![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
91 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Epidermis
|
Composed of epithelial cells, outermost protective shield
|
|
|
Dermis
|
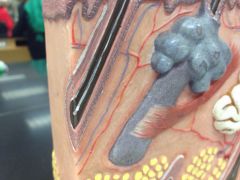
Second major skin region, strong flexible connective tissue
|
|
|
Apocrine sweat gland
|
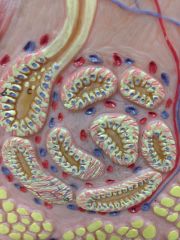
In axillary and anogenital areas
|
|
|
Sebaceous (oil) glands
|

Found all over the body except thick skin of palms and sole
|
|
|
Arrector Pili Muscle
|
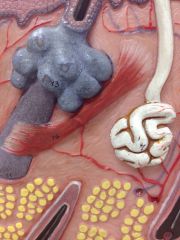
Smooth muscle cells
|
|
|
Stratum cornum
|
Very top, dead cells keratinocytes
|
|
|
Stratum Lucidum
|
Single layer of translucent, dead cells found in thick skin
|
|
|
Stratum granulosum
|
Deep cells are alive contain protein keratin and oily waterproofing substance
|
|
|
Stratum Spinosum
|
First actively metabolizing cells and melanin is found here, protection from UV light
|
|
|
Tactile Meissner Corpuscle
|
Touch receptors and provide blood supply
|
|
|
Eccrine Merocrine Glands
|
Abundant on the palms, soles of the feet, forehead. Simple, coiled, tubular gland.
|
|
|
Lamellar Pacinian Corpuscle
|
Contain a water-resident glycolipid that is spewed into extra cellular space. Slowing water loss across epidermis.
|
|
|
Epithelial Tissue
|
Covers the outside of the body and lines all body cavities. provide protection.
|
|
|
Epithelial Tissue
|
Covers the outside of the body and lines all body cavities. provide protection.
|
|
|
Types of Epithelial
|
Simple Squamous, Simple Cuboidal and Simple Columnar
|
|
|
Connective Tissue
|
Binding and supportive for all other tissues in the body.
|
|
|
Connective Tissue
|
Binding and supportive for all other tissues in the body.
|
|
|
Types of connective tissue
|
Dense Regular, Adipose and Bone
|
|
|
Muscle Tissue
|
Tissue adapted to contract.
|
|
|
Types of Muscle Tissue
|
Skeletal, Cardiac and Smooth
|
|
|
Nervous Tissue
|
Functions to receive stimuli and transmit signals from one part of the body to another.
|
|
|
Types of Nervous Tissue
|
Neuron and Neuroglial Cell
|
|
|
Simple Squamous Epithelium
|
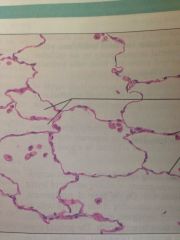
Located in Kidney, air sacs of lungs, lining of heart, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and lining of ventral body cavity. Diffusion and filtration.
|
|
|
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
|
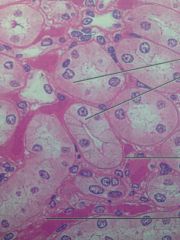
Found in Kidney Tubules. Secretes and absorbs.
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium
|
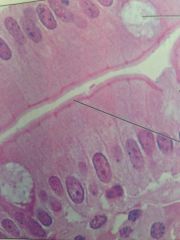
Located in small intestine, digestive tract, gallbladder
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium
|
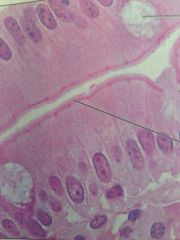
Located in small intestine, digestive tract, gallbladder
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
|
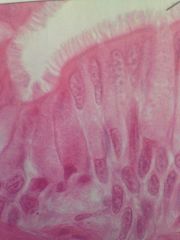
Located in ciliated lines of trache, and most of upper respiratory tract
|
|
|
Simple columnar epithelium
|
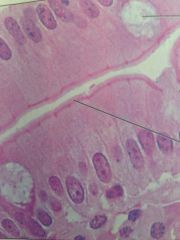
Located in small intestine, digestive tract, gallbladder. Absorption, secretion of enzymes.
|
|
|
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium
|
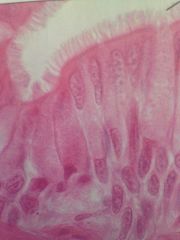
Located in ciliated lines of trache, and most of upper respiratory tract. Secretion, mostly of mucus.
|
|
|
Stratified squamous epithelium
|
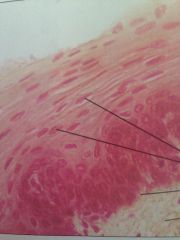
Nonkeratinized type forms lining of esophagus, mouth, skin, a dry membrane. Protects underlying tissue in areas subjected to abrasion.
|
|
|
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
|
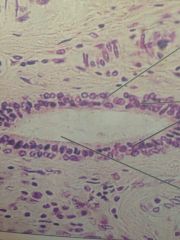
Largest ducts of sweat glands, mammary glands and salivary glands. Protection.
|
|
|
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
|
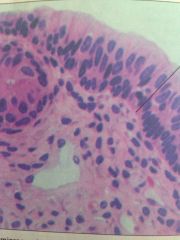
In male urethra and large ducts of some glands. Protection & secretion.
|
|
|
Stratified Columnar Epithelium
|
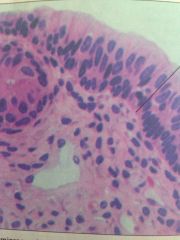
In male urethra and large ducts of some glands. Protection & secretion.
|
|
|
Transitional Epithelium
|
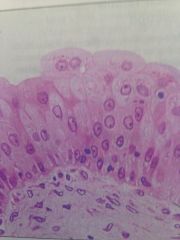
Lines ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. Stretches and allows urine to pass.
|
|
|
Areolar Loose Connective Tissue
|

