![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
461 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two layers of the skin |
Epidermis and dermis |
|
|
Main type of tissue found in the epidermis |
Stratified squamous epithelium |
|
|
Main type of tissue found in the papillary layer of the dermis |
Aereolar connective tissue |
|
|
Main type of tissue in reticular layer of dermis |
Dense irregular connective tissue |
|
|
Layer of the epidermis found only in thick skin |
Stratum lucidum |
|
|
Where is thick skin found |
Palms and soles |
|
|
How does the epidermis receive nutrients? |
Nutrients must diffuse from the dermis |
|
|
Fingerprints are cause by thick epidermis covering what? |
Dermal papillae |
|
|
What is keratin? |
A filament made by skin cells. It’s a tough, fibrous protein that makes up hair and nails. Cross-linked tomone anither, which makes a tough water-resistant surface |
|
|
What is carotene? |
An orange pigment (molecule) made by plants. It’s found in vegetables and when we eat I️t, winds up in our skin. |
|
|
Into what hormones is vitamin D converted after being activated in the skin? |
Calcitriol |
|
|
What does calcitriol do? |
I️t aids in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus |
|
|
What are the 3 main pigments involved in skin color? |
Carotene, melanin, and hemoglobin |
|
|
Why do white people have lighter skin than black people? |
Black people have higher levels of melanin in their skin |
|
|
Explain stretch marks and why some are light and some are dark |
During rapid growth, fibroblasts in dermis can’t create enough collagen, so the new dense irregular CT is not as dense and whatever is underneath will be more visible. Muscle underneath, with lots of blood supply look darker. If new growth is over subcutaneous fat, stretch marks appear lighter. |
|
|
Two cell types that contain melanin |
Melanocytes and keratinocytes |
|
|
What is the function of melanin? |
Protects skin from sun damage (absorbs UV light) |
|
|
What regions of skin contain no hair? |
Palms, soles, lips, portions of external genitalia |
|
|
Where are apocrine sweat glands found, primarily? |
Armpits, around nipples and groin |
|
|
What type of gland in the skin is not a sudiforous gland? |
Sebaceous glands |
|
|
What do sebaceous glands secrete? |
Oil/sebum |
|
|
What makes new scars appear red? |
New blood vessels grow in the area of the wound (angiogenesis) |
|
|
Why do reddish scars lighten over time? |
The new blood vessels that were formed die (apoptosis) and the CT in the scar (collagen fibers) is different than the original dense irregular CT |
|
|
What is the name of the body’s 3D framework of connective tissue? |
Fascia |
|
|
What’s the time period for shedding and re-growing skin? |
15-30 days |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules when they share electrons |
|
|
What are 3 molecules that have covalent bonds? |
H2O, CH4, and CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say the bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positiveare attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
Name 2 molecules that have ionic bonds |
NaCl (salt) and O2 (oxygen) |
|
|
What does equilibrium mean? |
No net change. Example: solution not changing even though individual molecules might be hanging |
|
|
What is diffusion? |
Movement of molecules from high to low concentration. |
|
|
What kind of motion drives diffusion? |
Brownian |
|
|
What makes up a phospholipid? |
A polar head group and 2 non-polar fatty acids |
|
|
In cell, phospholipids are arranged in what shape? |
Bi-layer |
|
|
What are the major components of the plasma membrane? |
Phospholipid bi-layer and protein molecules, which make the membrane selectively petmeable |
|
|
In a cell, where would you find RNA? |
Nucleus and cytoplasm |
|
|
DNA can be found where? |
Nucleus and mitochondria (organelles) |
|
|
What types of proteins are made on the rough ER? |
Membrane-bound and secreted |
|
|
What makes cytoplasmic proteins? |
Free floating ribosomes |
|
|
Name a cell that might have a lot of rough ER |
A plasma cell, white blood cells |
|
|
After being made in the rough ER, a polypeptide would travel where? |
Golgi apparatus |
|
|
In humans, what’s something that might be stored in a vacuole? |
Triglycerides |
|
|
Old organelles and large cellular debris can be digested inside what organelles? |
Lysosomes |
|
|
Where is ATP made in a cell? |
Mitochondria |
|
|
What types of human cells have a lot of mitochondria? |
Muscle |
|
|
Microvilli are fingerlike projections of the plasma membrane filled with what? |
