![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
31 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
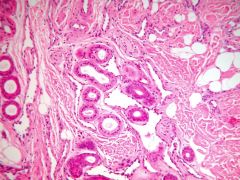
clinical presentation? |
Eccrine Angiomatous Hamartoma-- increased number of BV and lymphatics, intimately associated with increased eccrine units
rare, usually present at birth as a brown verrucous plaque with hyperhidrosis and hypertrichosis on extremities |
|
|
Mutation in Sturge Weber? Syndrome? |
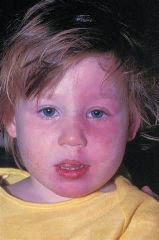
GNAQ
Sturge–Weber syndrome
Sturge–Weber syndrome, sometimes referred to as encephalotrigeminal angiomatosis, is a rare congenital neurological and skin disorder. It is one of the phakomatoses and is often associated with port-wine stains of the face (V1 distribution- ophthalmic branch), glaucoma, seizures, mental retardation, and ipsilateral leptomeningeal angioma (cerebral malformations and tumors). **tram track calcifications |
|
|
Mutation in Parkes Weber? Syndrome? |
RASA1
PWS is characterized by the venous malformations, cutaneous capillary malformations, and lymphatic malformations found in Klippel–Trénaunay–Weber syndrome along with arteriovenous malformation. It also can include fistulas occurring with skeletal or soft tissue hypertrophy
This is a FAST FLOW |
|
|
Mutation in capillary malformation-AVM syndrome? |
RASA1
|
|
|
Mutation in Klippel Trenaunay? Clinical? |
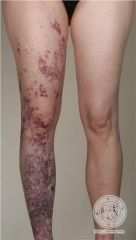
VG5Q, RASA1, GNAQ
sporadic, vascular malformation of a limb associated with bone and soft tissue hypertrophy of the affected extremity with lymphatic and deep venous insufficiency
|
|
|
Mutation in microcephaly-capillary malformation syndrome? |
STAMBP |
|
|
Mutation in macrocephaly capillary malformation polymicrogyria syndrome? Presentation? |
PIK3CA
macrocephaly, congenital macrosomia, extensive cutaneous capillary malformation (naevus flammeus or port-wine stain type birthmark over much of the body; a capillary malformation of the upper lip or philtrum is seen in many patients with this condition), body asymmetry (also called hemihyperplasia or hemihypertrophy), polydactyly or syndactyly of the hands and feet, lax joints, doughy skin, variable developmental delay and other neurologic problems such as seizures and low muscle tone.
|
|
|
Mutation in Rubinstein Taybi syndrome? Clinical? |
CREBBP
vascular malformation, broad thumbs, beaked nose, mental retardation, congenital heart defects, cryptochidism |
|
|
Mutation in Beckwidth Wiedemann syndrome? Clinical? |
KIP2 (imprinting defect H19/IGF2)
facial vascular malformation, macroglossia, hemihypertrophy of viscera a/w Wilms tumor, hepatoblastoma, circular depression over rim of helices, linear earlobe crease |
|
|
Mutation in Proteus syndrome? Clinical? |
AKT/PTEN
cutaneous findings of hyperkeratotic epidermal nevi, palmoplantar cerebriform connective tissue nevi, capillary malformation, hemangiomas wtih gigantism of hands/feet, hyperostoses of epiphyses and skull (esp ext auditory canal), thin limbs, lung cysts, bilateral ovarian cystadenomas |
|
|
Mutation in Bannayan Riley Ruvalcaba? Clinical? |
PTEN
macrocephaly, pigmented macules of the glans penis, and benign mesodermal hamartomas (primarily subcutaneous and visceral lipomas, multiple hemangiomas, and intestinal polyps). Dysmorphy as well as delayed neuropsychomotor development can also be present.
