![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
56 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Photosynthesis and cellular respiration equation
|
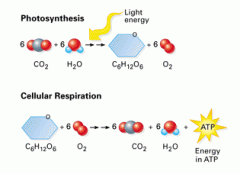
|
|
|
The cells release chemical energy from carbohydrates by the process called ________.
|
CELLULAR RESPIRATION
|
|
|
Cellular respiration includes the __________ of aerobic and anaerobic respiration, which breakdown organic molecules for the production of ATP
|
catabolic pathways
|
|
|
Catabolic pathways
|
A metabolic pathway that releases energy by breaking down complex molecules to simpler molecules
|
|
|
Aerobic respiration
|
Break down of organic molecules in the presence of oxygen
|
|
|
Aerobic respiration
|
Break down of organic molecules in the presence of oxygen Ex : Eukaryotic cells
|
|
|
Anaerobic respiration
|
Breakdown of organic molecules in the absence of oxygen. Ex: Some eukaryotic cells(under low oxygen levels),Prokaryotic and protists.
|
|
|
Aerobic respiration and fermentation both begin with _______, which converts one molecule of glucose into two molecules of ______
|
glycolosis, pyruvate
|
|
|
Fermentation is completed in the ______, yielding _____ per glucose molecule
|
cytoplasm, 2 ATP
|
|
|
Aerobic respiration is completed in ______, yielding ____ per glucose molecule
|
mitochondria, 36 ATP
|
|
|
Three stages of aerobic respiration
|
1. Glycolysis
2. Acetyl-CoA formation and Krebs cycle 3. Electron transfer phosphorylation (ATP formation) ( Coenzymes NADH and FADH2 carry electrons and hydrogen ions to ETP for the production of ATP) |
|
|
Pyruvate
|
3 carbon compound formed from glucose in glycolosis
|
|
|
Substrate level phosphorylation
|
The formation of ATP by an enzyme directly transferring a phosphate group to ADP from an intermediate substrate.
|
|
|
______ are formed by substrate-level phosphorylation (______). 2 ____molecules are produced.
|
Four ATP, net 2 ATP, NADH
|
|
|
ATP requiring and ATP generating steps
|
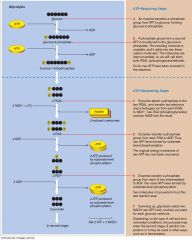
|
|
|
The two stages of second part of aerobic respiration
|
Occurs in mitochondria
Includes two stages: Acetyl CoA formation Krebs cycle (each occurs twice in the breakdown of one glucose molecule) |
|
|
Process of Acetyle-CoA formation
|
Two pyruvate formed by glycolysis enter the inner compartment of a mitochondrion
In the inner compartment of the mitochondrion, enzymes split pyruvate, forming acetyl CoA( has a lot of energy and very reactive) and CO2 (which diffuses out of the cell) 2 NADH is formed |
|
|
Krebs Cycle
|
A sequence of enzyme-mediated reactions that break down 2 acetyl CoA into 4 CO2
Oxaloacetate is used and regenerated 6 NADH and 2 FADH2 are formed 2 ATP is formed |
|
|
Reactions happening inside a mitochondrion
|

|
|
|
Krebs Cycle steps
|

|
|
|
Steps of electron transfer phosphorylization
|
Coenzymes NADH and FADH2 donate electrons and H+ to electron transfer chains
Active transport forms a H+ concentration gradient in the outer mitochondrial compartment H+ follows its gradient through ATP synthase, which attaches a phosphate to ADP Finally, oxygen accepts electrons and combines with H+, forming water |
|
|
Electron transfer phosphorylization steps
|

|
|
|
Oxidative Phosphorylization
|
The production of ATP using energy derived from the redox reactions of an electron transport chain
|
|
|
Chemiosmosis
|
An energy coupling mechanism that uses energy stored in the form of hydrogen ion gradient across a membrane to drive cellular work, such as the synthesis of ATP. Most ATP synthesis in cells occurs by chemiosmosis
|
|
|
The summary of energy harvest in aerobic respiration
|
Typically, the breakdown of one glucose molecule yields 36 – 38 ATPs
Glycolysis: 2 ATPs Krebs cycle: 2 ATPs Electron transfer phosphorylation: 32 – 34 ATPs |
|
|
Summary of aerobic respiration
|