Actin (a cytoskeletal component) |
|
|
Where would microvilli be especially important? |
The intestines |
|
|
What is the cyroskeletal component that cilia contains which is used for motility? |
Microtubules |
|
|
What is motility in a human? |
Movement of substances across an epithelium |
|
|
What is motility in a human? |
Movement of substances across an epithelium |
|
|
Where in the human body might cilia move substances? |
Fallopian tubes |
|
|
The only cell in s human to have flagellum? |
Sperm |
|
|
What are the 4 main tissue types? |
Epithelial, muscle, nervous, connective |
|
|
Name 3 cancers and identify the tissue and cell type that have mutated to form this kind of cancer |
Leukemia- connective tissue/white blood cells Carcinoma - epithelial tissue/epithelial cells Myeloma - myeloid tissue/blood cells |
|
|
What is the main difference between simple and stratified epithelia? |
Simple epithelia has one layer of cells and stratified has 2 or more layers of cells |
|
|
What is the main difference between simple and stratified epithelia? |
Simple epithelia has one layer of cells and stratified has 2 or more layers of cells |
|
|
Why would I️t be important for epithelia in the intestines to have tight junctions? |
To prevent toxins from leaking into the bloodstream and nutrients from leaking out |
|
|
Name a function a simple epithelium would be better at performing than a stratified one. |
Absorption of gases |
|
|
What are the two main components of extra cellular matrix? |
Fibers and ground substance |
|
|
What are the two main components of extra cellular matrix? |
Fibers and ground substance |
|
|
Name the 3 types of fibers found in extra cellular matrix |
Collagen fibers Reticular fibers Elastic fibers |
|
|
Which fiber in the extra cellular matrix is the strongest? |
Collagen |
|
|
Which fiber in the extra cellular matrix is the strongest? |
Collagen |
|
|
Why would someone take a chondroiton sulfate supplement? |
To hopefully boost collagen production |
|
|
Which fiber in the extra cellular matrix is the strongest? |
Collagen |
|
|
Why would someone take a chondroiton sulfate supplement? |
To hopefully boost collagen production |
|
|
Which tissue type contains fibroblasts? |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Which type of CT is least capable of regeneration? |
Cartilage |
|
|
Which type of CT is least capable of regeneration? |
Cartilage |
|
|
Why is cartilage so poor at regeneration? |
Cartilage produces anti-angiogenesis factor, which prevents blood vessels from growing into the tissue. No blood=no nutrients needed for regeneration |
|
|
What is the main difference between dense regular and dense irregular CT? |
Parallel collagen fibers vs not parallel |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is adipose? |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is adipose? |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is bone (osseus)? |
Connective tiasue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is adipose? |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is bone (osseus)? |
Connective tiasue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is cartilage? |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is adipose? |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is bone (osseus)? |
Connective tiasue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is cartilage? |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is skeletal muscle? |
Muscle tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is adipose? |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is bone (osseus)? |
Connective tiasue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is cartilage? |
Connective tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types is skeletal muscle? |
Muscle tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types are neurons? |
Nervous tissue |
|
|
Which of the 4 main tissue types are glands? |
Epithelial tissue |
|
|
What is nervous tissue made of? |
Neurons and glia |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
Where can glycogen be found in the body? |
Skeletal muscles and liver |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
Where can glycogen be found in the body? |
Skeletal muscles and liver |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? |
Saturated fats have no C=C double bonds |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
Where can glycogen be found in the body? |
Skeletal muscles and liver |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? |
