![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
33 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What 4 syndromes are associated with facial angiofibromas? |
Tuberous Sclerosis
Birt Hogg Dube
MEN1
NF2 |
|
|
Angiofibromas are histologically dermal proliferations of fibroblasts....
synonyms? |
Fibrous papule
Adenoma sebaceum (TS)
Pearly penile papules
Acrofibrokeratoma |
|
|
Angiofibromas may grow secondary to increase in what growth factor? |
Basic fibroblast growth factor |
|
|
Sclerotic fibromas can be indicative of what syndrome? |
Cowdens |
|
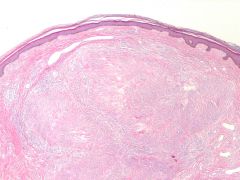
The mutation that causes the syndrome which can present with this lesion produces aberrant activity of:
A. helicase B. hydroxylase C. tyrosine kinase D. acyltransferase |
COWDENS
tyrosine kinase |
|
|
The fibromatosis are proliferations of myofibroblasts and are locally invasive. Names of:
Palmar: Plantar: Penile:
|
Palmar: Dupuytrens Plantar: Ledderhose Penile: Peyronies |
|

All of the following is associated with this except:
-AD inheritance -DM -alcoholic cirrhosis -RA -chronic epilepsy |
not associated with RA |
|
|
Myofibroblasts in dupuytren's contracture express what types of receptors? |
5 alpha DHT, blocked by finasteride
*DHT stimulates myofibroblasts |
|
|
Knuckle pads can be seen in what genodermatosis? |
Bart Pumphrey Syndrome |
|
|
What is Bart Pumphrey Syndrome? |
AD inherited mutation in GJB2 --> PPK + mixed hearing loss (sensorineural and conductive), total leukonychia, knuckle pads |
|
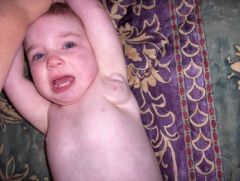
treatment? |
Fibrous hamartoma of infancy
painless, solitary, subQ, skin colored nodule to axilla/shoulder/UE
Presents birth to 2 years old, M>F
Tx: conservative excision |
|
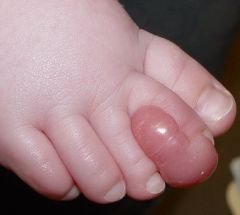
staining pattern? |
Infantile digital fibroma
PAT an infant on the head with your digit
PAT= PTAH (purple), actin, trichrome (red) |
|
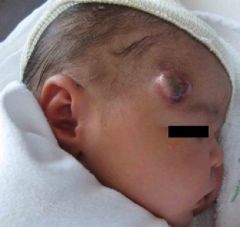
Subtypes of this lesion? |
Infantile Myofibromatosis
1. Solitary (50-80%)- MC in boys, H/N, spontaneous resolution in 1-2 years
2. Multicentric (33%)- skin and bone only, good prognosis, spontaneous resolution in 1-2 years
3. Congenital generalized fibromatosis (15%)- skin, bone, viscera, MC in females, very poor prognosis |
|
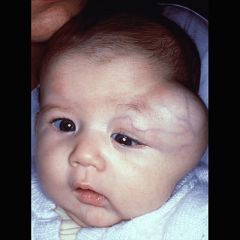
Fibrosarcoma is a malignant tumor of fibroblasts, can arise in old scars and XRT; what age groups are these seen in? Prognosis? |
Fibrosarcoma is a malignant mesenchymal tumor of fibroblasts, can be seen in infants to middle age
Tx: wide local excision, XRT, chemo, often mets to lung and bone (40% 5 year survival) |
|
|
Staining differences between DF and DFSP? |
DF: factor XIII +, CD34-
DFSP: factor XIII -, CD 34+ |
|
|
Multiple DFs are found in associated with all of the following except:
CML SLE HIV DFSP Prednisone use |
multiple DFs typically not seen in DFSP
multiple DFs can be seen in pregnancy, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, kidney disease, immunosuppression --> stimulated by basic fibroblastic growth factor |
|
|
DFSP is associated with what chromosomal translocation? |
t(17;22)- PDGFB and Col1A1 |
|
|
Prognosis of DFSP? |
recurs in 1/3
99% 5 year survival
infrequent mets to blood > lungs > LN
can progress to MFH |
|
|
What is the juvenile form of DFSP? |
Giant Cell FIbroblastoma |
|
|
What is the most common location for an atypical fibroxanthoma? |
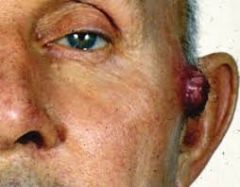
H+N/sun damaged skin of older adults |
|
|
What is the SLAM'dd differential? Stains for each entity? |
Spindle cell SCC- cytokeratin HMW Leiomyosarcoma- Desmin, actin AFX- CD10, procollagen, vimentin Melanoma- S100 DF- factor XIII, ST3 DFSP- CD34 |
|
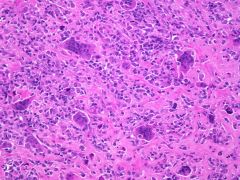
population usually affected? |
Giant Cell tumor of the tendon sheath (osteoclast like giant cells)- F>M, 30-50years old |
|
|
Prognosis of epithelioid sarcoma? |
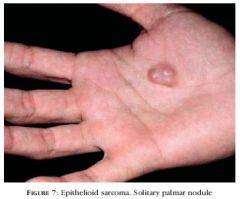
80% recur after excision, 30-45% metastasize to LN or lungs, 50% 5 year survival rate |
|
|
What factor is elevated in keloids? |
TGFB1 (produced by dermal fibroblasts) |
|
|
What is the mechanism of ILK for keloids? |
kenalog stimulates B-FGF and inhibits TGF-B1 |
|
|
What is the classic presentation of a malignant fibrous histiocytoma? |
MC soft tissue sarcoma of middle age adults --> MC in thigh or buttocks, especially of sites of chronic radiation and ulceration |
|
|
What is Buschke Ollendorf syndrome? |
loss of function mutation in LEMD3 gene with loss of antagonism to TGF-B and bone morph protein pathways --> hereditary disorder of connective tissue
AD inherited
Multiple skin color to yellow papules (dermatofibrosis lenticularis disseminata), osteopoikilosis |
|
|
Juvenile hyaline fibromatosis and infantile systemic hyalinosis:
What is the mutated protein? |
Capillary morphogenesis protein 2 (CMG2) |
|
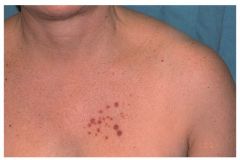
Diagnosis? Prognosis? |
Multinucleate cell angiohistiocytoma- discrete but grouped red/violet papules, MC on LEs and dorsal hands in females over 40 years old
Benign course |
|
|
Desmoid tumors are large, deep, well defined masses of muscular aponeurosis. In what patient population are these most common? |
Women, peri/post partum |
|
|
Most common site for a desmoid tumor? Most dangerous site? |
Remember, these are in peri/post partum women
MC location is in the abdominal wall
Most dangerous location is at the root of the neck and intra-abdominal |
|
|
What syndrome is associated with multiple desmoid tumors? Mutation? |
Gardners (APC gene mutation) |
|
|
What syndromes present with hereditary connective tissue nevi? |
Buschke Ollendorff (LMD)
Familial Cutaneous Collagenoma
Proteus Syndrome (AKT1)
Tuberous Sclerosis (TS1, 2)
Papular Elastorrhexis |

