D-forms; Both carboxylic and amino groups c) L-forms; Only carboxylic group d) L-forms; Both carboxylic and amino groups |
D |
|
|
A 42-amino acid peptide related to Alzheimer disease has the amino acid residues immersed in the membrane bilayer. Based on your knowledge about interactions between membrane proteins and membrane lipids, which of the following sequences most probably identifies four amino acids in this 42 amino acid peptide immersed in cell membrane? Assume that this 42-amino acid peptide folds into an α helix. Assume that the thickness of a membrane bilayer is 6 nm = 60 Å. Is it possible for this 42-amino acid peptide to have three N-terminal amino acids outside the cell membrane and three C-terminal amino acids in the cytoplasm of the cell? |
a) Glu-Val-Ala-Ser; possible b) Glu-Val-Ala-Ser; not possible c) Val-Leu-Ile-Ala; possible d) Val-Leu-Ile-Ala; not possible |
D |
|
|
There are two peptides: Peptide A: Ala-Tyr-Trp-Trp-Leu-Pro-Trp Peptide B: Ala-Val-Met-Ser-Leu-Ile-Thr Which of the peptides would absorb(s) UV light at 280 nm, and which of the peptides can be phosphorylated? |
a) Only peptide A; Only peptide B b) Only peptide A; Peptides A and B c) Peptides A and B; Only peptide B d) Peptides A and B; Peptides A and B |
B |
|

Glutamatic acid has three dissociable H+ with three pKa shown below. pKa = 2.2 pKb = 9.7 pKR = 4.3 pI of Glu is ______________. The form of Glu predominates in a solution at pH 5 is ______________ . |
a) 3.25; Glu0 b) 3.25; Glu- c) 5.4; Glu0 d) 5.4; Glu- |
B |
|
|
peptide bond is a covalent chemical bond formed between two molecules when the carboxyl group of one molecule reacts with the amino group of the other molecule, causing the release of a molecule of water, hence the process is a dehydration synthesis reaction (also known as a condensation reaction). The peptide bond has a ___________ character due to a resonance structure. Due to this character, six atoms of the peptide bond group are always planar. Dipole of amide linkage of a peptide bond is due to partially ___________charged carbonyl oxygen and partially ___________ charged amide nitrogen |
a) free rotation; negatively; positively b) free rotation; positively; negatively c) partial double bond; negatively; positively d) partial double bond; positively; negatively |
C |
|
|
Keratin is the key structural material making up the outer layer of human skin. It is also the key structural component of hair and nails. α-keratin is an example of fibrous proteins. The folding process for α-keratin can be summarized as ___________ . The interactions between α helices are mainly mediated by hydrophobic interactions. What determines quaternary structure of keratin? |
a) helix Æ triple helix Æ fibril Æ fiber; Amino acid sequence b) helix Æ triple helix Æ fibril Æ fiber; Hydrogen bonds c) helix Æ coiled coil Æ protofilament Æ filament; Amino acid sequence d) helix Æ coiled coil Æ protofilament Æ filament; Hydrogen bonds |
C |
|
|
A genetics regulator is found to contain a lysine residue that is important for its binding to DNA. If a mutation were to occur such that a different amino acid replaces the lysine at that location, which of the following resulting amino acids would likely be the least harmful to its ability to bind DNA? Which of the following resulting amino acids would likely be the most harmful to its ability to bind DNA? |
a) Glutamate; Arginine b) Glutamate; Proline c) Arginine; Proline d) Arginine; Glutamate |
D |
|

