![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
135 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Arachnoid mater
|
|
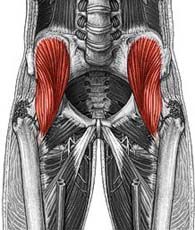
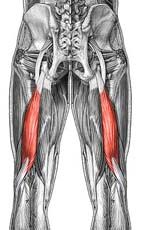
Name the muscle
|
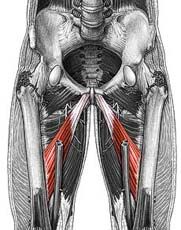
Iliacus
|
|
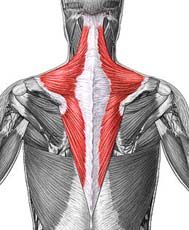
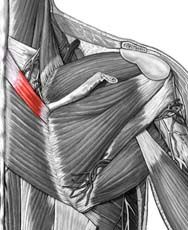
Trapezius
|
Origin: occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae & spinous processes of thoracic vertebrae
Insertion: clavicle and scapula (acromion and scapular spine) Action: elevate, retract, depress, or rotate scapula upward and/or elevate clavicle; extend neck |
|
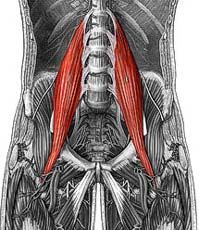
Name the muscle
|
Psoas Major
|
|
|
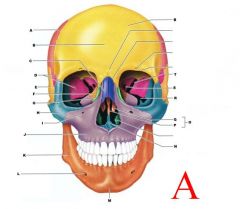
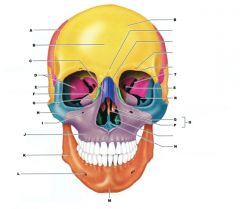
PARIETAL BONE
|
|
Rhomboideus Minor
|
Origin: spinous process of vertebrae C7-T1
Insertion: vertebral border of scapula Action: adducts & performs downward rotation of scapula |
|
Name the muscle
|
Adductor longus
|
|
|
define osteoid
|
the unmineralized, organic portion of the bone matrix that forms prior to the maturation of bone tissue
|
|
|
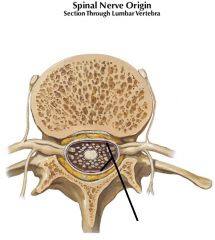
Dorsal root and rootlets
|
|
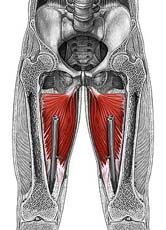
Name the muscle
|
Adductor magnus
|
|
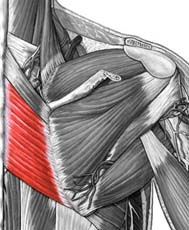
Rhomboideus Major
|
Origin: spinous process of superior thoracic vertebrae
Insertion: vertebral border of scapula from spine to inferior angle Action: adducts and downward rotation of scapula |
|
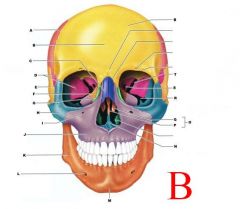
B
|
FRONTAL BONE
|
|
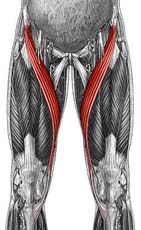
Name the muscle
|
Sartorius
|
|
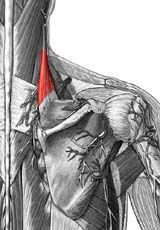
Levator Scapulae
|
Origin: transverse precesses of C1-C4 vertebrae
Insertion: vertebral border of scapula near superior angle Action: elevates scapula |
|
|
Epidural space
|
|
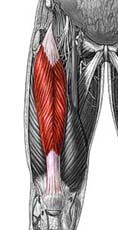
Name the muscle
|
Quadriceps femoris group: Rectus femoris
|
|
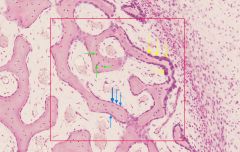
what component of the extracellular matrix is stained pink in this slide?