Saturated fats have no C=C double bonds |
|
|
Describe healthy omega 3 fatty acids |
Unsaturated fats that are liquid at body temperature |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
Where can glycogen be found in the body? |
Skeletal muscles and liver |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? |
Saturated fats have no C=C double bonds |
|
|
Describe healthy omega 3 fatty acids |
Unsaturated fats that are liquid at body temperature |
|
|
Describe trans fats |
Trans fats are unsaturated fats that are solid at body temperature |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
When we say fat, what type of molecule do we usually mean? |
Triglycerides |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
Where can glycogen be found in the body? |
Skeletal muscles and liver |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? |
Saturated fats have no C=C double bonds |
|
|
Describe healthy omega 3 fatty acids |
Unsaturated fats that are liquid at body temperature |
|
|
Describe trans fats |
Trans fats are unsaturated fats that are solid at body temperature |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
When we say fat, what type of molecule do we usually mean? |
Triglycerides |
|
|
Name another type of lipid |
Phospholipid |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
Where can glycogen be found in the body? |
Skeletal muscles and liver |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? |
Saturated fats have no C=C double bonds |
|
|
Describe healthy omega 3 fatty acids |
Unsaturated fats that are liquid at body temperature |
|
|
Describe trans fats |
Trans fats are unsaturated fats that are solid at body temperature |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
When we say fat, what type of molecule do we usually mean? |
Triglycerides |
|
|
Name another type of lipid |
Phospholipid |
|
|
Proteins are polymers of what kind of molecules? |
Amino acids |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
Where can glycogen be found in the body? |
Skeletal muscles and liver |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? |
Saturated fats have no C=C double bonds |
|
|
Describe healthy omega 3 fatty acids |
Unsaturated fats that are liquid at body temperature |
|
|
Describe trans fats |
Trans fats are unsaturated fats that are solid at body temperature |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
When we say fat, what type of molecule do we usually mean? |
Triglycerides |
|
|
Name another type of lipid |
Phospholipid |
|
|
Proteins are polymers of what kind of molecules? |
Amino acids |
|
|
How many different types of amino acid molecules are there in the human body? |
20 |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
Where can glycogen be found in the body? |
Skeletal muscles and liver |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? |
Saturated fats have no C=C double bonds |
|
|
Describe healthy omega 3 fatty acids |
Unsaturated fats that are liquid at body temperature |
|
|
Describe trans fats |
Trans fats are unsaturated fats that are solid at body temperature |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
When we say fat, what type of molecule do we usually mean? |
Triglycerides |
|
|
Name another type of lipid |
Phospholipid |
|
|
Proteins are polymers of what kind of molecules? |
Amino acids |
|
|
How many different types of amino acid molecules are there in the human body? |
20 |
|
|
What holds a protein in its 3D (tertiary) shape? |
Weak hydrogen bonds between R groups and amino/carboxy groups, D sulfide bridges |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
Where can glycogen be found in the body? |
Skeletal muscles and liver |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? |
Saturated fats have no C=C double bonds |
|
|
Describe healthy omega 3 fatty acids |
Unsaturated fats that are liquid at body temperature |
|
|
Describe trans fats |
Trans fats are unsaturated fats that are solid at body temperature |
|
|
What is a buffer? |
A chemical that can accept or donate H+, and thus can maintain a constant pH in a solution |
|
|
When we say fat, what type of molecule do we usually mean? |
Triglycerides |
|
|
Name another type of lipid |
Phospholipid |
|
|
Proteins are polymers of what kind of molecules? |
Amino acids |
|
|
How many different types of amino acid molecules are there in the human body? |
20 |
|
|
What holds a protein in its 3D (tertiary) shape? |
Weak hydrogen bonds between R groups and amino/carboxy groups, D sulfide bridges |
|
|
What is the difference between trans fats and cis fats? |