Ion exchange chromatography (or ion chromatography) is a process that allows the separation of proteins based on their charges. Commonly used matrixes in ion exchange chromatography include carboxymethyl-celllulose (CM-cellulose) and diethylaminoethyl- celllulose (DEAE-cellulose). CM-cellulose is used in __________ exchange chromatography and while DEAE-cellulose is used in __________ exchange chromatography. You are given three types of oligopeptides, A: K-L-A-K-K-R; B: A-L-V-I-I-L; C: E-D-D-D-A-D. Which oligopeptide will come out first from CM-cellulose column? |
a) anion; cation; A b) anion; cation; C c) cation; anion; A d) cation; anion; C |
D |
|
|
Transcription factor E2F promotes transcription of genes for certain enzymes essential to DNA synthesis during cell cycle. Which of the following proteins can activate E2F function and which of the following proteins can inhibit E2F function? Main function of Cyclin E is to bind CDK2 and ______________ kinase activity of CDK2. A. Reduced level of Cyclin E B. CDK2-Cyclin E complex C. Unphosphorylated Rb D. Phosphorylated Rb |
a) A or D; B or C; activates b) A or D; B or C; inhibits c) B or D; A or C; activates d) B or D; A or C; inhibits |
C |
|
|
Which of the following processes requires molecular chaperon in order to facilitate correct biological function? An insoluble form of a prion protein accumulates in the brains of patients who have Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD).CJD is a degenerative neurological disorder that is incurable and invariably fatal. Conversion of the normal soluble of the prion protein to the pathologic insoluble form is though to involve conversion of α-helices to β-pleated sheets. In order for this structural transition to occur, which of the followings is the most likely disrupted and reformed? |
a) correct folding of nascent proteins; disulfide bonds b) correct folding of nascent proteins; hydrogen bonds c) correct formation of disulfide bonds; disulfide bonds d) correct formation of disulfide bonds; hydrogen bonds |
B |
|
|
Determine the correct amino acid sequence of a hexapeptide (a small peptide containing six amino acids) on the basis of the following data. Note: when the amino acid sequence is not given, a comma separates the amino acids. (i) Amino acid composition: (2Arg, Ala, Ser, Val, Tyr). It means that this hexapeptide contains two Arg, one Ala, one Ser, one Val and one Tyr. (ii) N-terminal analysis of the hexapeptide: Ala (iii)Trypsin digestion (cleavage) of the hexapeptide yielded two fragments: (Arg, Ala, Val) and (Arg, Ser, Tyr) (iv) Carboxypeptidase A digestion of the hexapeptide: no digestion (v) Chymotrypsin digestion of the hexapeptide produced two fragments: (Ala, Arg, Val, Tyr) and (Arg, Ser) The correct amino acid sequence of this hexapeptide from N-terminal to C-terminal is |
a) Ala-Tyr-Val-Arg-Arg-Ser b) Ala-Val-Arg-Tyr-Arg-Ser c) Ala-Val-Arg-Tyr-Ser-Arg d) Arg-Ser-Ala-Tyr-Val-Arg |
C |
|
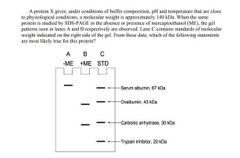
|
a) The protein X has two polypeptide chains with different molecular weight. The protein X contains one disulfide bond between two polypeptides. b) The protein X has two polypeptide chains with different molecular weight. The protein X contains two disulfide bonds between two polypeptides. c) The protein X has four polypeptide chains. Two polypeptides are identical and the other two are also identical. The protein X contains one disulfide bond between two identical polypeptides. d) The protein X has four polypeptide chains. Two polypeptides are identical and the other two are also identical. The protein X contains two disulfide bonds between two polypeptide chains with different molecular weight |
D |
|
|
A sequence of amino acids in a certain part of protein is -S-G-P-G-. The sequence is most probably part of a(n): |
a) random loop b) beta sheet c) beta turn d) alpha helix |
C |
|
|
You are studying the protein folding characteristics of a particular protein. You find that under certain conditions the protein does not fold correctly and its precipitates within in the cytosol/cytoplasm. Which of the following processes is the most directly responsible for aggregation and precipitation of the misfolded protein in the cytoplasm? Additionally, you found that the protein forms α-helical structure more rapidly in an alcohol medium than it does in water. Which of the followings is the best explanation for this difference? |
a) exposure of hydrophobic residues from the core onto the surface of the protein; competition for hydrogen bonding is lower for ethanol than for water b) exposure of hydrophobic residues from the core onto the surface of the protein; van der Waals interactions are lower in ethanol than water c) phosphorylation of threonine or serine side chains of the protein; competition for hydrogen bonding is lower for ethanol than for water d) phosphorylation of threonine or serine side chains of the protein; van der Waals interactions are lower in ethanol than water |
A |
|
|
A technique for determining protein structure that requires crystals of the protein is _____________. A technique for determining protein structure where the protein is in solution is _____________ . |
a) NMR spectroscopy; X-ray crystallography b) NMR spectroscopy; mass spectrometry c) X-ray crystallography; mass spectrometry d) X-ray crystallography; NMR spectroscopy |
D |
|
|
How many left handed helical structures does one collagen molecule have? Show your calculation or justify your answer. |
Calculate |
3×8×13=312 |
|
|
Analysis of a tumor cell line indicates that there is dramatically increased level in the activity of the transcription factor E2F. Which of the followings is the most likely explanation for this observation? |
A. An increase in the expression of Rb protein (pRb) resulting in increased binding of Rb to E2F B. Hypophosphorylation of Rb protein (pRb) so that it can no longer interact with E2F C. Loss of expression of Rb protein (pRb) which normally activates E2F D. Mutation in Rb protein (pRb) that prevents its phosphorylation so that it cannot interact with the gene to which it normally binds and coactivates with E2F E. Mutation in the domain of Rb protein (pRb) to which E2F binds, the consequences of which lead to constitutive E2F activity |
E |
|

