![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
74 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Gonads |
organs that produce reproductive cells |
|
|
Sex hormones |
chemical compounds that control the development and function of the reproductive system (testosterone, estrogen and progesterone) |
|
|
Primary sex characteristics |
structures that play a direct role in reproduction |
|
|
Secondary sex characteristics |
structures that are indirectly related to reproduction |
|
|
Function of male reproductive system |
to produce and large numbers of sperm cells - to release sperm within the female reproductive tract |
|
|
Testes |
regulates temperature - site of sperm production |
|
|
Seminiferous tubules |
makeup testes |
|
|
Sertoli cells |
develop and nourish sperm |
|
|
Epididymis |
where sperm mature and become motile |
|
|
Spermatogenesis |
production of sperm - testes, epididymis, vas deferens, ejaculatory duct |
|
|
Structure of the Sperm |
head: to penetrate the protective layer of the egg middle: provide energy for movement of tail tail: to propel sperm |
|
|
Seminal fluid |
mucus-like fluid which provides energy for sperm - contains sugar fructose |
|
|
Ovaries |
produce ova |
|
|
Uterus |
holds and nourishes a developing fetus |
|
|
Endometrium |
provides nutrients for fetus |
|
|
Vagina |
entrance for penis to deposit sperm |
|
|
Follicles |
barrier/protection for ovum > when ruptured = ovulation |
|
|
Ovulation |
rupture of follicles, releasing eggs |
|
|
Oogenesis |
development of oocytes in the embryo before birth |
|
|
Menstrual cycle |
the process of ovulation and menstruation in women |
|
|
Menarche |
used to describe first menstruation |
|
|
Menopause |
used to describe cessation (ending) of menstruation |
|
|
Menstrual Phase |
beginning of cycle - shedding of endometrium |
|
|
Follicular phase |
development of follicles in the ovary - secretion of estrogen > promotes repair and thickening of endometrium |
|
|
Ovulation |
one follicle becomes dominant in follicular phase - matures and ruptures at the surface of the ovary |
|
|
Luteal phase |
from ovulation to end of the cycle - progesterone and estrogen are secreted by corpus luteum |
|
|
Gonadotropins |
FSH and LH > regulate menstrual cycle and indirectly causes the development of secondary sex characteristics |
|
|
FSH |
- development of endometrium - negative feedback to switch off FSH - positive feedback to switch on LH |
|
|
LH |
- causes ovulation - differentiation of the follicles into the corpus luteum which secretes progesterone (and some estrogen) |
|
|
HCG |
maintains the corpus luteum until the placenta begins to secrete its own progesterone as it develops |
|
|
FSH (male) |
stimulates production of sperm cells in seminiferous tubules |
|
|
LH (male) |
promotes production of testosterone by the interstitial cells |
|
|
Inhibin |
produced by Sertoli cells - inhibits FSH production and controls the production of sperm without reducing testosterone levels |
|
|
Male hormone production (diagran) |
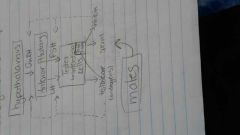
|
|
|
Female hormone production (diagram) |
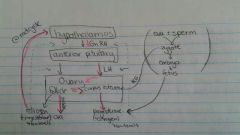
|
|
|
Penis diagram |
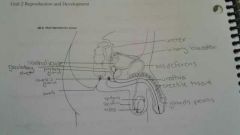
|
|
|
Female reproductive tract diagram |
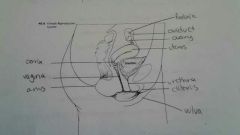
|
|
|
Effects of estrogen (female) |
- Promotes female secondary sex characteristics - Promotes development of the endometrium - Has a negative feedback effect on the pituitary to switch off FSH - Has a positive feedback effect on the pituitary to switch on LH |
|
|
FSH stimulates... |
follicle development |
|
|
LH effects |
- causes ovulation - causes the differentiation of the follicular cells into the corpus luteum which secrete progesterone (and some estrogen) |
|
|
Differentiation |
the process by which cells or tissues change from relatively generalized to specialized kinds, during development |
|
|
Testosterone effects |
- Growth and development of musculature - Lengthening of the vocal cords (Causes Deepening of the voice) - Development of facial and body hair |
|
|
Zygote |
fertilized egg |
|
|
Morula |
when the zygote moves down the fallopian tubes and divides (cleavage) into a ball of cells |
|
|
Blastocyst |
when the morula reaches the uterus where it absorbs fluid and develops into a hollow ball of cells |
|
|
Implantation |
blastocyst is imbedded into the endometrium |
|
|
First Trimester |
- end of 3rd week > embryo has developed into a 3 layer disc called the gastrula |
|
|
Gastrulation |
migration of cells between the 2 layers of cells found in the blastocyst |
|
|
Ectoderm |
outer layer - becomes the epidermis (skin, hair, etc.) - nervous system |
|
|
Mesoderm |
middle layer - muscles, bone and blood vessels (circulatory system) |
|
|
Endoderm |
inner layer - linings of digestive and respiratory tracts |
|
|
Development of organs and organ systems involve: |
Growth, morphogenesis (development of body form), differentiation |
|
|
Effects of some teratogens |
- formation of facial features - formation of extra digits on limbs - formation of the nervous system-mental retardation - spina bifida - formation of eye-cataracts - formation of heart abnormalities |
|
|
Progesterone (birth and lactation) |
drop in progesterone levels to signal end of pregnancy and release of oxytocin |
|
|
Relaxin |
produced by placenta prior to labour - loosens ligaments of the pelvis |
|
|
Oxytocin |
causes strong uterine contractions to bring about birth - maintains production until after birth |
|
|
Prolactin |
stimulates breast glands to produce milk - initially contains only sugar and protein (colostrum) - contains antibodies to provide passive immunity against disease |
|
|
Seminal Vesicle |
secretes hormones that cause the uterus to contract |
|
|
Structures responsible for components of semen |
seminal vesicle, prostate, cawpers gland, testes |
|
|
Fertilization happens in... |
oviduct |
|
|
Estrogen in females comes from... |
ovaries |
|
|
Haploid vs. diploid |
haploid: has half of the amount of chromosomes diploid: complete set of chromosomes |
|
|
Sexually transmitted infection |
transmitted by sexual contact |
|
|
AIDS/HIV |
attacks white blood cells > may be infected themselves by before or during birth |
|
|
Hepatitis |
contamination of water with fecal matter - affects placenta |
|
|
Genital Herpes |
type 1 > oral infections type 2 > genital contact - increase risk of infection to baby |
|
|
Chlamydia/Gonorrhoea |
caused by Chlamydia trachtomitis - causes infertility |
|
|
Syphilis |
Treponema pallidum - can infect a developing embryo |
|
|
sterile vs. infertile |
- unable to have children - difficulty to conceive |
|
|
Artificial Insemination |
collected sperm is concentrated before being placed in the vagina |
|
|
In Vitro Fertilization |
retrieval of immature eggs and combined with sperm in a glass container > once fertilized it's placed in the uterus |
|
|
Surrogates |
infertile couple gets another woman to carry a baby for them |
|
|
Superovulation |
production of multiple eggs through hormone treatments |
|
|
What happens to the blastocyst |
Amnion > amnionic fluid sac Chorion > placenta |