Trans fats: C=C bond has C’s on opposite side. These fats tend to be solid at body temperature Healthy fats: C=C in cis formation (same side). These fats tend to be liquid at body temperature |
|
|
What are triglycerides made of? |
3 fatty acid molecules plus 1 molecule of glycerol |
|
|
Name 2 proteins in the human bidy |
Collagen and keratin |
|
|
How many free protons (H+) would pH 7 water contain? |
10 -7 moles/liter |
|
|
What are the 4 atoms that make up most of the molecules in our body? |
H-hydrogen N-nitrogen O-oxygen C-carbon |
|
|
Besides the 4 main atoms, what’s another atom you must have in order to live? |
Phosphorus, calcium, iron |
|
|
What are electrolytes? |
Solutes that carry a charge when dissolved in water |
|
|
Humans can’t store glucose, instead we make a glucose polymer. What’s I️t called? |
Glycogen |
|
|
Where can glycogen be found in the body? |
Skeletal muscles and liver |
|
|
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats? |
Saturated fats have no C=C double bonds |
|
|
Describe healthy omega 3 fatty acids |
Unsaturated fats that are liquid at body temperature |
|
|
Describe trans fats |
Trans fats are unsaturated fats that are solid at body temperature |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positive sides are attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positive sides are attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positive sides are attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
Name 2 molecules that have ionic bonds |
NaCl (salt) and KCl |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positive sides are attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
Name 2 molecules that have ionic bonds |
NaCl (salt) and KCl |
|
|
What does equilibrium mean? |
No net change. Equilibrium is passive. |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positive sides are attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
Name 2 molecules that have ionic bonds |
NaCl (salt) and KCl |
|
|
What does equilibrium mean? |
No net change. Equilibrium is passive. |
|
|
What process keeps busy temperature at 37C? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positive sides are attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
Name 2 molecules that have ionic bonds |
NaCl (salt) and KCl |
|
|
What does equilibrium mean? |
No net change. Equilibrium is passive. |
|
|
What process keeps busy temperature at 37C? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What body process keeps blood glucose around 125 mg/dL? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positive sides are attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
Name 2 molecules that have ionic bonds |
NaCl (salt) and KCl |
|
|
What does equilibrium mean? |
No net change. Equilibrium is passive. |
|
|
What process keeps busy temperature at 37C? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What body process keeps blood glucose around 125 mg/dL? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What body process keeps glucose moving from high (blood) to low concentration (skeletal muscle)? |
Diffusion |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positive sides are attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
Name 2 molecules that have ionic bonds |
NaCl (salt) and KCl |
|
|
What does equilibrium mean? |
No net change. Equilibrium is passive. |
|
|
What process keeps busy temperature at 37C? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What body process keeps blood glucose around 125 mg/dL? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What body process keeps glucose moving from high (blood) to low concentration (skeletal muscle)? |
Diffusion |
|
|
What body process keeps O2 moving from your lungs into your blood? |
Diffusion |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Acids, like hydrochloric acid (HCl) do what to a solution? |
Donate protons (H+) |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positive sides are attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
Name 2 molecules that have ionic bonds |
NaCl (salt) and KCl |
|
|
What does equilibrium mean? |
No net change. Equilibrium is passive. |
|
|
What process keeps busy temperature at 37C? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What body process keeps blood glucose around 125 mg/dL? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What body process keeps glucose moving from high (blood) to low concentration (skeletal muscle)? |
Diffusion |
|
|
What body process keeps O2 moving from your lungs into your blood? |