|
type I collagen (protein)
|
|
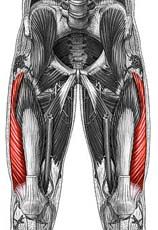
Name the muscle
|
Quadriceps femoris group: Vastus lateralis
|
|
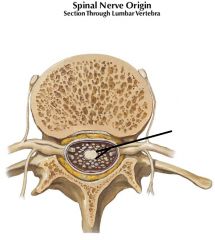
|
Pia Mater
|
|
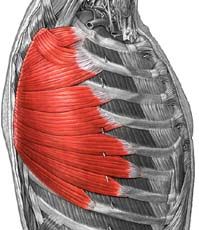
Serratus Anterior
|
Origin: anterior and superior margins of ribs 1-8 or 1-9
Insertion: anterior surface of vertebral border of scapula Action: protracts shoulder: rotates scapula so glenoid cavity moves upward rotation |
|
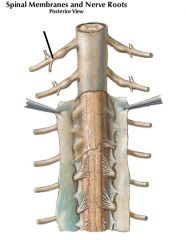
|
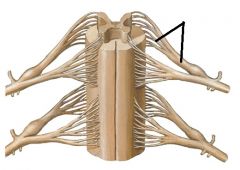
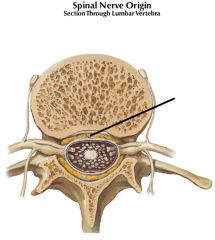
spinal nerve
|
|
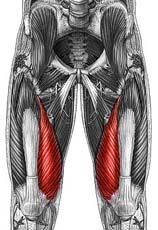
Name the muscle
|
Quadriceps femoris group: Vastus medialis
|
|
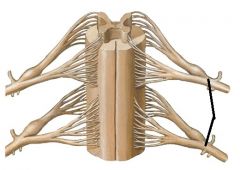
|
spinal nerve
|
|
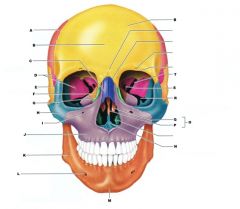
C
|
NASAL BONE
|
|
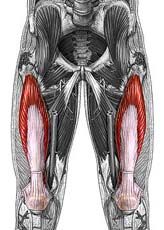
Name the muscle
|
Quadriceps femoris group: Vastus intermedius
|
|
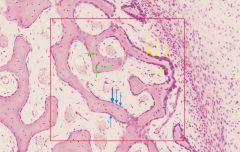
name the cell type indicated by the yellow arrows
|
osteoblast (cuboidal)
|
|
|
Ventral root and rootlets
|
|
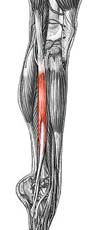
Name the muscle
|
fibular muscle group
|
|
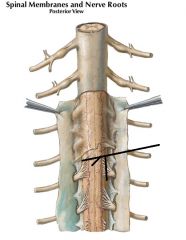
|
Sub Arachnoid Space
|
|
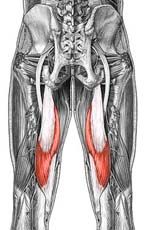
Name the muscle
|
Semimembranosus
|
|
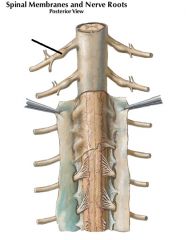
|
Dorsal Root Ganglion
|
|
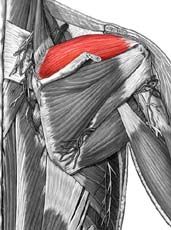
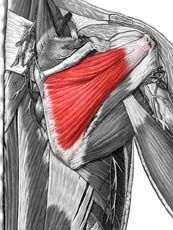
Supraspinatus
|
Origin: supraspinous fossa of scapula
Insertion: greater tuberacle of humerus Action: abduction at the shoulder |
|
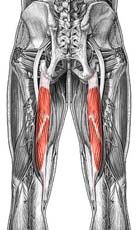
Name the muscle
|
Semitendinosus
|
|
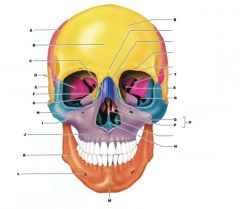
D
|
SPHENOID (GREATER WING)
|
|
Name the muscle
|
Biceps femoris
|
|
Infraspinatus
|
Origin: infraspinous fossa of scapula
Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus Action: lateral rotation at shoulder |
|
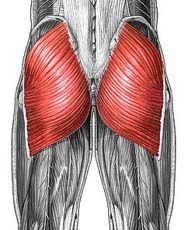
Name the muscle
|
Gluteus maximus
|
|
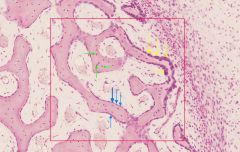
name the cell type indicated by the blue arrows
|
osteoprogenitor
|
|
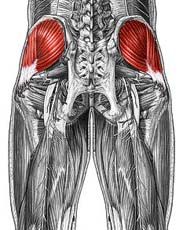
Name the muscle
|
Gluteus medius
|
|
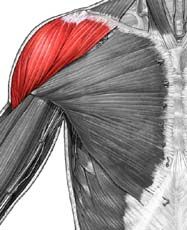
Deltoid
|
Origin: clavicle and scapula (acromion and adjacent scapular spine)
Insertion: deltoid tuberosity of humerus Action: abducts shoulder, flexion and extension, medial and lateral rotation of humerus |
|
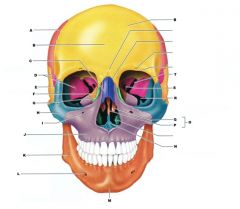
E
|
TEMPORAL BONE
|
|
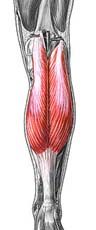
Name the muscle
|
Gastrocnemius
|
|
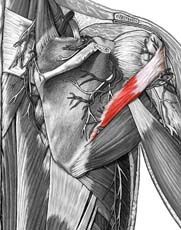
Teres Minor
|
Origin: lateral border of scapula
Insertion: greater tubercle of humerus Action: lateral rotation at shoulder |
|
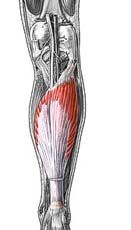
Name the muscle
|
Soleus
|
|
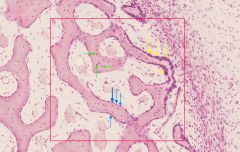
name the bone covering formed collectively by the cells indicated by the yellow and blue arrows
|
endosteum
|
|
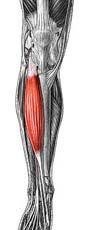
Name the muscle
|
Tibialis anterior
|
|
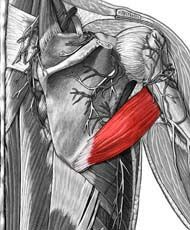
Teres Major
|
Origin: inferior angle of scapula
Insertion: medial lip of intertubercular groove of humerus Action: extension, adduction & medial rotation at shoulder |
|
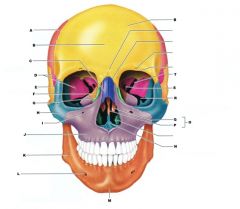
F
|
ETHMOID BONE
|
|
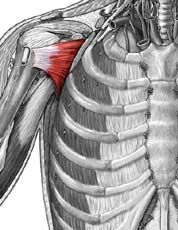
Subscapularis
|
Origin: subscapular fossa of scapula
Insertion: lesser tubercle of humerus Action: medial rotation at shoulder |
|
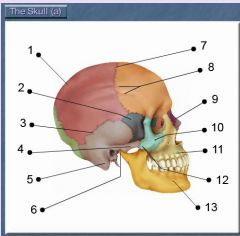
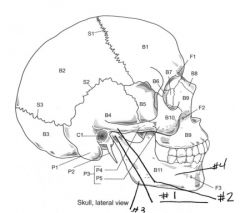
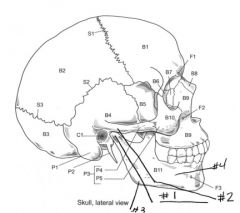
Identify # 4.
