![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Immature mast cells circulate in the peripheral blood and express:
Mature mast cells develop in the presence of stem cell factor and express: |
Immature mast cells: CD34, KIT (CD117), IgG receptor FcyRII
Mature mast cells: KIT (CD117), FcER1, loss of CD34 and FcyRII |
|
|
What stimulated mast cell maturation?
|
Stem cell factor (bone marrow, fibroblasts, keratinocytes, endothelial cells)
IL-3 > 4, 6, 9 |
|
|
Cytokine mileu of mast cell secretion?
|
TH2!
IL1, IL3, IL4, IL5, IL6, GM-CSF, TGFB, TNFa |
|
|
Mast cells can be degranulated via immunologic and non immunologic stimuli...
|
Immunologic caused by antigen/autoantibodies binding to IgE or FcERI receptors --> crosslinking --> degranulation (can be a drug like PCN)
Non immunologic caused by direct binding of substance P, stem cell factor, C5a*, drugs (PIANOS) |
|
|
Which drugs cause mast cell degranulation?
|
Immunologic: d/t antigen/autoantibodies, drug like PCN
Non immunologic: d/t direct binding, PIANOS, polymixin, IV contrast, ASA, etoh, amphotericin B, NSAIDS, opiates, systemic anesthetics, scopalamine |
|
|
Preformed mediators?
|
Preformed and easy!
histamine, heparin, tryptase, neutrophil chemotactic factor, eosinophil chemotactic factor |
|
|
Newly formed mediators?
|
Prostaglandin D2, leukotrienes C4, D4, E4, platelet activating factors
|
|
|
What is the ligand for KIT on mast cells?
|
stem cell factor --> activation leads to cellular growth and prevents apoptosis
|
|
|
Activating mutation of KIT? Inactivating mutation?
|
Activating: mastocytosis, GIST, testicular seminoma, melanoma, AML
Inactivating: piebaldism |
|
|
What chromosome is KIT on? Most common mutation for mastocytosis?
|
Chromosome 4
D816V (intracellular region) |
|
|
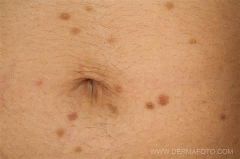
Children are more likely to have cutaneous mastocytosis with a limited course, while adults are more likely to have systemic symptoms and evidence of extracutaneous involvement.
What are the common cutaneous mastocytoses in children? |
Urticaria pigmentosa
Solitary mastocytoma Diffuse cutaneous mastocytosis |
|
Prognosis?
|
Urticaria pigmentosa: most common form of cutaneous mastocytosis in children, variable numbers of tan/brown macules and apules beginning in first weeks of life
Most resolve before adolescence |
|
|
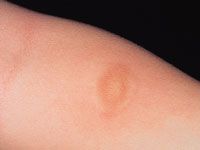
Most common site of a solitary mastocytoma?
|
dorsal hand
|
|
prognosis?
|
Solitary mastocytoma: 10-35% of childhood cases, may be present at birth or first few weeks of life, most common site dorsal hand, usually involutes before age 10
|
|
|
Which entities can exhibit a pseudo Dariers sign?
|
JXG, piloleiomyoma
|
|
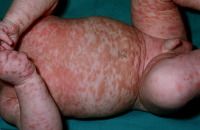
dx?
|
diffuse cutaneous mastocytosis
|
|
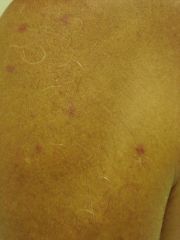
Mastocytosis of the skin is almost always indicative of systemic disease in adults. What systemic symtpoms associated?
|
CNS: headache, cognitive disorganization, fatigue, mixed organic brain syndrome
GI: cramping, diarrhea, epigastric pain, NVD, HSM CV: CP, dizziness, palpitations, syncope MSK: bone pain |
|
|
You can see manifestation so mast cell disease on radiographs, why?
|
due to increased numbers of mast cells and effect of mediators on bones --> heparin induced osteoporosis, KIT on osteoclasts, histamine promotes bone sclerosis, IL6 promotes resorptive activity
|
|
|
Survival rate of aggressive systemic mastocytosis? Mast cell leukemia?
|
Aggressive systemic mastocytosis: 3.5 years
Mast cell leukemia: less than 1 year |
|
|
Mast cell stains?
|
Leder, Giemsa, Toluidine blue, KIT (CD117)
|
|
|
Major criteria for systemic mastocytosis?
|
more than 15 mast cells in bone marrow or extracutaneous tissue
|
|
|
Total serum tryptase must remain elevated above X for diagnosis of systemic mastocytosis?
|
>20ng/ml
|
|
|
Types of tryptase?
|
Alpha tryptase useful to assess total mast cell burden
Beta tryptase is only increased during acute episodes Normal tryptase is <20ng/ml |
|
|
Which urinary metabolite is directly proportional to the extent of mast cell disease?
|
Urinary histamine and its metabolite 1,4 methylimidazole acetic acid
|
|
|
Tx of GI symptoms in systemic mastocytosis?
|
oral cromolyn
|
|
|
Systemic mastocytosis with associated hematological non mast cell lineage disease (SM-AHNMD) is associated with what?
|
underlying malignancy
|
|
|
What systemic anesthetic can be used safely in mastocytosis?
lidocaine succinylcholine tubocurarine thiopental propofol |
propofol also: non-depolarizing muscle relaxants are less likely to cause an anaphylactic reaction than depolarizing |
|
|
Mastocytosis can be diagnosed via measurement of:
tryptase kinase bile acids histamine IgE |
tryptase
|
|
|
Which organ system is least likely to be involved in systemic mastocytosis?
liver spleen GI GU bone marrow |
GU
|