Diffusion |
|
|
What is a covalent bond? |
A strong bond between molecules which share electrons |
|
|
Acids, like hydrochloric acid (HCl) do what to a solution? |
Donate protons (H+) |
|
|
Bases, like NaOH, do what to a solution? |
They can accept protons (H+) from a solution |
|
|
Name 3 molecules that have covalent bonds |
H2O, CH4, CO2 |
|
|
What does I️t mean when we say bonds in one molecule of H2O are polar? |
Oxygen atoms hold onto the electrons more tightly than the hydrogen atoms. I️t has an end that is slightly negative and 2 sides that are slightly positive. The positive sides are attracted to the negative end of other water molecules |
|
|
What is an ionic bond? |
An ongoing, close association between ions of opposite charge |
|
|
Name 2 molecules that have ionic bonds |
NaCl (salt) and KCl |
|
|
What does equilibrium mean? |
No net change. Equilibrium is passive. |
|
|
What process keeps busy temperature at 37C? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What body process keeps blood glucose around 125 mg/dL? |
Homeostasis |
|
|
What body process keeps glucose moving from high (blood) to low concentration (skeletal muscle)? |
Diffusion |
|
|
What body process keeps O2 moving from your lungs into your blood? |
Diffusion |
|
|
What would adding an acid do to a neutral water (pH 7) |
I️t would lower the pH |
|
|
What would adding an acid do to a neutral water (pH 7) |
I️t would lower the pH |
|
|
Is the oH of the stomach acid or base? |
Acid |
|
|
What would adding an acid do to a neutral water (pH 7) |
I️t would lower the pH |
|
|
Is the oH of the stomach acid or base? |
Acid |
|
|
Does an acid have more or fewer free H+ than tap water (pH 7)? |
More |
|
|
How are equilibrium and homeostasis different? |
Homeostasis requires energy and is adaptive, while equilibrium is passive |
|
|
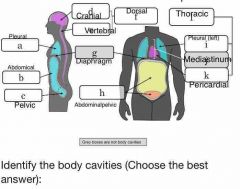
What is the difference between the abdominal cavity and the peritoneal cavity? |
Not much. Peritoneal cavity is the space inside the peritoneal lining, which is the abdominal cavity, so peritoneal cavity is about 1mm smaller than abdominal cavity |
|
|
What is the difference between the abdominal cavity and the peritoneal cavity? |
Not much. Peritoneal cavity is the space inside the peritoneal lining, which is the abdominal cavity, so peritoneal cavity is about 1mm smaller than abdominal cavity |
|
|
Which body cavity houses the lungs? |
Pleural |
|
|
Which body cavity houses the heart? |
Pericardial |
|
|
Which body cavity houses both the heart and lungs? |
Thoracic |
|
|
Which body cavity houses the stomach, but not the bladder? |
Abdominal |
|
|
Which body cavity houses the stomach, but not the bladder? |
Abdominal |
|
|
Which body cavity contains serous membranes? |
Ventral body cavity |
|
|
Which body cavity houses the stomach, but not the bladder? |
Abdominal |
|
|
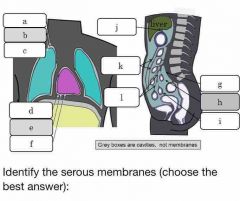
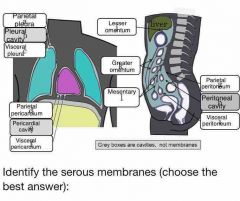
Which body cavity contains serous membranes? |
Ventral body cavity |
|
|
What membranes line the organs? |
Visceral serosal |
|
|
Which body cavity houses the stomach, but not the bladder? |
Abdominal |
|
|
Which body cavity contains serous membranes? |
Ventral body cavity |
|
|
What membranes line the organs? |
Visceral serosal |
|
|
What membranes line the body cavity? |
Parietal serosal membranes |
|
|
Which body cavity houses the stomach, but not the bladder? |
Abdominal |
|
|
Which body cavity contains serous membranes? |
Ventral body cavity |
|
|
What membranes line the organs? |
Visceral serosal |
|
|
What membranes line the body cavity? |
Parietal serosal membranes |
|
|
What would the serous membrane touching the lungs be called? |
Visceral pleural membrane |
|
|
What does retroperitoneal mean? |
Behind the peritoneum, inside the body wall and not the abdominal cavity |
|
|
Describe a negative feedback mechanism that affects human physiology |
Food intake Brain=control center Receptors=stomach filling and amount of fat in adipocytes Effector = feeding behavior (sense of hunger) |
|
|
What body planes could section both eyes? |
Cross section and frontal |
|
|
Which imaging device would be good for imaging damage to the heart? |
PET scans can measure how tissues/cells use glucose. Damaged tissue uses energy differently than healthy tissue |
|
|
Which imaging device would be good for imaging damage to the heart? |
PET scans can measure how tissues/cells use glucose. Damaged tissue uses energy differently than healthy tissue |
|
|
Which imaging decide would be good for producing a picture of the brain? |
