![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
97 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The stuff of the universe |
Matter
|
|
|
The four forms of energy found in the body are |
chemical, electrical, mechanical, radiant |
|
|
The number of protons in the nucleus is also known as the ________ ________. |
Atomic number |
|
|
The number of neutrons in the nucleus is also known as the ________ ________. |
Mass number |
|
|
An ________ is one or more atoms that contain the same number of protons but different neutrons. |
Isotope |
|
|
The larger the atom, the more ________ it can have. |
Isotopes |
|
|
A _________-_______ can lose a particle or a ray to try to become more stable. |
Radio isotope |
|
|
Two or more atoms held together by a chemical bond is known are known as a ________. |
Molecule |
|
|
Two or more different kinds of atoms bound together are known as a molecule, but also as a ________. |
Compound |
|
|
In this bond one atom gives up an electron to another. |
Ionic bond |
|
|
Ionic bonds cannot have ________ or ________ as part of their makeup. |
Carbon or water |
|
|
In this type of bond, two atoms share electrons. |
Covalent bond |
|
|
Carbon and water bonds are always ________. |
Covalent |
|
|
A weak polar bond involving hydrogen is known as a ________ bond. |
Hydrogen |
|
|
The combining of two things to make something new is called ________. |
Synthesis |
|
|
Synthesis is a ________ process. |
Anabolic |
|
|
The breakdown of something in which it gives up energy is called ________. |
Decomposition |
|
|
Decomposition is a ________ process |
Catabolic |
|
|
An ________ reaction is one in which both synthesis and decomposition occur. |
Exchange. |
|
|
A ________ is the first kind of mixture and is homogeneous. |
Solution |
|
|
A ________ is the second kind of mixture and is heterogeneous. |
Colloid / Emulsion |
|
|
A ________ is the third type of mixture and is heterogenous with large particles. |
Suspension |
|
|
The chief difference between a mixture and a compound is that a mixture does not ________ combine. |
Chemically |
|
|
The ________ ________ ________ of membrane structure depicts the plasma membrane as an exceedingly thin structure composed of a double layer of lipid molecules with protein molecules dispersed throughout. |
Fluid mosaic model |
|
|
Transport, enzymatic activity, signal transmission, intercellular joining, cell to cell ignition, and attachment to the cytoskeleton and extracellular matrix are all functions of ________ |
Proteins |
|
|
The ________ ________ regulates intake and output. |
Plasma Membrane |
|
|
________ ________ is a passive process in which molecules or ions will scatter evenly throughout the environment. An example is breathing. |
Simple Diffusion |
|
|
________ causes things to diffuse faster. |
Heat |
|
|
________ ________ transports things from high to low concentration using no energy but does use a carrier to transport things in and out of the cell. (Example: glucose/insulin) |
Facilitated diffusion |
|
|
________ ________ uses energy and can go from a high to low concentration or low to high concentration. |
Active transport |
|
|
_________ is the mechanism by which substances are moved from the cell interior to the extracellular space as a secretory vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane. |
Exocytosis |
|
|
________ is the mechanism by which fairly large extracellular molecules or particles enter cells |
Endocytosis |
|
|
________ is the engulfing of extracellular fluid by the cells |
Pinocytosis |
|
|
Cells lose water and crenate in a ________ solution. |
Hypertonic |
|
|
Cells gain water and lyse in a ________ solution. |
Hypotonic |
|
|
The powerhouse of the cell is ________. |
Mitochondria |
|
|
The sites of protein synthesis in the cell are the ________. |
Ribosomes |
|
|
The parts of the cell responsible for transport are the ________ and ________ ________ ________. |
Rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
|
|
The part of the cell that packages, modifies, and segregates proteins for secretion from the cell is the ________ ________. |
Golgi apparatus |
|
|
The tubular extensions of the plasma membrane are the ________. |
Microvilli |
|
|
The ________ detoxify the cell and breaks down hydrogen peroxide. |
Peroxisomes |
|
|
The sites of intracellular digestion are ________. |
Lysosomes |
|
|
________ support the cell and give it shape. |
Microtubules |
|
|
An ________ compound has both carbon and hydrogen. |
Organic |
|
|
An ________ compound has any chemicals other than carbon and hydrogen. |
Inorganic |
|
|
The five functions of ________: - High heat capacity - High heat of vaporization - Polar solvent properties - Reactivity - Cushioning |
Water |
|
|
________ release hydrogen ions when dissolved in water. |
Acids |
|
|
When mixed with a base, an ________ will neutralize. |
Acid |
|
|
A ________ will make both an acid and a base neutral. |
Buffer |
|
|
________ are also known as sugars and contain carbon, hydrogen, and water. Usually in a 1 carbon to 2 hydrogen to 1 oxygen ratio. |
Carbohydrates |
|
|
A ________ is a simple sugar like glucose whose function is energy and structure. |
Monosaccharides |
|
|
A ________ is a double sugar (containing two monosaccharides) like sucrose (table sugar), lactose, and maltose. |
Disaccharide |
