![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
|
|
|

|
|
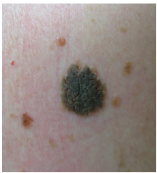
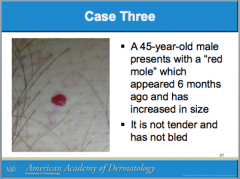
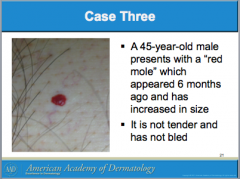
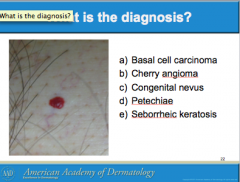
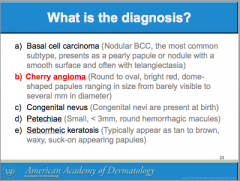
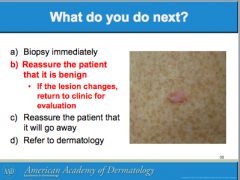
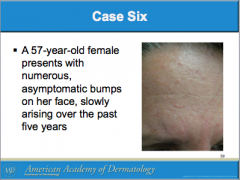
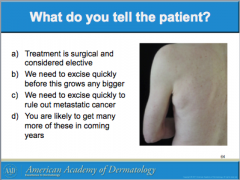
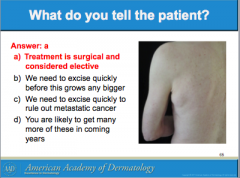
What is this called? Characteristics? (border, color) It can arise all over the body except where?
Is it usually papular or macular? |

|
|
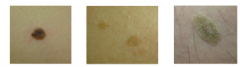
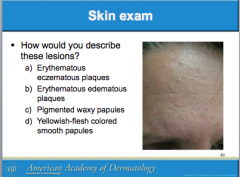
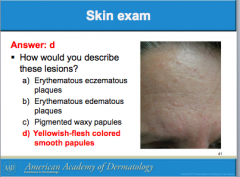
Different colors, different textures? What is the diagnosis? |

|
|
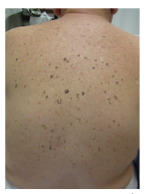
Can SKs be extensive? What decades of life do they often appear? As opposed to the nevi which often appear in which decades? What should a new nevus at age 50 raise suspicion of? |

|
|
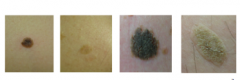
Are SKs superficial or deep? Dermal or epidermal? They are stuck on the skin like a piece of ________. |

|
|
|
If you are in doubt about the diagnosis of seborrheic keratosis, what should you do? |
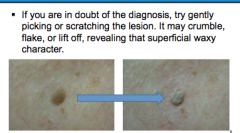
|
|
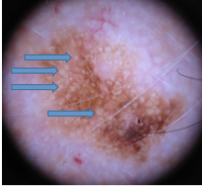
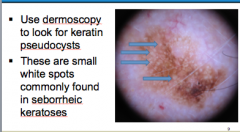
Using dermoscopy, how can you tell if a lesion is seborrheic keratosis? Will you see? Describe. |
|
|
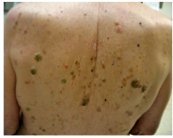
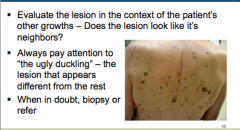
Does the lesion look like its neighbors? What should you always pay attention to when you have multiple lesions? What should you do if you have doubts? |
|
|
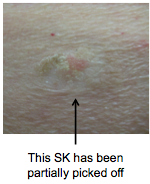
SKs can occasionally become irritated. What are some removal options? |

|
|
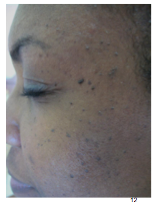
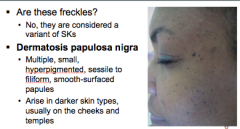
Are these freckles? What do you call them? What skin types do they arise in? |
|
|
|
Is dermtosis papulosa nigra harmful? Do you treat them with liquid nitrogen? Why or why not? What treatment could you use? |