What is the order of low to high molecular weight for spots A, B, C, D and E in. What is the order of low to high pI for spots A, B, C, D and E in.
|
A) A = B < E = C < D B) A < E < D < B < C C) C < B < D < E < A D) D < C = E < B = A E) A = B =C = D = E |
C |
|

If the native polypeptides of A, C and D are purified by cation exchange chromatography, what is the order of first to last coming out of from the column for them? |
A) A < C < D B) A < D < C C) C < D < A D) D < C < A E) A, C and D come out at almost same time from the column. |
D |
|
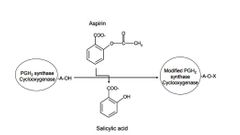
PGH2 synthase or cyclooxygenase (COX) is a homodimer, composed of two 70 kDa monomers. It can be covalently modified by in presence of aspirin demonstrated by John Vane’s group in 1971. Please see the diagram below. (Total 15 points) (a) The following diagram shows the molecular mechanism of aspirin. What are A and X in the following diagram respectively? |
A) Proline; Acetyl group B) Proline; Carboxylic group C) Serine; Acetyl group D) Serine; Carboxylic group |
C |
|
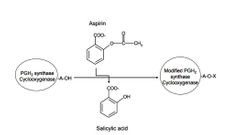
Explain the consequences when PGH2 synthase or cyclooxygenase (COX) is covalently modified in the presence of aspirin. |
I. PGH2 synthase or cyclooxygenase (COX) becomes active form. II. PGH2 synthase or cyclooxygenase (COX) becomes inactive form. III. Inflammation response will be enhanced. IV. Inflammation response will be decreased. A) I and III B) I and IV C) II and III D) II and IV |
D |
|
|
The collagen has unique amino acid composition. Draw out the structure of -(G-X-Y)- and show one phi () angle and one psi () angle. Label the atoms that are planar. |
Draw |

|
|
|
Draw out the structure of the product, Edman reagent-Gly, after the peptide bond of Edman reagent-G-X-Y is broken |
Draw |
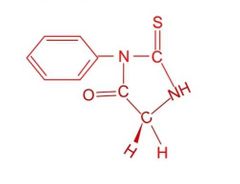
|
|
|
Explain the detailed function of vitamin C in biosynthesis of collagen |
Vitamin C is essential for ________ in collagen |
Hydroxylation of Proline |
|
|
Aspirin has a pKa of 3.5. The pH of the stomach is about 1.0, while that of the intestines is about 6.0? What are percents of weak acid and conjugate forms of aspirin in stomach? Show your calculation |
Work out |

|
|
|
Carboxypeptidase, which sequentially removes carboxyl-terminal amino acid residues from its peptide substrate, is a single polypeptide of 307 amino acids. The two essential catalytic groups in the active site are Arg145 (amino acid position is 145) and Glu270 (amino acid position is 270). If the carboxypeptidase chain were a perfect α-helix, how far apart in angstroms (Å) would Arg145 and Glu270 be? Please show your work |
Work out |

|