|
Zygomatic process [of temporal bone]
|
|
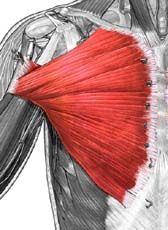
Pectoralis Major
|
Origin: cartilages of ribs 2-6, gladiolus & inferior, medial portion of clavicle
Insertion: crest of greater tubercle & lateral lip of intertubercular groove of humerus Action: flexion, adduction & medial rotation at shoulder |
|
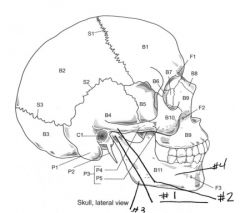
S1
|
Coronal Suture
|
|
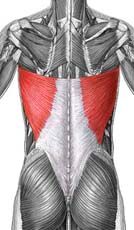
Latissimus Dorsi
|
Origin: spinous process of inferior T and all L vertebrae, ribs 8-12, and lumbodorsal fascia
Insertion: floor of intertubercular groove of the humerus Action: extension, adduction, and medial rotation at shoulder |
|
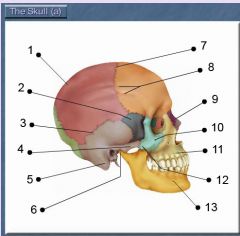
Identify # 5.
|
Mastoid process [of temporal bone]
|
|
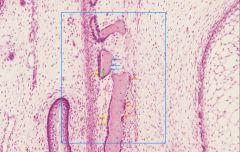
name the cell type indicated by the orange arrows
|
osteoclasts
|
|
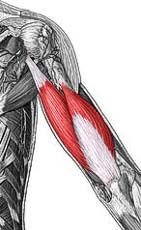
Triceps Brachii (lateral head, long head, medial head)
|
Origin: (Lateral) Superior, lateral margin of humerus:(Long) Infraglenoid tubercle of scapula;(Medial) Posterior surface of humerus, inferior to radial groove
Insertion: Olecranon of ulna Action: (Lateral) extension at elbow;(Long) extension at elbow, extension & aduction at shoulder;(Medial) extension at elbow |
|
S2
|
Squamous Suture
|
|
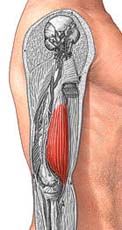
Brachialis
|
Origin: anterior, distal surface of humerus
Insertion: ulnar tuberosity Action: flexion at elbow |
|
G
|
LACRIMAL BONE
|
|
S3
|
Lambdoid Suture
|
|
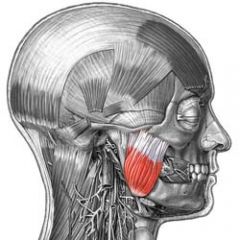
Name the muscle
|
Masseter
|
|
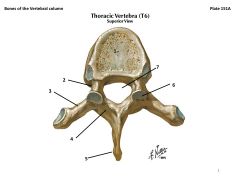
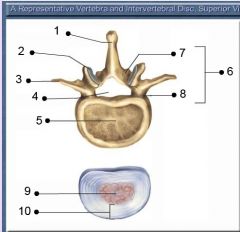
What are these?
|
1. Body
2. Pedicle 3. Transverse Process 4. Lamina 5. Spinous Process 6. Articular Process (superior and inferior) 7. Vertebral Foramen (vertebral canal) |
|
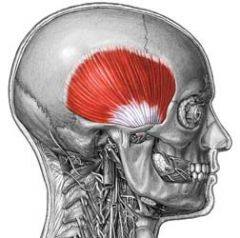
Name the muscle
|
Temporalis
|
|
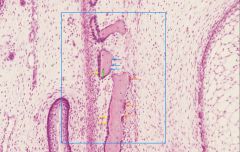
which arrow is pointing to a cell that is surrounded by bone matrix?
|
green arrow
|
|
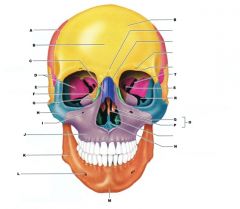
H
|
ZYGOMATIC BONE
|
|
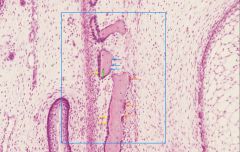
which arrow is pointing to a cell that is producing osteoid?
name this cell type |
blue arrow; osteoblast
|
|
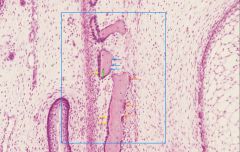
which arrow is pointing to a cell that is resorbing bone?