Found everywhere under epithelia of body. Wraps and cushions organs.
|
|
|
Adipose Loose Connective Tissue
|
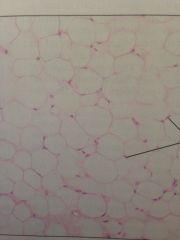
Under skin, fats of the body. Reserve fuel, insulates, supports and protects.
|
|
|
Adipose Loose Connective Tissue
|
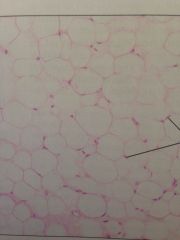
Under skin, fats of the body. Reserve fuel, insulates, supports and protects.
|
|
|
Reticular loose connective tissue
|
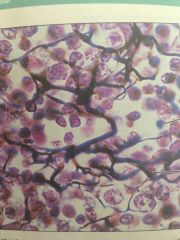
Lymphoid organs, lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen. Supports other cell types like WBC, mast cells, and macrophages.
|
|
|
Adipose Loose Connective Tissue
|
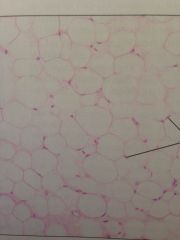
Under skin, fats of the body. Reserve fuel, insulates, supports and protects.
|
|
|
Reticular loose connective tissue
|
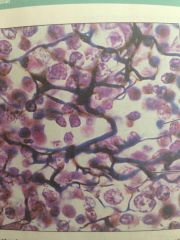
Lymphoid organs, lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen. Supports other cell types like WBC, mast cells, and macrophages.
|
|
|
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
|

Tendons & Ligaments. Attaches misled to bones or to muscles, tensile stress when pulled force.
|
|
|
Adipose Loose Connective Tissue
|
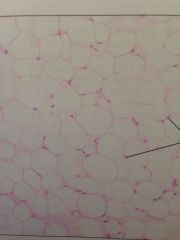
Under skin, fats of the body. Reserve fuel, insulates, supports and protects.
|
|
|
Reticular loose connective tissue
|
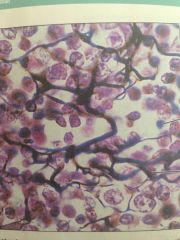
Lymphoid organs, lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen. Supports other cell types like WBC, mast cells, and macrophages.
|
|
|
Dense Regular Connective Tissue
|

Tendons & Ligaments. Attaches misled to bones or to muscles, tensile stress when pulled force.
|
|
|
Elastic Connective Tissue
|
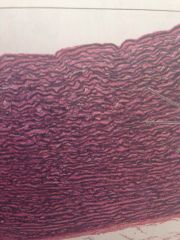
In walls of large arteries, in certain ligaments, in vertebral column and in walls of bronchial tubes. Recoil following stretching, maintains blood flow through arteries and aids passive recoil of lungs.
|
|
|
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
|
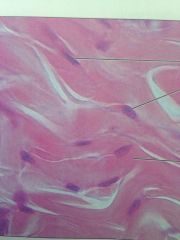
Located in joints, dermis of skin, and digestive tracts. Able to withstand tension, provides structural strength.
|
|
|
Hyaline Cartilage
|
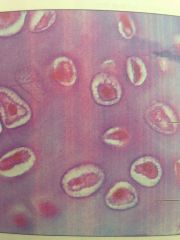
Forms costal cartilages of ribs, nose, trachea and larynx. Supports, reinforces and cushions, resists compressive stress.
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage
|
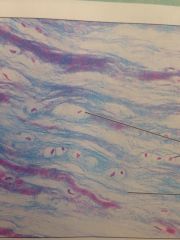
Intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, and disc knee joints. Tensile strength with ability to absorb shock.
|
|
|
Elastic Cartilage
|
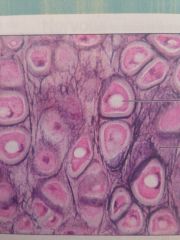
Supports external ear and epiglottis. Maintains shape of a structure while allowing great flexibility.
|
|
|
Fibrocartilage
|
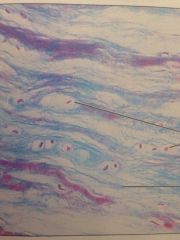
Intervertebral discs, public symphysis, and disc of knee joint.
|
|
|
Bone
|
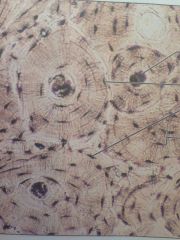
Bones. Supports and protects.
|
|
|
Blood
|
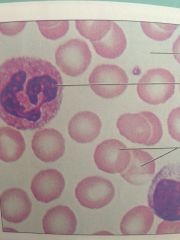
Contains within blood vessels. Transport of respiratory gases, nutrients, wastes and other substances.
|
|
|
Nervous Tissue
|
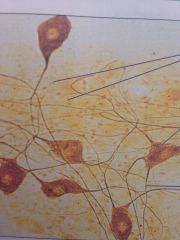
Brain, spinal cord and nerves. Transmits electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors.
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|