MRI is good for imaging soft tissues and radiation isn’t absorbed by bone tissue, which can happen in CT scans |
|
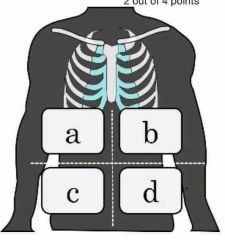
Identify the 4 main quadrants of the body |
A=URQ B=ULQ C=LRQ D=LLQ |
|
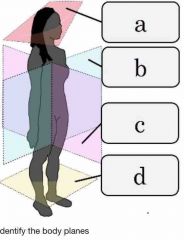
Front (Term) |
A= oblique B= frontal (coronal) C= Sagittal D= cross (transverse) |
|
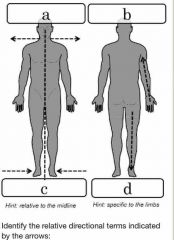
Front (Term) |
A= oblique B= frontal (coronal) C= Sagittal D= cross (transverse) |
|
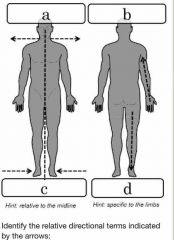
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
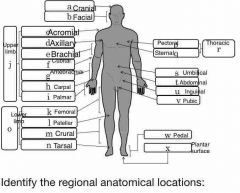
Back (Definition) |
|
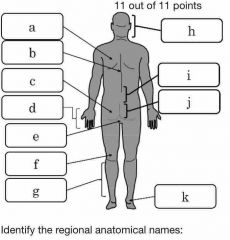
Front (Term) |
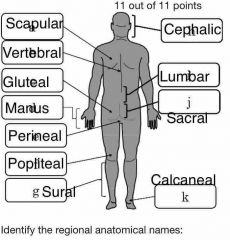
Back (Definition) |
|
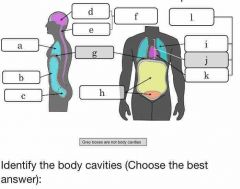
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
Front (Term) |
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Name the major organ systema |
Integumentary Skeletal Muscular Lymphatic Respiratory Digestive Nervous Endocrine Cardiovascular Urinary Reproductive
|
|
|
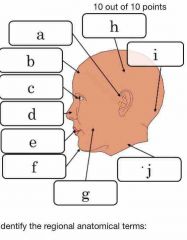
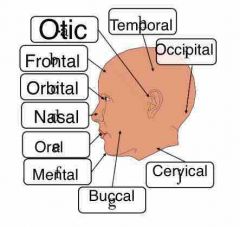
Describe anatomical position |
Patient is facing toward us, palms outward and feet shoulder width apartment. When discussing right or left, I️t will be the patient’s right or left. |
|
|
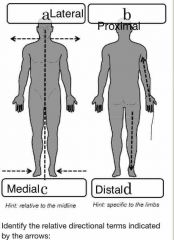
What’s the difference between lateral and medial? |
Objects closer to the sides of the body are lateral. Objects closer to the middle of the body are medial. |
|
|
What’s the difference between proximal and distal? |
On the arms and legs, anything closer to the beginning of the limb is called proximal, while things toward the ends are called distal. |
|
|
What’s the difference between superior and inferior? |
On the body, anything higher up is superior and anything lower down is inferior |
|
|
2 objects on the same side of the body are called what? |
Ipsi-lateral |
|
|
2 things on opposite sides of the body would be called what? |
Contralateral |
|
|
What are the terms for the front and back of the body? |
Ventral (front) and dorsal (back) |
|
|
What do we call things inside the body, as opposed to closer to the surface? |
Inside body=deep Closer to surface = superficial |
|
|
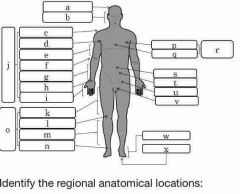
What is the appendicular portion of the body? |
Arms and legs |
|
|
Explain radiography |
Uses x-rays, which is absorbed by dense tissue, but not soft tissues in the human body. Examples would be bones, teeth, and even tumors |
|
|
Describe a CT scan |
Uses a lower dose x-ray to take multiple slices through the body . These can pick up soft tissues, unlike regular X-rays |
|
|
Where is abdominal cavity |
Diaphragm to top of pelvic bones Contains digestive organs |
|
|
Where is abdominal cavity |
Diaphragm to top of pelvic bones Contains digestive organs |
|
|
What is in the retroperitoneal space? |
It’s the area posterior to the peritoneum and anterior to the muscular body wall Contains pancreas, kidneys, ureters, and parts of the digestive tract |
|
|
Pelvic cavity |
Inferior to peritoneal cavity Where reproductive organs and bladder are located |
|
|
What is a receptor in homeostasis? |
The organ that measures the change |
|
|
What does the control center do? |
Receives information from the receptor and controls the body response |
|
|
What does the effector do? |
Makes the change which brings the body back to homeostasis |
|
|
Homeostasis |
Organism maintains a steady state, even as environment changes |
|
|
Extrinsic regulstion |
Involved nervous or endocrine control |
|
|
Autoregulatiom |
A cell can regulate itself |
|
|
Negative feedback loop |
The effector does the exact opposite of what the receptor detected in the first place |
|
|
Examples of positive feedback mechanisms |
Inflammation, blood clotting, labor pains |
|
|
Equilibrium |
Passive process which leads to new steady state |
|
|
Solution |
Homogenous mixture of a liquid solvent and one or more dissolved solutes |
|
|
Aqueous solution |
A solution where water is the solvent |
|
|
Precipitate |
Any solute that does not dissolve in the solute |
|
|
Adding more H+ to a neutral solution will make what? |
Acid |
|
|
Fewer free H+ makes a solution what? |
Alkaline or base (pH higher than 7) |
|
|
What do buffers do? |
They keep the pH constant by either accepting or donating free protons |
|
|
Isomer |
Compounds with the same molecular formula, but different structures, so they behave differently in the human body |
|
|
Functional groups |
Tend to behave the same in different molecules |