name this cell type |
orange arrow; osteoclast
|
|
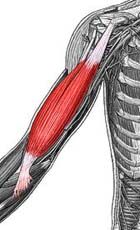
Biceps Brachii
|
Origin: (short head) from coracoid process;(long head) from supraglenoid tubercle (scapula)
Insertion: radial tuberosity Action: flexion at elbow and shoulder; supination |
|
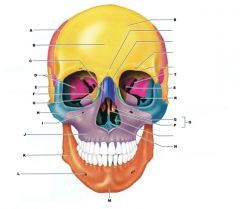
J
|
MAXILLA
|
|
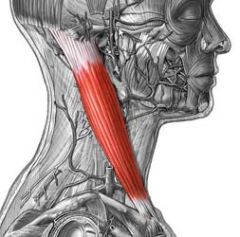
Name the muscle
|
Sternocleidomastoid: Clavicular Head
|
|
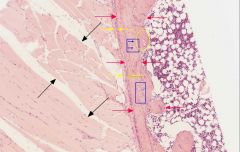
name the cell type indicated by the blue arrows
|
osteocytes
|
|
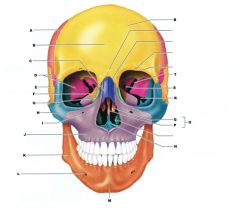
K
|
MANDIBLE
|
|
Identify # 2.
|
Superior articular facet
|
|
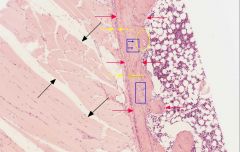
name the space in which the cells indicated by the blue arrows reside
|
lacunae
|
|
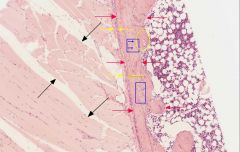
what kind of tissue is within the blue squares?
what are the characteristics of this tissue type? |
primary bone tissue; it is more cellular, contains less mineral content, and its collagen fibers lack organization
|
|
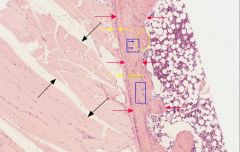
what tissue type is in the yellow circle?
what are the characteristics of this tissue type? |
secondary bone tissue; the tissue is layered
|
|
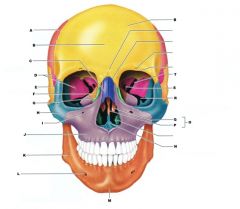
N
|
VOMER
|
|
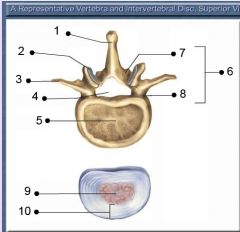
Identify # 7.
|
Lamina
|
|
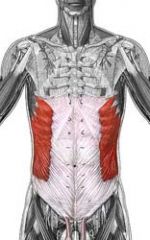
Name the muscle
|
External Oblique
|
|
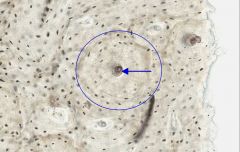
what is the structure surrounded by the blue circle?
the blue arrow? |
osteon; osteonic canal
|
|
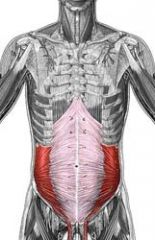
Name the muscle
|
Internal Oblique
|
|
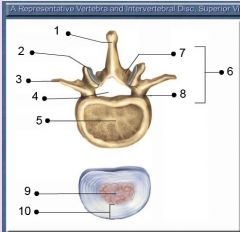
Identify # 6.
|
Vertebral arch
Note: 1/2 ring of bone |
|
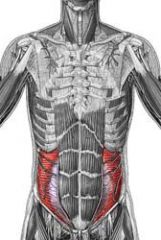
Name the muscle
|
Transverse Abdominis
|
|
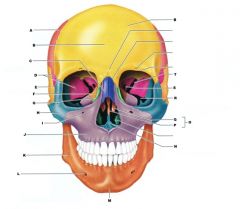
O
|
ETHMOID BONE
|
|
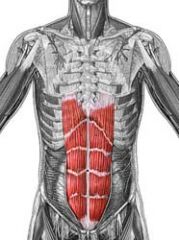
Name the muscle
|
Rectus Abdominis
|
|

what is the name of the tissue surrounded by the red square?