Attached to bones or to skin occasionally. Voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression and voluntary control.
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|

Attached to bones or to skin occasionally. Voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression and voluntary control.
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|
The walls of the heart. As it contracts, it propels blood into circulation; involuntary control.
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|

Attached to bones or to skin occasionally. Voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression and voluntary control.
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|

The walls of the heart. As it contracts, it propels blood into circulation; involuntary control.
|
|
|
Smooth muscle
|

Mostly in walls of hollow organs. Propels substances of objects along passageways; involuntary control.
|
|
|
Anterior/Posterior
|
Most forward-face, chest, abdomen. Toward the back.
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|

Attached to bones or to skin occasionally. Voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression and voluntary control.
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|

The walls of the heart. As it contracts, it propels blood into circulation; involuntary control.
|
|
|
Smooth muscle
|

Mostly in walls of hollow organs. Propels substances of objects along passageways; involuntary control.
|
|
|
Anterior/Posterior
|
Most forward-face, chest, abdomen. Toward the back.
|
|
|
Medial/Lateral
|
Toward midline/away from the midline or median plane
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|

Attached to bones or to skin occasionally. Voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression and voluntary control.
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|

The walls of the heart. As it contracts, it propels blood into circulation; involuntary control.
|
|
|
Smooth muscle
|

Mostly in walls of hollow organs. Propels substances of objects along passageways; involuntary control.
|
|
|
Anterior/Posterior
|
Most forward-face, chest, abdomen. Toward the back.
|
|
|
Medial/Lateral
|
Toward midline/away from the midline or median plane
|
|
|
Dorsal/Ventral
|
Backside/belly side.
|
|
|
Skeletal Muscle
|

Attached to bones or to skin occasionally. Voluntary movement, locomotion, facial expression and voluntary control.
|
|
|
Cardiac Muscle
|

The walls of the heart. As it contracts, it propels blood into circulation; involuntary control.
|
|
|
Smooth muscle
|

Mostly in walls of hollow organs. Propels substances of objects along passageways; involuntary control.
|
|
|
Anterior/Posterior
|
Most forward-face, chest, abdomen. Toward the back.
|
|
|
Medial/Lateral
|
Toward midline/away from the midline or median plane
|
|
|
Dorsal/Ventral
|
Backside/belly side.
|
|
|
Proximal/Distal
|
Near the trunk or attached end/Farther from the trunk or point of attachment.
|
|
|
Umbilical region
|
The center most region includes the umbilicus
|
|
|
Umbilical region
|
The center most region includes the umbilicus
|
|
|
Epigastric Region
|
Immediately superior to the umbilical region; overlies most of stomach.
|
|
|
Hypogastric (pubic) Region
|
Immediately inferior to the umbilical region; encompasses the pubic area
|
|
|
Hypogastric (pubic) Region
|
Immediately inferior to the umbilical region; encompasses the pubic area
|
|
|
Iliac (inguinal) regions
|
Lateral to the hypogastric region and overlying the superior parts of the hip bones.
|
|
|
Hypogastric (pubic) Region
|
Immediately inferior to the umbilical region; encompasses the pubic area
|
|
|
Iliac (inguinal) regions
|
Lateral to the hypogastric region and overlying the superior parts of the hip bones.
|
|
|
Lumbar regions
|
Between the ribs and the flaring portions of the hip bones; lateral to the umbilical region.
|
|
|
Hypogastric (pubic) Region
|
Immediately inferior to the umbilical region; encompasses the pubic area
|
|
|
Iliac (inguinal) regions
|
Lateral to the hypogastric region and overlying the superior parts of the hip bones.
|
|
|
Lumbar regions
|
Between the ribs and the flaring portions of the hip bones; lateral to the umbilical region.
|
|
|
Hypochondriac regions
|
Flanking the epigastric region laterally and overlying the lower ribs.
|