increased risk of thyroid cancers and autoimmune thyroid conditions |
|
|
Mutation in blue rubber bleb nevus? Clinical? |
Venous malformations (slow flow)
TIE2/TEK on ch 9p21
multiple tender cutaneous and GI venous malformations (MC colon), cardiac malformations
presents at birth or develops by puberty
compressive blue papulonodules on trunk/arms, painful with increased hyperhidrosis and nocturnal pain
GI malformations can cause GI bleeding and intussusception |
|
|
Mutation in Maffucci syndrome? Clinical? |
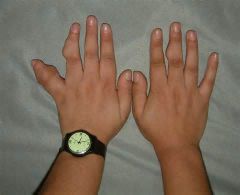
IDH1 > IDH2 (PTH/PTHrP type I receptor)
venous malformations (superficial and deep) of hands/feet, benign endochondromas, increased risk of chondrosarcomas and less often sarcomas, angiosarcomas can be fatal |
|
|
What are the PTEN mutation syndromes? |
Cowden syndrome, Proteus syndrome, and Proteus-like syndrome, Bannayan Riley Ruvalcaba syndrome |
|
|
What is Ollier syndrome? |
endochondromas only |
|
|
What is the mutation in Cornelia de Lange? clinical? |
NIPBL
cutis marmorata, synophris, trichomegaly, craniofacial abnormalities, MR, deafness, low pitched cry, clindodactyly |
|
|
Vascular stains? |
CD31, CD34, D2-40, GLUT 1, ERG |
|
|
Look up phakomatosis pigmentovascularis |
LOOK IT UP |
|
|
What is CLOVES syndrome? Mutation? |
Congenital Lipomatosis Overgrowth, Vascular malformations, Epidermal nevi, Skeletal spine abnormalities
PIK3CA defect |
|
|
What is Gorham-Stout syndrome? |
vascular and/or lymphatic malformations of the skin
diffuse skeletal and muscular abnormalities
osteolysis ('disappearing bone disease')
pathologic fractures |
|
|
What is Bockenheimer syndrome? |
diffuse phlebectasia, upper > lower extremities, may involve muscles |
|
|
What is cutis marmorata telangiectatica congenita? |
onset at birth, presents with a blanching reticulated vascular pattern on trunk/extremities with segmental distribution
associated anomalies in 50% of patients (varicosities, nevus flammeus, macrocephaly, ulceration, hypoplasia, hypertrophy of soft tissue/bone) |
|
|
What is adams oliver syndrome? |
aplasia cutis congenita on scalp (with skull ossification defect), extensive cutis marmorata, limb defects, cardiac abnormalities
abnormal vascular development |
|
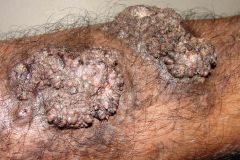
Staining pattern? |
Verrucous hemangioma
GLUT1+, WT1+, CD31+, CD34+
D2-40 negative |
|
|
Differences between HHT1 and HHT2? |
HHT1: ENG gene (endoglin), earlier onset telangiectases, epistaxis, pulmonary AVM
HHT2: ACVRL1/ALK1 (activin A receptor type II like kinase), more hepatic involvement |
|
|
Generalized essential telangiectasia is more common in what populations? |
women, more prominent in puberty, pregnancy and with hormones |
|
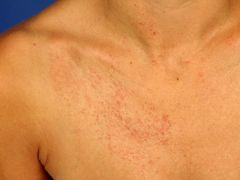
This is present at birth and exacerbated by heat and sweating. |
Unilateral nevoid telangiectasia |
|
|
Mutation in Ataxia Telangiectasia? Inheritance? |
AR
ATM |
|
|
Clinical presentation of Ataxia Telangiectasia? What typically presents first? |
mutation in ATM (inability to repair chromosomal strand breaks --> sensitivity to ionizing radiation)
presents first with ataxia (2-3 years old) --> telangiectasias on bulbar conjunctivae, premature aging, decreased purkinje fibers in cerebellum, recurrent sinul and pulmonary infections
death in 2nd or 3rd decade, heteroxygoes have elevated risk of cancer, esp breast
|
|
|
Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum is characteristic of what disease? |
Fabry disease: a-galactosidase A deficiency |
|
|
Clinical presentation of Fabry disease? |
a-galactosidase A deficiency: X linked, accumulation of neutral glycolipid ceramide trihexidose in lysosomes
painful paresthesias in extremities, angiokeratomas in bathing suit distribution, corneal/lenticular opacities, progressive renal disease, coronary and CNS vascular disease, 'maltese cross' in urine |

