![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
73 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atom
|
The smallest unit of matter that still retains the proterties of an element.
|
|
|
Element
|
a substance that cannot be broken down chemically.
|
|
|
compound
|
a substance consisting of two or more different elements combined in a fixed ration
|
|
|
molecule
|
two or more atoms held together by a covalent bond
|
|
|
isotope
|
atoms of the same element with different number of neutrons.
|
|
|
ion
|
A charged atom or molecule
|
|
|
About how many elements are required for life?
|
25
|
|
|
Which four elements are most common in living things?
|
C,H,O,N
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen |
|
|
Seven elements of than CHON that are common in living things?
|
Calcium, Phospherous, Potassium, Sulfur, Sodium, Chlorine, and Magnesium
|
|
|
Why are certain elements called trace elements?
|
Because they appear less than 0.01% but are still essential for life.
|
|
|
What is a proton?
|
A subatomic particle that is found in the nucleous and is positivily charged.
weighs one dalton |
|
|
What is a neutron
|
A subatomic particale that is found in the nucleous and it has no charge.
weighs one dalton |
|
|
What is an electron?
|
A subatomic particale that is found in the valence shell of a cell.
weighs 9.1×10^−31 kg |
|
|
Atomic number
|
is the of protons an element has
|
|
|
Atomic weight
|
The total weight of an element. typically it is equal to the sum of the protons and nuetrons.
|
|
|
molecular weight
|
the sum of the masses of all the atoms in a molecule
|
|
|
Mass number
|
the sum of protons and neutrons of an atom.
|
|
|
potiential engergy
|
the energy that matter possesses as a result of its location
|
|
|
What happens when the potential energy of an electron changes?
|
Kentic energy also changes?
|
|
|
what is another name for electron shell?
|
energy level
|
|
|
What is the valence electron
|
the outer shell of an atom
|
|
|
what are valence electrons?
|
the electrons in the outer shell.
|
|
|
What is a polar molecule?
|
electrons are not shared equally. ex. water
|
|
|
What is a non-polar molecule?
|
Electrons are shared equally. ex. H2 and O2
disolve in water. |
|
|
What is a covalent bond?
|
Is the sharing of a pair of valence electrons. covalent bonds are the strongest interaction in biology.
|
|
|
What are the four weak interactions in biology? what do they allow?
|
Ionic bonds, hydrogen bonds, van der waals interactions, and hydrophobic interactons. they allow two biomolecules to bind together.
|
|
|
What are ionic bonds?
|
a weak chemical bond that occurs when the stronger electronegative atom takes an electron from a weaker electronegative atom.
|
|
|
What are hydrogen bonds?
|
when a hydrogen atom with a positive charge bonds to a partial negative charge
|
|
|
What are Van Der Waals Interactions?
|
Occur between transient partial charges in non polar molecules.
|
|
|
What are hydrophobic interactions?
|
the clustering of non-polar molecules away from water
|
|
|
Intermolecular interactions
|
interactions between two molecules
|
|
|
intramolecular interactions
|
interactions within ONE molecule.
|
|
|
How many covalent bonds do C,H,O,N usually form?
|
H- 1
O- 2 N- 3 C- 4 |
|
|
Which atoms among CHON undergo sp3 hybridization?
|
Carbon, Oxygen and Nitrogen when they have only single covalent bonds
|
|
|
What do the obrital shapes have to do with the space arrangement of any covalently bonded atoms?
|
single covalent bonds will form sp3 hybrid.
-- need more info |
|
|
reactant
|
the material you start with
|
|
|
product
|
the material you end with
|
|
|
reversible reaction
|
once you can take the product use it as a reacted and produce the starting material again.
|
|
|
chemical equilibrium
|
when the rates of the forward and the reverse reactions become equal. the concentrations stop changing.
|
|
|
When did life appear on earth?
|
3-4 billion years ago
|
|
|
Why is water an effective solvent?
|
its polar molecules are attracted to charged and polar substances capable of forming hydrogen bonds.
|
|
|
What makes a substance hydrophilic?
|
"water loving" water will stick to it
|
|
|
What makes a substance hydrophobic?
|
"Water fearing" the substance will avoid water. ex. oils and non polar substances
|
|
|
How do water molecules dissociate?
|
Water molecules dissociate when the oxygen does not make its usual two covalent bonds but forms one or three. this happens in pure water.
|
|
|
What does the pH of a solution tell you about the [H+] and the [OH-]?
|
The more acidic a solution is the more [H+] in it.
