![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
State Ohm's Law
|
Current in a circuit is DIRECTLY proportional to the Voltage and INVERSELY proportional to the Resistance
|
|
|
What is Kirkoff's Law for Current (I) in a Series Circuit?
|
Current is the same at all points in a Series Circuit. (I-tot = I-1 = I-2 = I-3...)
|
|
|
What is Kirkoff's Law for Voltage (E) in a Series Circuit?
|
The sum of all Voltage around a closed path = 0. (Sum of Voltage drops = Total source Voltage)
(E-tot = E-1 + E-2 + E-3...) |
|
|
State Kirkoff's Law for a Series Circuit, generally.
|
When Current (I) flows through a Resistance (R), Voltage (E) will drop, Current (I) is opposed, and Power (P) is consumed.
|
|
|
What does Kirkoff's Law say about Resistance in a Series Circuit?
|
That the sum of the individual Resistances in the circuit = the total Resistance.
(R-tot = R-1 + R-2 + R-3...) |
|
|
What does Kirkoff's Law say about Power in a Series Circuit?
|
The sum of Power (P) dissipated across each individual load Resistance (R) = Total Power.
(P-tot = P-1 + P-2 + P-3...) |
|
|
Name 4 factors that affect the Resistance of a Conductor.
|
1) Length
2) Temperature 3) Cross-sectional area 4) Conductor type (In aircraft, ususally either Aluminum or Copper) |
|
|
State Kirkoff's Law for Current in a Parallel Circuit.
|
The Total Current (I-tot) in a Parallel Circuit will be the sum of the individual Currents (I-1, I-2...) in each of its branches.
(I-tot = I-1 + I-2 + I-3...) |
|
|
State Kirkoff's Law for Power in a Parallel Circuit.
|
The Total Power (P-tot) consumed in a Parallel Circuit is equal to the sum of the Power consumed in each of the individual branches.
(P-tot = P1 + P2 + P3 +...) |
|
|
State Kirkoff's Law for Voltage in a Parallel Circuit.
|
The Total Voltage (E-tot) in a Parallel Circuit is equal to the Voltage across each of the individual branches.
(E-tot = E1 = E2 = E3 = ...) |
|
|
State Kirkoff's Law for Resistance in a Parallel Circuit.
|
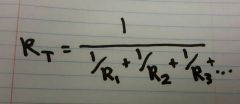
The Total Resistance (R-tot) in a Parallel Circuit will be less than that of the branch with the least Resistance.
|

