![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Origin of connective tissues |
Mesodermal |
|
|
Function of connective tissues |
Support and connect epithelial with body organs |
|
|
Structure of connective tissues |
Relatively few cells Extracellular matrix: protein fibers, glycoproteins, proteoglycans |
|
|
Importance of connective tissue components |
Nutrient exchange between two different organ systems |
|
|
Types of connective tissues |
Collagenous Specialized |
|
|
Classification of collagenous connective tissue is based on |
Amount and arrangement of collagen |
|
|
Types of collagenous connective tissues |
Loose Dense regular Dense irregular |
|
|
Examples of specialized connective tissues |
Osteocytes Adipose Hyaline cartilage Macrophage |
|
|
Function of adipose tissues |
Store triglycerides, for energy source and thermal insulation Replace cellular and fibrous elements |
|
|
Function of hyaline cartilage |
Contains chondrocytes: cells responsible for cartilage formation Extracellular matrix is composed of collagen, chondroitin sulfates, and proteins |
|
|
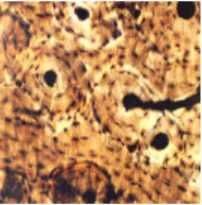
Function of bone |
Contains osteocytes: mature bone cells Osteoblasts, immature bone cells, secrete collagen fibers and ground substance of extracellular matrix Hardened by the precipitation of calcium salts |
|
|
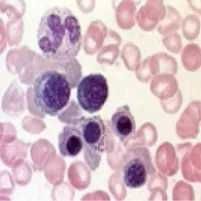
Function of blood |
Composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets that circulate throughout body |
|
|
Types of muscle tissues |
Skeletal Cardiac Smooth |
|
|
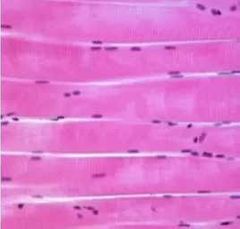
Function of skeletal muscle |
Voluntary Movement of skeleton, eye, and tongue Innervated motor neurons Release hormones and neurotransmitters that activate sacrolemma: plasma nembrane of muscle cell |
|
|
Function of nervous tissue |
Regulate central and peripheral nervous systems Vary per organ, in terms of shape, size, and complexity |
|
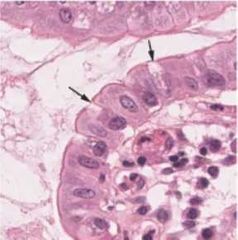
|
Epithelial tissue |
|
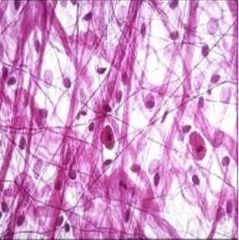
|
Connective tissue |
|
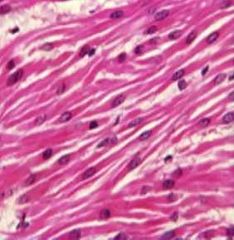
|
Muscle tissue |
|
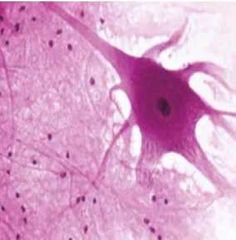
|
Nervous tissue |
|
|
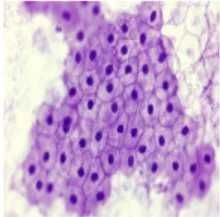
Squamous epithelium |
|
|
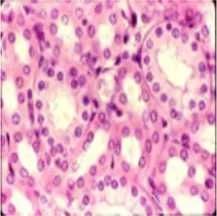
Cuboidal epithelium |
|
|
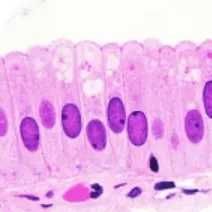
Columnar epithelium |
|
|
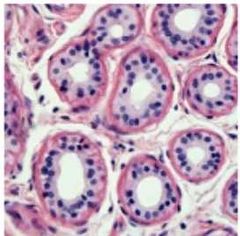
Simple epithelium |
|
|
Stratified epithelium |
|
|
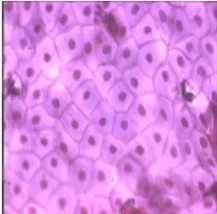
Simple squamous epithelium |
|
|
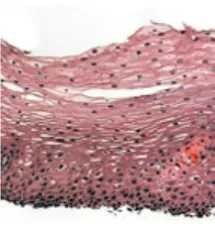
Stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
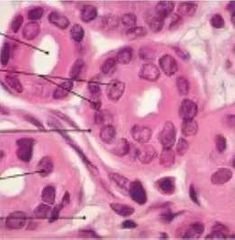
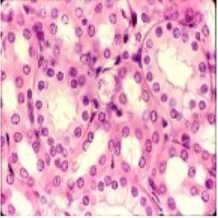
Simple cuboidal epithelium |
|
|
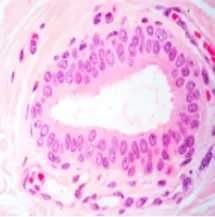
Stratified cuboidal epithelium |
|
|
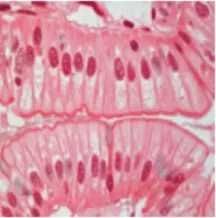
Simple columnar epithelium |
|
|
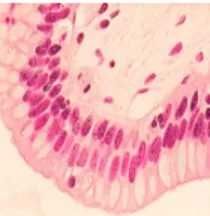
Stratified columnar epithelium |
|
|
Dense regular collagenous connective tissue |
|
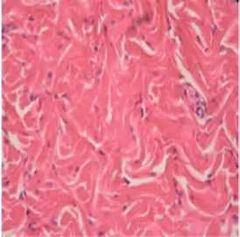
|
Dense irregular collagenous connective tissue |
|
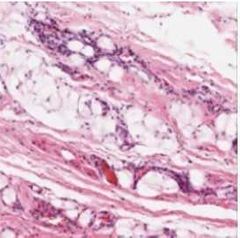
|
Loose collagenous connective tissue |
|
|
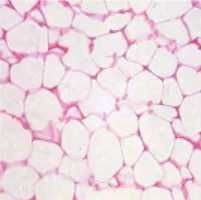