|
|
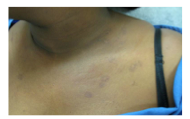
This patient was treated with cryotherapy? What does she now have? |
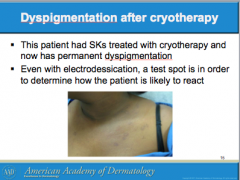
|
|
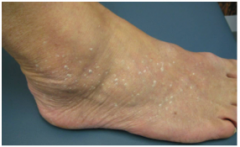
What type of keratosis is this? Is it harmful? |
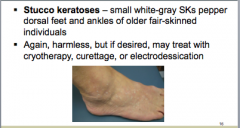
|
|
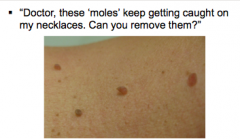
What is this? What color are they usually? Can the be pedunculated?
Where do they arise?
Are they usually asymptomatic? |

|
|
|
What factors play a role in skin tags? (obvious, food, rub)
Are they more common in pregnancy?
What disease can they be a marker for (just like acanthosis nigricans)? |

|
|
|
What are the methods for removing skin tags? (3)
Can they fall off on their own sometimes? How? |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
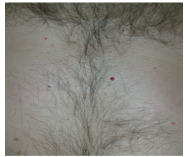
What are these?
Common acquired _______ proliferation.
What decade do they develop in?
Where is the highest concentration? |

|
|
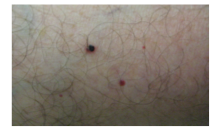
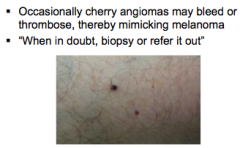
Occasionally, cherry angiomas may bleed or thrombose. What do they resemble? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
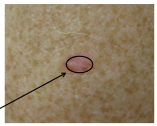
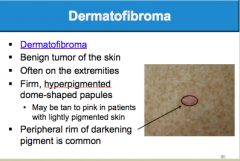
What is this benign tumor of the skin? Where is it often located? Is it firm or not, hyper or hypopignmented? Peripheral rim of (darkening or lightening) is common. |
|
|
|
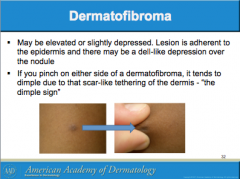
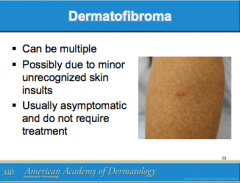
What is the sign to identify dermatofibroma? |
|
|
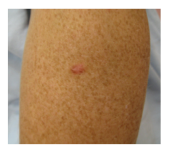
What can dermatofibromas be due to? Due they usually required treatment? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
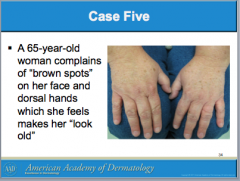
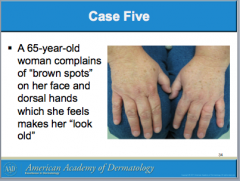
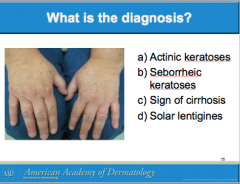
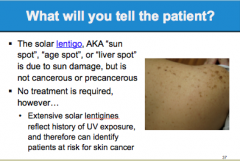
What is solar lentigo due to? Are they cancerous or precancerous? Is treatment required? What can these lesions be used to identify? |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
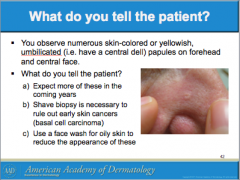
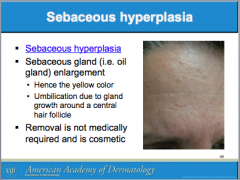
Sebaceous hyperplasia is associated with enlargement of what gland which gives it a yellowish color? Is removal medically required? |
|
|
|
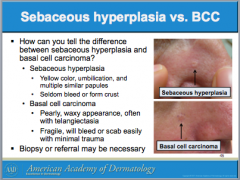
How do you tell the difference between sebaceous hyperplasia and basal cell carcinoma? (think color, presence of telangiectasia, scabbing) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
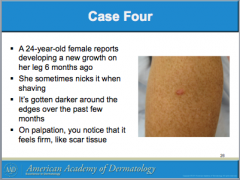
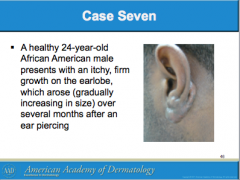
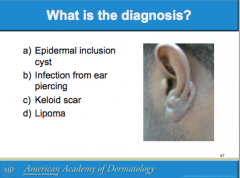
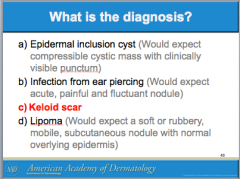
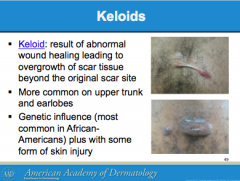
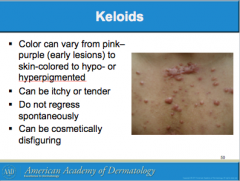
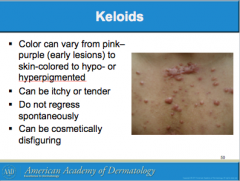
What is a result of abnormal wound headlong to overgrowth of scar tissue beyon the original scar site? Where is it most common? What group is it most common among? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Are keloids easy or difficult to treat surgically? Is there a reliable therapy available? Patients pre-disposed to developing keloids should avoid what type of surgeries? What is the mainstay of treatment for keloids? |