|
|
A ________ is a long chain of simple sugars (three or more) such as starch, cellulose, and glycogen. |
Polysaccharide |
|
|
A ________ is an oil or fat that is unsoluble in water. |
Lipid |
|
|
A ________ is a neutral fat found underneath the skin making up fatty acids and glyceral. It is the storage form of energy in the body. |
Triglyceride |
|
|
A __________ is a lipid making up part of the cell membrane and important in structure. |
Phospholipid |
|
|
A ________ is a lipid such as cholesterol needed for human life. It also makes up the sex hormones in the human body. |
Steroid |
|
|
Proteins comprise ________-________% of the body. |
10-30% |
|
|
The ________ is the control center of the cell. |
Nucleus |
|
|
The _______ ________ separates the neoplasm. |
Nuclear Envelope |
|
|
The two main parts of the skin are the ________ and the ________. |
Epidermis and dermis |
|
|
The sublayer of the dermis is the ________. |
Hypodermis |
|
|
The composition of the skin can be broken down to four cell types: the ________, the ________, the ________, and the ________. |
Keratinocytes, melanocytes, dendritic, and tactile |
|
|
________ is found on fingers, hands, and the soles of feet to offer protection. |
Thick |
|
|
________ is found everywhere other than the fingers, hands, and soles of feet. |
Thin |
|
|
The stratum ________, stratum ________, stratum ________, stratum ________, and stratum ________ are the five layers of the epidermis. |
Basale, Spinosum, Granulosum, Lucidum, Corneum |
|
|
The Stratum ________ is found only in areas of thick skin. |
Lucidum |
|
|
The dermis has two vascular layers, the ________ and the ________. |
Papillary and Reticular |
|
|
The three things that determine skin color are ________, _________, and ________. |
Melanin, Carotene, Hemaglobin |
|
|
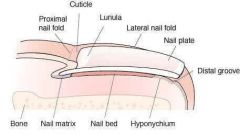
The hair is made up of three layers, the inner ________, the middle ________, and the outer _________. |
Medulla, Cortex, Cuticul |
|
|
The pigment that colors our hair comes from the ________ at the beginning of the ________. |
Melanocytes, follicle |
|
|
Stretch marks come from the ________ ________ of the dermal and epidermal layers. |
Reticular Layers |
|
|
|
|
|
The sweat glands are also known as ________ glands. |
Sudoriferous |
|
|
Two modified sweat glands that produce ear wax and milk are ________ and ________ respectively. |
Ceruminous and mammry |
|
|
Oil glands are also known as ________ glands. |
Sebaceous |
|
|
The physical function of the skin is ________. |
Protection |
|
|
The biological function of the skin is ________. |
Dendritic (immunological) |
|
|
The chemical function of the skin is ________ _________ and regulates things like body temperature and cutaneous sensation. |
Metabolic reactions |
|
|
________ ________ ________ is the least malignant and most common form of skin cancer - it occurs in the stratum basale. |
Basal cell carcinoma |
|
|
________ ________ ________ is the second most common form of skin cancer and occurs in the keratinoctyes in the stratum spinosum - it will metastasize if not removed. |
Squamous cell carcinoma |
|
|
________ is the least common but most deadly form of skin cancer. It affects the ________. |
Melanoma, melanocytes |
|
|
In a first degree burn, only the ________ is damaged. They generally heal in ____-____ days. |
Epidermis, 2-3 |
|
|
A second degree burn injures the epidermis and the first two layers of the ________. They generally heal in ____-____ weeks. |
Dermis, 3-4 |
|
|
Third degree burns injure the entire ______ of the skin; ________ ________ are also destroyed. These burns usually require ________ ________. |
Thickness, nerve endings, skin grafting |
|
|
Another name for first and second degree burns is ________ ________ burns. Third degree are also known as ________ _________ burns. |
Partial thickness, full thickness |
|
|
The seven characteristics of living organisms are ________, ________, ________, ________, ________, ________, and ________. |
Nutrition, excretion, respiration, sensitivity, reproduction, growth, and movement |
|
|
The four elements found most often in the human body are ________, ________, ________, and ________. |
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen |
|
|
During ________ the chromosomes duplicate, and the copies remain attached to each other. |
Interphase |
|
|
After Interphase is ________ during which the chromosomes condense and become visible. In the cytoplasm, the spindle forms. |
Prophase |
|
|
After prophase is ________ during which the nuclear membrane dissolves and the spindle starts to interact with the chromosomes. |
Prometaphase |
|
|
After Prometaphase comes ________ during which the copied chromosomes align in the middle of the spindle. |
Metaphase |
|
|
After Metaphase comes ________ during which the chromosomes separate into two genetically identical groups and move to the opposite sides of the cell. |
Anaphase |
|
|
After Anaphase is ________ during which nuclear membranes form around the two sets of chromosomes, the chromosomes spread out, and the spindle breaks down. |
Telophase |
|
|
After Telophase comes ________ during which the cell splits into two daughter cells. |
Cytokinesis |
|
|
Each daughter cell will have ____ copies of ____ chromosomes which is known as a ________. |
2, 23, diploid |
|
|
|

