![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Three types of interferons? |
Leukocyte (a)- type I INF --> a/B receptor
Fibroblast (B)- type I INF --> a/B receptor
Immune (y)- type II INF --> seperate receptor |
|
|
Which pathway is affected by interferons? |
IFN receptors signal via JAK/STAT pathway --> increase MHC I, promote NK activity, promote development of TH1 response (cellular immunity)
All of these effects are antiviral, antiproliferative, immunoregulatory |
|
|
What are the TH1 cytokines? |
INFgamma!!! IL2, IL12, IL15, IL18, TNFa |
|
|
What are the TH2 cytokines? |
IL4, IL5, IL10, IL13 |
|
|
What are the TH17 cytokines? |
IL1, IL6, TNFa, TGFB, IL17, IL22, IL23 |
|
|
INF gamma does what? |
increases TH1, decreases TH2, increase opsonization, increase macrophage activity |
|
|
What are the main dermatologic applications of interferon therapy? |
genital warts (HPV 6, 11): 1 million IU/wart 3x/week x 3 weeks
Kaposi Sarcoma: AIDS associated
Keloids
Behcets
Metastatic Melanoma |
|
|
What is the most common side effect of interferon therapy? |
flu like symptoms |
|
|
What are the cutaneous adverse side effects of interferon therapy? |
Necrosis (2/2 vasculopathy) Psoriasis Alopecia |
|
|
Contraindications to interferon therapy? |
arrhythmias, SI/HI, pregnancy, leukopenia, SOT |
|
|
Interleukin therapy has what mechanism of action? |
increased TH1, antitumor activity, proliferation of T cells, enhance NK cells |
|
|
Dermatology applications of interleukin therapy? |
Melanoma
approved in 1998, 15-20% response rate |
|
|
Adverse effects of interleukins? |
Can require ICU care!!!
fever, chills, hypotension, thrombocytopenia, pulmonary edema, cardiac arrhythmias |
|
|
MOA of imiquimod? |
stimulated TLR-7 --> cytoplasmic portion interacts with MyD88, stimulated NK-KB signaling also --> produces IFNa, IL12, IL18 |
|
|
MOA of resiquimod? Application in CTCL? |
TLR-7/8 --> gel to lesions of CTCL in 8 week cycles x 2, saw improvement in both treated and untreated lesions |
|
|
What are the most common dermatologic applications of imiquimod? |
Imiquimod (Aldara)
Genital/perianal warts
Common warts
Molluscum
Keloids
BCC
AK
Bowens
Pagets
LM and cutaneous mets
CTCL |
|
|
Adverse effects of imiquimod? |
erythema at site of application, flu like symptoms, erosive pustular dermatosis (when used to treat scalp AK) |
|
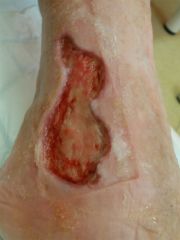
Which immunomodulators have a role in treating chronic wounds? |
GM-CSF/G-CSF (Filgrastim)
PDGF (Chemicon) |
|
|
Cutaneous side effects of G-CSF? |
SWEETS!!!! morbilliform eruption, injection site reaction, vasculitis |
|
|
Chemicon (PDGF) is FDA approved fo treatment of diabetic foot ulcers and ulcerated facial and diaper hemangiomas... MOA of PDGF? |
promotes granulation tissue, fibroblast migration, angiogenesis, reepithelialization |
|
|
MOA of topical calcineurin inhibitors? |
APC presents to the T cell receptor (FK-506-binding protein) --> increase in calcium --> activates calmodulin --> calcineurin inhibited --> NFAT remains phosphorylated --> no transcription of inflammatory cytokines (IL2, IL3, IL4, TNFa)
Prevents dephosphorylation of NFAT |
|
|
Clinically, IVIG protects against infection and decreases inflammation.. What are the dermatologic applications? |
Dermatomyositis Kawasaki disease SJS/TEN PV/BP EBA necrotizing fasciitis Pyoderma gangrenosum
AD |
|
|
Prior to administering IVIG, what labs do we need to check? |
Check for IgA deficiency --> decreased titre more likely to have an anaphylactic reaction |