The more basic a solution the more [OH-] in it. |
|
|
Why must cells maintain and control their pH?
|
If the pH of a cell changed the chemistry of the cell would change. The weak interactions would be disrupted which allow molecules to interact and give shape to a molecule.
|
|
|
What is the pH of most biological fluids?
|
6-8
|
|
|
What is the pH of cells?
|
about 7
|
|
|
What is the importance of buffers in biological fluids?
|
They matain the pH of fuild.
|
|
|
How do buffers function?
|
it accepts [H+] from the solution when they are in excess and donations hydrogen ions when they have been depleted.
|
|
|
How did the experiments performed by Wohler and Miller challenge vitalism?
|
they both made biomolecules in a labratory without a "life force"
|
|
|
What is Vitalism?
|
the intial fundation of organic chemistry, in which people believed biomolecules were mae by a "life force"
|
|
|
What shapes do carbon backbones form in biological molecules?
|
chains?
|
|
|
what are eight of life as it is known on earth?
|
complex/ordered, well-adapted, responsive, uses energy, regulated, carries instructions, grows and reproduces
|
|
|
What is a prokaryote organism?
|
has no nucleus. examples are bacteria and archaea.
|
|
|
what is a eukaryotic organism?
|
has a nucleous. example all forms of life (plant and animals)
|
|
|
What shapes do carbon backbones form in biological molecules?
|
Straight, branched, or closed rings.
|
|
|
How do double bonds affect a molecules shape and flexibility?
|
when the carbons are double bonded they are in the same plane. it makes the carbon atoms unable to spin. (making it flat)
|
|
|
Hydroxyl Functional group
|
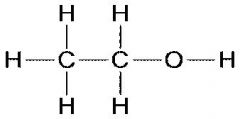
polar, hydrophilic
ex. alcohols such as methenal |
|
|
Carbonyl Functional Group
|
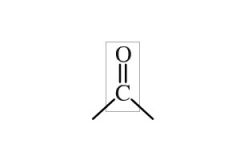
A carbon double bonded to an oxygen. Can make keytones and aldehides
|
|
|
Keytones
|
form when a carbonyl group is within a carbon backbone.
|
|
|
aldehydes
|
form when a carbonyl group is at the end of the carbon backbone.
|
|
|
Carboxyl Functional Group
|

When an oxygen atom is double bonded to a carbon atom that is also bonded to a hydroxyl group. Acts as an acid, can donate an H+ because the covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is very polar. can have a charge.
|
|
|
Amino Group
|
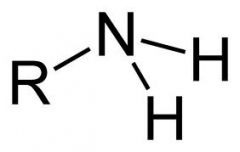
consists of a nitrogen atom bonded to two hydrogen atoms and to the carbon backbone. acts as a base, can have a 1+ charge.
|
|
|
Sulfhydryl Group
|

Consists of a sulfur atom bonded to an atom of hydrogen; resembles a hydroxyl group in shape. form special covalent bonds in proteins.
|
|
|
Phosphate Group
|
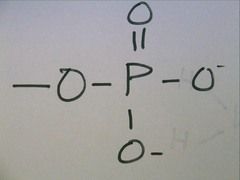
when a phosphorus atom is bonded to four oxygen atoms; one oxygen is bonded to the carbon backbone. two oxygens carry negative charges. have the potential to react with water, releasing energy. can have a 1- chare.
|
|
|
What is a polymer?
|
a polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar or identical building blocks linked by covalent bonds.
|
|
|
What is dehydration ?
|
when monomers are connected by a reaction in which two molecules are covalently bonded to each other. produces a water molecule.
|
|
|
What is Hydrolysis?
|
Polymers are disassembled to monomers by using water. the bond between the monomers is broken by the addition of water, with the hydrogen from the water attaching t one monomer and the hydroxyl group attaching to the adjacent monomer.
|
|
|
Which of the four classes of biological molecules form polymers?
|
Carbs, proteins and nucleic acids
|
|
|
What is a macromolecule?
|
are proteins, nucleic acids and carbohydrates. They weigh greater than or equal to 1000 daltons.
|
|
|
What carb functions are monosaccharides?
|
energy source and carbon source
|
|
|
what carb functions are polysaccharides?
|
storage and structural
|