Adipose specialized connective tissue |
|
|
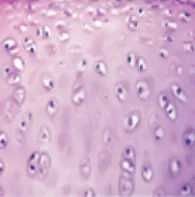
Hyaline cartilage specialized connective tissue |
|
|
Bone specialized connective tissue |
|
|
Blood specialized connective tissue |
|
|
Skeletal muscle |
|
|
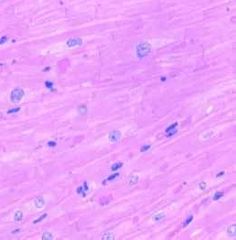
Cardiac muscle |
|
|
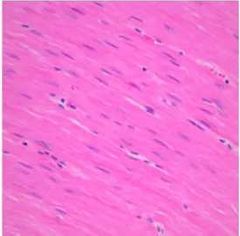
Smooth muscle |
|
|
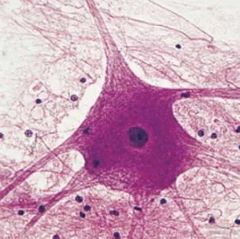
Typical neuron |
|
|
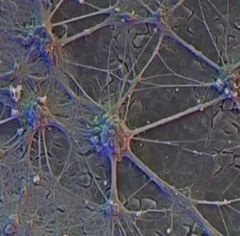
Neurons in the brain |
|
|
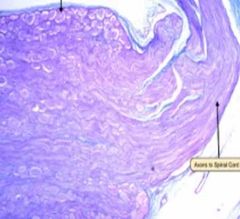
Sensory neuron |
|
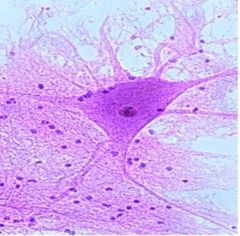
|
Motor neuron from spinal cord |
|
|
Characteristics of sperm cell |
Very small Has lots of mitochondria, which provide energy to move tail Haploid |
|
|
Characteristics of egg cell |
Holds many nutrients needed to start a new organism Haploid |
|
|
Stem cells |
Completely undifferentiated Have capacity to specialize |
|
|
Embryonic stem cells |
Found in early human embryos |
|
|
Differentiation |
Process by which cells become specialized for their role |
|
|
Cells in developed organisms |
Most are specialized and lose the ability to differentiate Those that can still differentiate replace lost cells |
|
|
Adult stem cells |
Found in bone marrow Can differentiate into different blood cells |
|
|
Characteristics of meristems |
Don't fully differentiate Stay as stem cells throughout plant's life |
|
|
Significance of meristems |
Plants can be cloned with meristems Rare species can be replicated to reduce extinction risk Identical crop plants with desirable characteristics can be grown |
|
|
Stem cell utilization process |
1. Isolate stem cells 2. Clone in laboratory |
|
|
Significance of human stem cells |
Potential to replace any damaged cell in body |
|
|
Process of replacing damaged blood cells with stem cells |
Adult stem cells from healthy person's bone marrow are transferred to bone marrow of the patient |
|
|
Issues with using stem cells to treat diseases |
Made in other organisms, so may be recognized as foreign and destroyed |
|
|
Process and significance of therapeutic cloning |
Embryo with same genetic material as patient is made Stem cells taken from embryo will not be rejected |
|
|
Risks of therapeutic cloning |
Stem cells may pick up a virus while being grown in lab Ethical issues: embryos have potential for human life But embryos are usually unwanted and would otherwise be destroyed |
|
|
Function of simple squamous epithelium |
Lines blood vessels and body cavities Regulates passage of substances into underlying tissue |
|
|
Function of simple cuboidal epithelium |
Glandular (secreting) tissue Kidney tubules |
|
|
Function of simple columnar epithelium |
Absorption Usually has apical cilia or microvilli Lines stomach and intestines |
|
|
Function of stratified squamous epithelium |
Protection against microorganisms, invading underlying tissue, and water loss Skin epidermis |
|
|
Function of stratified cuboidal epithelium |
Excretory ducts of salivary and sweat glands |
|
|
Function of stratified columnar epithelium |
Mucous membrane (conjunctiva) lining eyelids Both protective and mucus-secreting |
|
|
Function of pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
Lines upper respiratory tract Has a lot of cilia |

