![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Axis/Revisionist powers
|
Germany, Italy, and Japan
|
|
|
Manchuria
|
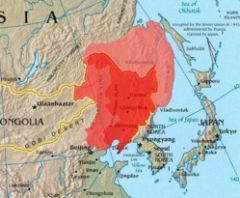
historical region of northeastern China. Strictly speaking, it consists of the modern provinces (sheng) of Liaoning (south), Kirin (central), and Heilungkiang (north)
|
|
|
Rape of Nanjing
|
Japanese conquest in 1937 led to more than four hundred thousand Chinese residents met death through unimaginable horrors, most gruesome example of brutality tied to an ethos of racial superiority
|
|
|
appeasement
|
policy adopted as Britain and France continued to seek peace, even if it meant acquiescing to Germany's aggressive actions
|
|
|
Munich Conference
|
September 1938 conference where the policy of appeasement was adopted
|
|
|
Warsaw Pact
|
Soviet created organization as a countermove to match NATO
|
|
|
U-boats
|

Unterseebootes or submarines
|
|
|
the Blitz
|
Blitzkrieg "lighting war" in which superior air force would soften resistance, thei
r swift and highly mobile Panzer, or tank units, would roll in, and finally their well-equipped troops would march in to clean up any remaining resistance |
|
|
Operation Barbarossa
|
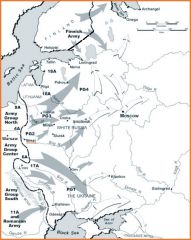
German invasion of Soviet Union, began in June 1941 and included supporting troops from Hungary, Finland, and Romania who augmented the massive German fighting force of men and equiptment
|
|
|
Stalingrad
|

operations by the Germany and its allies and Soviet forces conducted with the purpose of possession of the city of Stalingrad, which took place between 17 July 1942 and February 2, 1943
|
|
|
"a date that will live in infamy"
|
phrase by FDR referencing December 7, 1941 when the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor took place
|
|
|
Greater Asian Co-Prosperity Sphere
|
oncept created and promulgated during the Shōwa era by the government and military of the Empire of Japan which represented the desire to create a self-sufficient "bloc of Asian nations led by the Japanese and free of Western powers"
|
|

Dresden
|

bombing of Dresden by the British Royal Air Force (RAF) and United States Army Air Force (USAAF) between February 13 and February 15, 1945, 12 weeks before the surrender of the Armed Forces (Wehrmacht) of Nazi Germany. Nearly 40,000 civilian casualties
|
|
|
Wannsee Conference
|
January 1942 conference in which members agreed to evacuate all remaining European Jews to camps in easter Poland where they could be worked to death or executed
|
|
|
Yalta Conference
|
major World War II conference of the three chief Allied leaders, President Franklin D. Roosevelt of the United States, Prime Minister Winston Churchill of Great Britain, and Premier Joseph Stalin of the Soviet Union (see photograph), which met at Yalta in the Crimea to plan the final defeat and occupation of Nazi Germany
|
|
|
Truman Doctrine
|
response to growing communisim it was issued March 1947 crystallizing the U.S. perception of the world divided between enslaved and free peoples and unequivicolly drew the battle lines of the cold war
|
|
|
N.A.T.O.
|
North Atlantic Treaty Association founded in 1949 as a regional military alliance against Soviet aggression
|
|
|
Allied Powers
|
Great Britain and the Commonwealth nations, Russia, France, China, the United States, and its Latin American allies
|
|
|
invasion of China
|
1937 invasion by Japan starting in Manchuria
|
|
|
Tripartite Pact
|
Axis pact that stated that should one of the signatories, consisting of Japan, Germany, and Italy, be aggressed upon by the United States, the other two were obliged to send help
|
|
|
Anschluss
|
political union of Austria with Germany, achieved through annexation by Adolf Hitler in 1938
|
|
|
Nonaggression Pact
|
pact between Russia and Germany which bought each nation a brief respite against fighting each other, and gave them free hands to divide much of easter Europe
|
|
|
Luftwaffe
|
German air force
|
|
|
Lebensraum
|
"living space" quested for by Germany. He wanted to evacuate Jews to make way for resettled Germans
|
|

Stalin
|

emerged as the unchallenged dictator of the Soviet Union by 1928 after struggle of Bolshevik leaders to decide on a leader post-Lenin's death. Stalin annihilated his rivals through treachery, deceit, and violence. He supported the ideal of "socialism in one country," and was determined to rapidly build Russia into an industrial powerhouse, no matter the cost in resources or lives.
|
|
|
lend-lease program
|
1941 shift away from the cash-and-carry policy, made American goods and weapons readily available to the Allies
|
|
|
"Asia for Asians"
|
Japanese used anti-European imperialism slogan
|
|
|
D-Day
|
increased offensive and bombing of civilian centers beginning on June 6, 1944 leading to the German surrender on May 8, 1944
|
|
|
the Final Solution
|
policy of extermination or working to death of Jews, Gypsies, and Slavs etc.
|
|
|
"comfort women"
|
prostitutes offered as rewards for Japanese soldiers
|
|
|
Potsdam Conference
|
meeting (July 17–Aug. 2, 1945) of the principal Allies in World War II (the United States, the USSR, and Great Britain) to clarify and implement agreements previously reached at the Yalta Conference
|
|
|
Marshall Plan
|
European Recovery Plan - the economic adjunct to the Truman Doctrine designed to rebuild European economies through capitalism and cooperation thus neutralizing communism's appeal to struggling peoples
|
|
|
United Nations
|
supranational organization dedicated to keeping world peace created by delegates from fifty nations, including the goals of maintaining international peace and security and of promoting friendly relations among the world's nations
|