what are the characteristics of this tissue type? |
interstitial lamellae; they are avascular because they are part of a degraded/previous lamellae
|
|

what is the space indicated by the red arrow?
what cell type occupies this space in living tissue? |
lacnuae; osteocytes
|
|

name the space indicated by the yellow arrows?
what are their function? |
canaliculi; the form a network of tunnel-like spaces in the bone matrix
|
|
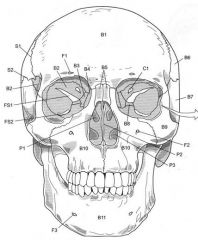
S1
|
Coronal Suture
|
|
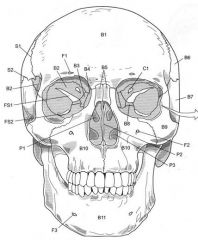
S2
|
Sauamous Suture
|
|
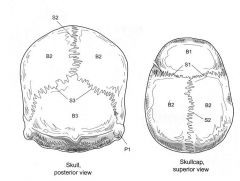
Name the following:
S1 S2 S3 |
Coronal Suture
Saggital Suture Lambdoid Suture |
|
|
cervical vertebrae -- how many? distinguishuing characteristics?
|
7; smaller in size, and have a foramen in the transverse process
|
|
Identify # 5.
|
Inferior articular process
|
|
|
thoracic vertebrae -- how many? distinguishing characteristics?
|
12; medium in size with a heart-shaped body
|
|
|
lumbar vertebrae -- how many? distinguishing characteristics?
|
5; large with a wide body
|
|
|
sacral vertebrae -- how many? distinguishing characteristics?
|
5 (fused); part of the back of the pelvis, very wide/short
|
|
|
coccyx vertebrae -- how many? distinguishing characteristics?
|
4 (fused); very small tip of the spine, much like a tail
|
|
|
kyphotic curve
|
spinal curve with convexity projecting posterior
|
|
|
lordotic curve
|
spinal curve with convexity projecting anterior
|
|

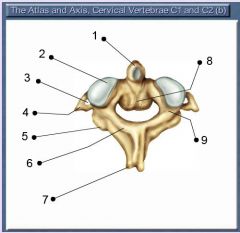
which bone is this? what are its distinguishing features?
|
C1 vertebra (atlas); lateral masses are round/column-like, the anterior arch is thin and bony,
|
|
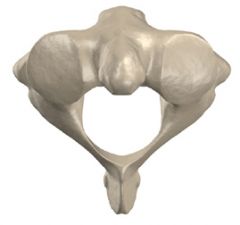
what bone is this? distinguishing characteristics?
|
C2 (axis); it has the dens -- the bony like projection that the base of the skill rests upon
|
|
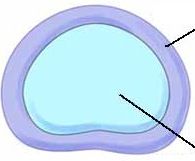
what is the outer loop of this tissue? the inner part?
|
annulus fibrosis and nucleus pulposus
|
|
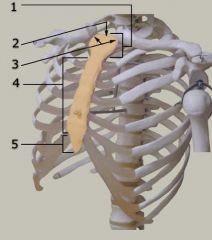
Identify # 1.
|
Manubrium
Tip: Top of sternum, flat like a spoon |
|
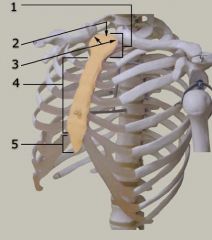
Identify # 4.
|
Body
|
|
|
how many ribs and of what character?
|
12 pairs of ribs in total; 7 pairs of true ribs which attach to the sternum via cartilage; 5 pairs are false ribs, the top 3 of which share a single piece of cartilage connected to the sternum, and the last two are floating w/o any attachment
|
|
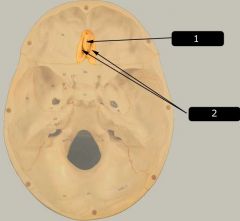
Identify # 2.
|
Cribriform plate
|
|
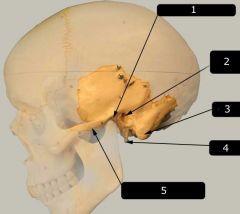
Identify # 2.
