![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pan-Slavism
|
movement supported by the Russian government that inspired resistance and rebellion in order to weaken their rival empires
|
|

Archduke Franz/Francis Ferdinand
|

Archduke of Austro-Hungary, assassinated by Serbs
|
|
|
Triple Entente
|
Russia, Britain, France
|
|
|
total war
|
military conflict in which nations mobilize all available resources in order to destroy another nation's ability to engage in war
|
|
|
Tsar Nicholas II
|
tsar of Russia that abdicated the throne after street demonstrations and military mutinies in 1917, ending three hundred years of Romanov rule
|
|
|
trench warfare
|
Life in the trenches was numbing boredom punctuated by sheer terror. the presence of waist-deep mud, half-decayed corpses, trench rats, and lice made for a grim existence.
|
|
|
No-man's-land
|
unoccupied land between military forces. Few people made it out of no man's land as it was filled with continuous machine-gun fire
|
|
|
home front
|
burden of producing supplies and maintaining industries that fell on the civilians not directly involved in conflict
|
|

V. I. Lenin
|

Marxist leader and anti-war activist, his activists were radical socialists called Bolsheviks. They pushed an end to the war and transference of legal authority to the soviets.
|
|
|
Petrograd
|
soviet workers' council in Saint Petersburg
|
|
|
"Peace, Land, Bread"
|
demands of peasants, battle cry of the 1917 revolution
|
|
|
Lusitania
|

British liner sunk in 1915, 128 Americans died and this began the public's movement away from neutrality
|
|
|
Weimar Republic
|
nickname given to the German state from 1919 to 1933. It was dubbed the "Weimar Republic" by historians in honor of the city of Weimar, where a national assembly convened to write and adopt a new constitution
|
|
|
Big four
|
Allied leaders who met at the Paris Peace Conference in January 1919, after World War. They were President Woodrow Wilson of the United States, Prime Minister David Lloyd George of Britain, Premier Georges Clemenceau of France, and Premier Vittorio Orlando of Italy. Edit
With selected items: |
|
|
League of Nations
|
an established attempt to stave off war bit it proved to be largely infeffectual. Its two major flaws were that it had no power to enforce its decisions and that it depended on collective security to preserve peace. The U.S. never joined because the Senate rejected the idea. Germany and Japan left the League in 1933 while Italy resigned in 1937. The Soviet Union joined in 1934 but was kicked out in 1940. Laid foundations for the United Nations.
|
|
|
U.S.S.R
|
Union of Soviet Socialist Republics
|
|
|
self-determination
|
assuaged the feelings of nationalists everywhere and, in some cases, functioned very well as Czechoslovakia, Poland, and Yugoslavia became independent nations Edit
|
|
|
Triple Alliance
|
Germany, Austro-Hungary, Italy
|
|
|
Schlieffen Plan
|
German plan to defeat France and then turn to meet the Russians
|
|
|
Kaiser Wilhelm II
|
emperor of Germany in 1888 following the death of Frederick II.
|
|
|
Western Front
|
describes the "contested armed frontier" between lands controlled by Germany to the East and the Allies to the Wes
|
|
|
Verdun
|
longest battle of the First World War based around the French stronghold in northeast France and the German's attempts to capture the city
|
|
|
mustard gas
|
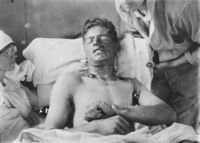
a strong vesicant (blister-causing agent) first utilized in warfare in WWI by Germany
|
|
|
Bolsheviks
|
radical socialists that followed Lenin
|
|
|
soviets
|
originally was a workers' local council in late Imperial Russia
|
|
|
Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
|
Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and Turkey, for the one part, and Russia, for the other part, declare that the state of war between them has ceased in 1918
|
|
|
Easter Rebellion
|
rebellion staged in Ireland in Easter Week, 1916. The Rising was an attempt by militant Irish republicans to win independence from Britain
|
|
|
influenza pandemic
|
an epidemic of the influenza virus that spreads on a worldwide scale and infects a large proportion of the human population. 1918-1920 pandemic of Spanish flu most serious, killed more people than WWI
|
|
|
Woodrow Wilson
|

twenty-eight president of the U.S.
|
|

Mustafa Kemal
|

army officer, revolutionary statesman, and founder of the Republic of Turkey as well as its first President.
|
|
|
mandate system
|
system devised to protect former colonies as they moved toward independence. Conveniently only applied it to the defeated Powers and failed to look at their own colonies
|
|
|
Treaties of Versailles, Neuilly, Sevres, St. Germain, Trianon
|
final treaties to end the war that saved the harshest treatment for the vanquished nations as France pushed to permanently weaken Germany. Germans were required to accept full responsibility for the war and pay the full costs of the war (reparations.) Denied navy and air force for the Germans and limited the size of its army to one hundred thousand troops. Territorial break-up of Austria-Hungary was recognized in granting self-determination.
|