|
|
|
__________ break down carbohydrates without using oxygen
|
Fermentation pathways
|
|
|
Fermenters
|
Anaerobes or Facultative anaerobes(organisms/cells that switch to fermentation in the absence of oxygen)
|
|
|
Aenorobes
|
Ex: Bacteria and single cell protists that inhabit
Sea sediments Animal guts Improperly canned food Sewage treatment ponds Deep mud and other anaerobic habitats. |
|
|
Facultative aenarobes
|
Yeast and animal muscle cells
|
|
|
Fermentation pathways
|
Glycolysis is the first stage of fermentation
Forms 2 pyruvate, 2 NADH, and 2 ATP Pyruvate is converted to other molecules, but is not fully broken down to CO2 and water Regenerates NAD+ but doesn’t produce ATP Provides enough energy for some single-celled anaerobic species |
|
|
Alcoholic fermentation
|
Pyruvate is split into acetaldehyde and CO2
Acetaldehyde receives electrons and hydrogen from NADH, forming NAD+ and ethanol |
|
|
Lactate fermentation
|
Pyruvate receives electrons and hydrogen from NADH, forming NAD+ and lactate
** NAD+ regeneration during both these pathways is crucial to the survival of the organism. When the supply of NAD+ is exhausted, glycolysis would stop, energy production would cease and the organism would almost instantly die |
|
|
Two pathways of fermentation
|

|
|
|
________ which moves bones, consists of cells fused as long fibers. The fibers differ in how they make ATP.
|
Skeletal muscle cells
|
|
|
Slow-twitch muscle fibers (“red” muscles)
|
make ATP by aerobic respiration
Have many mitochondria Dominate in prolonged activity |
|
|
Fast-twitch muscle fibers (“white” muscles)
|
make ATP by lactate fermentation
Have few mitochondria and no myoglobin Sustain short bursts of activity |
|
|
Pathways that break down molecules other than ________ also keep organisms alive
|
carbohydrates
|
|
|
When blood ____concentration rises, the pancreas increases ______ secretion
|
glucose, insulin
|
|
|
A few different pathways yield ATP by breaking down carbohydrates, but a typical _______ uses aerobic respiration most of the time.
|
eukaryotic cell
|
|
|
One way energy flow
|

|
|
|
Aerobic respiration overview
|

|
|
|
Many bacteria, archaea, and protists harvest energy from carbohydrates by anaerobic pathways of _____
|
fermentation
|
|
|
The reactions of glycolysis convert one molecule of glucose to two molecules of ______ for a net yield of two ATP.
|
pyruvate
|
|
|
An energy investment of ___ is required to start glycolysis.
|
ATP
|
|
|
The enzyme that catalysis glycolysis
|
Hexokinase
|
|
|
Glycolosis summary
|

|
|
|
Krebs Cycle overview
|

|
|
|
The Krebs cycle breaks down _____ to _____.
|
acetyl–CoA, CO2
|
|
|
Acetyl CoA and Krebs Cycle Summary
|

|
|
|
The third stage of aerobic respiration, electron transfer phosphorylation, occurs at the __________.
|
inner mitochondrial membrane
|
|
|
Electron transfer phosphorylation steps
|
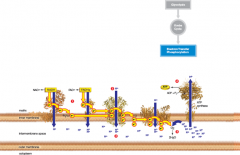
One NADH and FADH2 deliver electrons to electron transfer chains in the inner mitochondrial membrane.
Two Electron flow through the chains causes hydrogen ions (H+) to be pumped from the matrix to the intermembrane space. Three The activity of the electron transfer chains causes a hydrogen ion gradient to form across the inner mitochondrial membrane. Four Hydrogen ion flow back to the matrix through ATP synthases drives the formation of ATP from ADP and phosphate (Pi). Five Oxygen combines with electrons and hydrogen ions at the end of the electron transfer chains, so water forms. |
|
|
Three stages of aerobic respiration
|

|
|
|
Fermentation pathways break down carbohydrates without using ______. The final steps in these pathways regenerate _____ but do not produce ___.
|
oxygen, NAD+, ATP
|
|
|
Alcoholic fermentation
|

|
|
|
Lactate fermentation
|
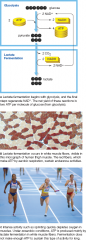
|