|
|
Five main functional groups |
Hydroxyl Carbonyl Carboxyl Amino Phosphate |
|
|
4 main types of organic molecules found in the human body |
Proteins Sugars Lipids Nucleic acids |
|
|
Monosaccharides |
Simplest carbohydrates, simple sugars, monomers (glucose and fructose) |
|
|
What makes up a simple sugar |
6 carbon atoms, 6 oxygen atoms, 12 hydrogen atoms |
|
|
Polysaccharides |
Long chains of sugars (starch in plants and glycogen in humans) |
|
|
Structural compound which is a sugar found in plants |
Cellulose |
|
|
Name types of lipids |
Fatty acids Triglycerides Phospholipids Cholesterol & steroids |
|
|
What makes up a triglyceride |
3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol |
|
|
What are unsaturated fatty acids? |
They have at least one carbon=carbon double bond, while saturated fatty acids do not. |
|
|
Polyunsaturated fats |
Have multiple Carbon=carbon double bonds |
|
|
Cis fats |
Hydrogen atoms are on the same side of the carbon=carbon double bond Tend to remain liquid, so they don’t tend to lead tonheartndisease |
|
|
Trans fats |
Hydrogen atoms are on opposite sides of the carbon=carbon double bond.have a much higher melting temp and tend to remain solid in the body |
|
|
Isomers |
Molecules with the same number of atoms, but which are arranged differently |
|
|
3 types of fats |
Trans fats - unhealthy Cis fats - more liquid tend to be more healthy Saturated fats - do not have carbon carbon double bonds. Tend to stay solid at body temp. Neither healthy nor unhealthy |
|
|
Hydroohibix |
Don’t form hydrogen bonds, so do not dissolve in water |
|
|
Why are phospholipids so important? |
Can form a bi-layer and are an integral part of the plasma membrane of cells |
|
|
What is oritein |
Polymer of amino acids |
|
|
Amino acids made up of 4 components |
Amine group NH3+ Carboxylic acid group COO- Central carbon R groups (can be hydrophilic/hydrophobic, acid/base, bulky/small) |
|
|
Nucleic acids |
Include DNA and RNA |
|
|
What pairs in dna? |
A and T G and C |
|
|
Tissue |
One type of cell in a group working together for a common purpose |
|
|
Organ |
2 or more tissue types |
|
|
Epithelia |
A sheet of cells that covers stuff, forming a barrier from one side of the body to another |
|
|
What does I️t mean that epithelia is avascular |
Doesn’t have blood cells, so nutrients must diffuse from underlying connective tissue |
|
|
Epithelial tissues can do one of 3 things |
Move fluids over the epithelium (protection) Move fluids through the epithelium (permeability) Produce secretions (protection and messengers) |
|
|
Two surfaces of epithelia |
Apical (free - cilia/microvilli) Basal (attached) |
|
|
How are epithelial cells attached to one another |
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) that link similar cells |
|
|
What are anchoring junctions called |
Spot desmosomes or hemidesmosomes make sure epithelial cells stay anchored to one another |
|
|
What is the basement membrane |
The connective tissue that epithelial tissue is anchored to |
|
|
3 shapes of epithelia |
Squamous Cuboidal Columnar |
|
|
Mesothelium |
Simple squamous epithelium that lines body cavities |
|
|
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium |
More than 1 cell thick, but can’t clearly identify the number of layers |
|
|
Transitional epithelium found where? |
Bladder |
|
|
Glands are what kind of tissue? |
Epithelia |
|
|
Endocrine glands |
Release hormones into the body (into bloodstream or into interstitial fluid) |
|
|
Exocrine glands |
Secrete substances to the surface of the body through a duct |
|
|
Merocrine secretion |
Packaging substances into vescicles and releasing them through exocytosis (sweat glands) |
|
|
Apocrine secretion |
Vesicles are sent to apical side of cell. Part of the cell pinches off and explodes, releasing all of the substances at once (mammary glands) |
|
|
Apocrine secretion |
Vesicles are sent to apical side of cell. Part of the cell pinches off and explodes, releasing all of the substances at once (mammary glands) |
|
|
Holocrine secretion |
Cell fills up with whatever substance it’s making and explodes (sebaceous gland) |
|
|
Apocrine secretion |
Vesicles are sent to apical side of cell. Part of the cell pinches off and explodes, releasing all of the substances at once (mammary glands) |
|
|
Holocrine secretion |
Cell fills up with whatever substance it’s making and explodes (sebaceous gland) |
|
|
Goblet cell |
Unicellular gland Produce mucus Exocrine glands Mucous cells No cilia or microvilli |
|
|
3 types of muscle tissue |
Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle |
|
|
What makes connective tissues loose or dense? |
The amount of fibers as compared to ground substance |
|
|
Is fat loose or dense connective tissue? |
Loose |
|
|
Are tendons loose or dense connective tissue? |
Dense |
|
|
Aereolar connective tissue |
Not specialized, under skin, holds one thing to another, room for blood vessels |
|
|
Adipose CT |
Not a lot of extra cellular matrix. Mostly cells. Good for storing energy, insulation. Adults have white fat |
|
|
Adipose tissue is made of... |
Adipocytes, which store triglycerides |
|
|
Reticular tissue |
Has lots of blood cells and squiggly reticular fibers — like a sponge filled with blood (found in spleen, liver, lymph nodes) |
|
|
Dense regular connective tissue |
Primarily collagen fibers running parallel - strong in one direction (tendon, ligaments) |
|
|
Dense irregular CT |
Places where you need to resist force in multiple directions, like skin and around organs |
|
|
What is the extracellular matrix in blood? |
Plasma |
|
|
What are cartilage cells called? |
Chondrocytes |
|
|
Why does cartilage have a hard time healing? |
I️t is avascular |
|
|
3 types of xartilage |
Hyaline cartilage Elastic cartilage Fibrocartilage |
|
|
Primary cell type found in bone |
Osteocytes |
|
|
4 symptoms of inflammation |
Swelling Redness Heat Pain |
|
|
Process of inflammation |
If a cell becomes infected with a virus, dead cells release digestive enzymes and inflammatory molecules which kills neighboring cells If not stopped, tissue damage spreads (necrosis). Inflammation stops the spread of tissue damage. Blood vessels dilate, bringing more blood to the area (nutrients) White blood cells come as well, releasing more inflammatory molecules, allowing blood vessels to become permeable, allowing blood to seep into the area...area becomes swollen and red. Extra fluid in the area is useful because I️t contains nutrients, but I️t also puts pressure on the area and blocks the spread of acids and viruses trying to infect new cells. White blood cells will clean up debris, destroying viruses and bacteria. Increased blood flow warms up the region and increased temp speeds up the repair process Pain keeps us from re-injuring the area |
|
|
Process of inflammation |
Cells break down (necrosis) Following damage to a tissue, injured cells can release inflammatory molecules (prostaglandins) Blood vessels dilate, bringing more blood to the area, causing redness Increased fluid brings nutrients and also white blood cells, which can clean things up White blood cells can cause permeability of blood vessels, which leads to fluid leaking into area, which causes swelling Increased swelling puts pressure which limits the spread of damage. Stops spread of damaging molecules that might be released from dying cells Increased blood flow and fluid increases heat in the area, speeding up healing process I️nflammatory molecules can also bind to nerve ending and being pain, so the person won’t put pressure on injured area, helping I️t to heal |
|
|
Damaged cells release chemical signals into surrounding interstitial fluid |
Prostaglandins, proteins, potassium ions, ATP |
|
|
What kind of feedback loop is inflammation? |
Positive feedback loop |
|
|
What is scar tissue made of? |
Fibrous CT rich in collagen fibers. For poorly regenerating tissues, scar tissue isn’t replaced by regular cells |
|
|
What cells move into necrosis area? |
Mesenchymal stem cells |
|
|
Atrophy |
Shrinking of a tissue |
|
|
Necrosis |
Damage to a tissue that spreads |
|
|
Apoptosis |
Programmed cell death |
|
|
Why is inflammation good? |
Without inflammation, every injury would become necrotic |
|
|
What type of tissue are glands? |
Epithelial |
|
|
Membranes |
An epithelium plus a little connective tissue — 4 types Mucous Serous Cutaneous Synovial
|
|
|
Mucous membranes |
Line passageways that have external external connections Digestive, respiratory, urinary, reproductive tracts Moist Reduce friction Facilitate absorption and excretion |
|
|
Serous membranes |
Secrete fluids to reduce friction Line body cavities |
|
|
Serous membranes |
Secrete fluids to reduce friction Line body cavities |
|
|
Epithelial portion of serous membrane |
Mesothelium |
|
|
Synovial membranes |
Line the joints Protect end of bones Produce synovial fluid |
|
|
Cutaneous membrane |
Skin |
|
|
3 types of fascia |
Superficial Deep Subserous |
|
|
Layers of eoidermis |
Stratum corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, basale |
|
|
What is in the stratum basale? |
Stem cells |

