![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Sui dynasty
|
followed the Southern and Northern Dynasties and preceded the Tang Dynasty in China. It ended nearly four centuries of division between rival regimes
|
|
|
Tang Taizong
|

second emperor of the Tang Dynasty of China, ruling from 626 to 649
|
|
|
Uighers
|

group of Turkic-speaking tribes that lived in the Altay Mountains
|
|
|
footbinding
|
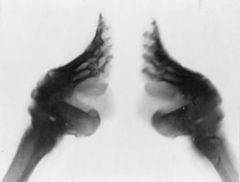
ustom practiced on young girls or females for approximately one thousand years in China, beginning in the 10th century and ending in the early 20th century that occurred due to the fashion of the deformity
|
|
|
gunpowder
|

developed by Daoist alchemists search of for the elixir of life, it was used in early flamethrowers and in primitive bombs
|
|
|
Chan/Zen Buddhism
|
Buddhism that focused on intuition, moments of clarity, and sudden flashes of insight
|
|
|
neo-Confucianism
|
a hybrid between Buddhist interests in the nature of the human soul and the individual's relationship with the cosmos with traditional Confucian beliefs
|
|
|
Silla dynasty
|
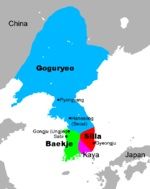
one of the Three Kingdoms of Korea
|
|
|
Samurai
|

term for the military nobility of pre-industrial Japan; the military talent and discipline of the samurai played the most distinctive role in political and military affairs
|
|

the Sind
|
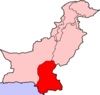
one of the four provinces of Pakistan and historically is home to the Sindhis
|
|
|
Chola
|
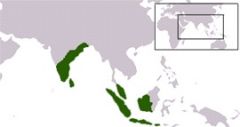
a Tamil dynasty that ruled primarily in southern India until the 13th century
|
|
|
Ceylon
|
Sri Lanka's name before 1972
|
|

dhows and junks
|

dhows being the ships from the Arab and Indian world and junks being Chinese equivalent; both ships were dependent on the direction of the wind, so trade occurred in stages
|
|
|
Sufism
|
Sufism is a branch of Islam that believes that the after-life privilege of becoming close to God can occur during life
|
|
|
Swahili states
|
Swahili derives from the Arabic word meaning "coastal peoples"; are a people and culture found on the coast of East Africa, mainly the coastal regions and the islands of Kenya and Tanzania, and north Mozambique
|
|
|
Yang Jian
|
imperial prince of the Chinese dynasty Sui Dynasty who reestablished centralized imperial rule through the use of tight political discipline and military force
|
|
|
Grand Canal
|
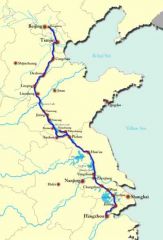
building project under Emperor Sui Yangdi, it established the foundation for cultural and political unity in China as it integrated the economics of both the north and south
|
|
|
Equal Field Systems
|
system of dividing land in which all land was owned by the government, which would then be assigned to individual families. Every individual, including slaves, was entitled to a certain amount of land, the amount depending on their ability to supply labor
|
|
|
fast-growing rice
|

introduced to China during the Sui & Tank expansion into Vietnam; it made it possible for Chinese farmers in the south to harvest two crops a year
|
|
|
porcelain
|

Porcelain is generally believed to have originated in China; although pottery fragments dating to around 9000 BCE have been unearthed in Jiangxi province, true porcelain is thought to have first emerged during the late Eastern Han Dynasty, which lasted from 100 to 200 CE
|
|
|
printing
|
printing became widespread during the Tang dynasty first with block printing, then with the development of moveable type
|
|
|
paper money
|
started by merchants to deal with the lack of copper currency and by the Qing dynasty, the government instituted tight fiscal controls over the issuance of paper money
|
|
|
Heian court
|
the Heian period took place when the capital of Japan was moved to Heian (modern Kyoto) and the new Japanese imperial state continued to draw inspiration from China but was careful to develop elaborate Japanese political and cultural traditions
|
|
|
The Tale of Genjii
|
written by Muraski Shikibu, this piece of writing chronicles the ultrarefined life at the Heian court and offers a meditation on the passing of life's joys, sorrows, and relationships
|
|
|
Harsha
|
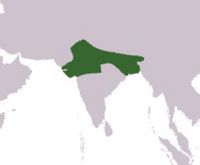
Indian emperor who ruled Northern India for over forty years
|
|
|
Sultanate of Delhi
|
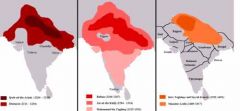
Muslim dynasties that ruled in India from 1206 to 1526 begun by the descendents of Mahmud of Ghazni who made seventeen incursions into India to plunder and demolish its temples to spread Islam
|
|
|
Vijayanagara Empire
|
South Indian empire based in the Deccan Plateau
|