|
External auditory meatus
Note: Where the ear would be |
|
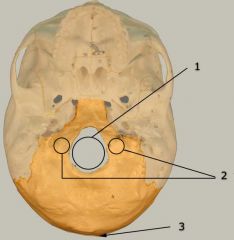
Identify # 2.
|
Occipital condyles
Note: To the left & right of foramen magnum |
|
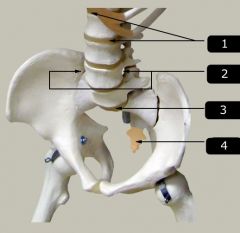
Identify # 2.
|
Intervertebral foramen
|
|
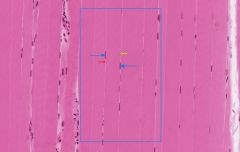
what type of tissue is this, and what are the defining characteristics?
|
skeletal muscle: it is striated and multi-nucleated with very long cells
|
|
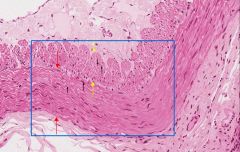
what type of tissue is this? what are its defining characteristics?
|
smooth muscle: no striations, single nucleus, smallest muscle cell type
|
|
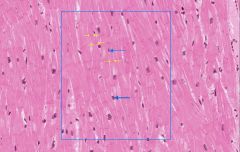
what type of tissue is this? what are its defining characteristics?
|
cardiac muscle: one or two central nuclei, striated, branched
|
|
|
what is isometric muscle contraction?
|
the muscle length remains constant; example:
|
|
|
what is isotonic muscle contraction?
|
muscle changes in length during contraction (eccentric = increase, concentric = decreases)
|
|
|
cauda equina
|
bundle of nerves exiting at the inferior end of the spinal cord (around L1-L2) -- "horse's tail"
|
|
|
conus medullaris
|
tapered/funnel-shaped region at end of spinal cord
|
|
|
filum terminale
|
continuation of the pia mater at the end of the cord through the sacrum and coccyx
|
|
|
phrenic nerve
|
motor nerve for diaphragm
|
|
|
axillary nerve
|
in the axilla; motor nerve for teres minor, deltoid, and triceps brachii; sensory: skin over shoulder
|
|
|
radial nerve
|
wraps across the AC; motor: triceps brachii and forearm muscles; sensory: majority of posterior forearm, forearm, and lateral hand
|
|
|
white matter
|
surround the gray matter; consists of myelinated axons and lacks cell bodies
|
|
|
gray matter
|
in the center of the spinal cord, butterfly shaped, containing unmyelinated ends of axons, dendrites, and neuron cell bodies
|
|
|
ulnar nerve
|
runs along the ulna; motor: ulnar/medial side of forearm/digit muscles; sensory: medial third of hand
|
|
|
median nerve
|
runs right down the middle of the arm; motor: forearm muscles for middle fingers; sensory: lateral side of hand
|
|
|
thoracodorsal nerve
|
runs under the lateral end of the scapula; motor: latissimus dorsi
|
|
|
pectoral nerves
|
runs into the pectoralis muscles; motor: pectoralis major/minor
|
|
|
suprascapular nerve
|
runs over back of shoulder above the scapula; motor: supra and infraspinatus muscles
|
|
|
long thoracic nerve
|
innervates serratus anterior
|
|
|
femoral nerve
|
runs over ventral side of leg; motor: quads; sensory: anterior/medial thigh, medal leg; medial foot
|
|
|
obturator nerve
|
runs through inside of thigh; motor: adductor muscles; sensory: medial thigh
|
|
|
superior gluteal nerve
|
runs in a superior direction behind the gluteal muscle; motor: gluteus medius
|
|
|
inferior gluteal nerve
|
runs in an inferior direction behind the gluteal muscle; motor: gluteus maxiumus
|
|
|
sciatic nerve
|
runs on the back of the leg and feeds into the tibial and common fibular
|
|
|
tibial nerve
|
starts at popliteal space and runs behind the leg; motor: hamstring, gastrocnemius, soleus; sensory: posterior leg and sole of foot
|
|
|
common fibular nerve
|
passes over lateral/ventral edge below the knee; superficial motor: fibular muscle group; superficial sensory: most of the lateral/bottom of foot; deep motor: tibialis anterior and toe extensors; deep sensory: webspace between 1st and 2nd toes
|