|
|
|
|
|
|
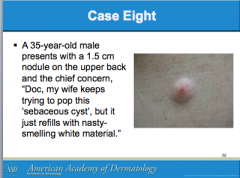
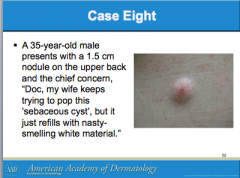
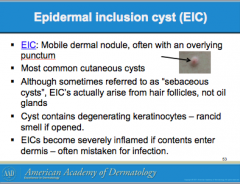
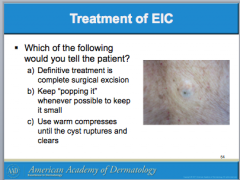
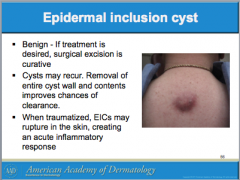
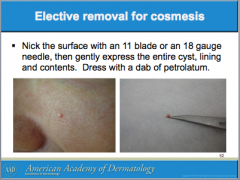
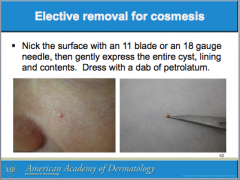
What are the most common cutaneous cysts? Are the mobile or not? What is usually overlying them? Where do they arise from? What do they contain (smells bad if opened)? If contents enter _______, this leads to severe inflammation. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
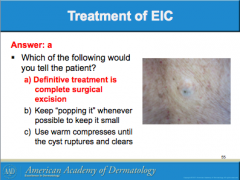
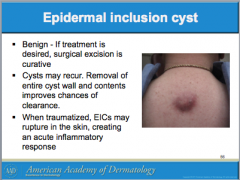
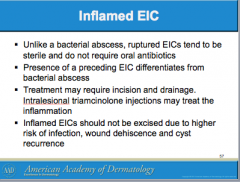
Do ruptured EICs require oral antibiotics? How do you differentiate from bacterial abscess? What can you use to treat inflammation? Should inflamed EICs be excised? |
|
|
|
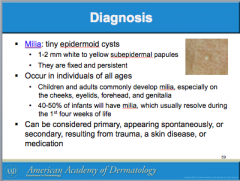
Milia |
|
|
What are tiny epidermoid cysts? Are they fixed and persistent or mobile? What layer of the skin? What ages? Locations? |
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
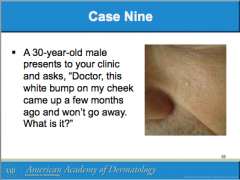
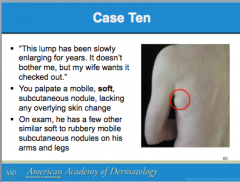
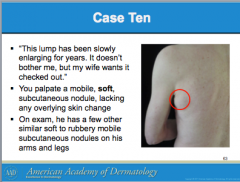
What is this? |
Lipoma |
|
|
What is the clue to lipomas?
Are they often solitary or multiple?
In what case will they be multiple or begin in early childhood? |

|
|
|
|
|
|
|

