![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Which genus of HPV is responsible for mucosal lesions? For epidermodysplasia verruciformis? |
Alpha: mucosal > cutaneous
Beta: EV |
|
|
Basic morphology of HPV? |
naked, dsDNA, papillomavirus |
|
|
Function of E6 as an oncogenic protein? |
E6 inactivates p53 (prevents apoptotic death and telomerase) |
|
|
Function of E7 as an oncogenic protein? |
E7 inactivates rb (by allowing uninhibited E2F) |
|
|
What are the early proteins of HPV and what is their function? What pathways do they target? |
Early proteins (E1-7)- viral replication, alter cell growth, contact inhibition
E1 forms heterodimer with E2, controls viral replication
E2 regulates early gene promoter and replication
E4 may be responsible for viral release from corneocytes
E5, E6, E7 are oncogenic
E6 inactivated p53, E7 inactivates rb
E7 allows uninhibited E2F transcription --> rb
Targets the INF pathway |
|
|
What are the late proteins of HPV and what is their function? |
Late proteins (L1, 2)- code capsid proteins
L1 is important for binding |
|
|
Target of gardasil vaccine? |
gardasil targets virus like proteins (VLP)- L1 |
|
|
Where is the most active HPV replication? |
superficial spinous layer |
|
|
Cervical cancer caused by HPV is usually... |
HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 45 |
|
|
Verruca vulgaris (common warts)
infection sites, HPV types |
hands, fingers, wrists, forearms, nail folds
1, 2, 4, 27, 57 (same as plantar warts) |
|
|
Periungual SCC has been linked to which HPV type? |
HPV 16 |
|
|
Plantar warts --> HPV types? |
1, 2, 4, 27, 57 (same as common warts) |
|
|
Myrmecia warts HPV type? |
HPV 1 |
|
|
Verrucous cyst HPV type? |
HPV 60
cysty- sixty |
|
|
Verruca plana (flat warts) are found where? HPV types? |
1-3mm, sharply demarcated, on face or dorsum of hands
HPV 3, 10, 28, 29 |
|
|
Butchers warts are caused by? Who gets em? |
HPV 7
verrucous papules on the dorsal, palmoplantar or periungual aspects of hands and fingers in meat and fish handlers |
|
|
Epidermodysplasia verruciformis is caused by which HPV? |
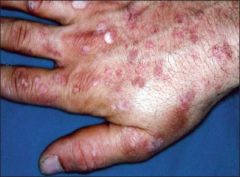
5, 8, 9
|
|
|
Inheritance of epidermodysplasia verruciformis? Genetic defect? |
Autosomal recessive
EVER1, EVER2 (transmembrane channel like (TMC) protein 6, 8) |
|
|
Which early genes are lacking in epidermodysplasia verruciformis? |
lacks E5
E6 and E7 have different function |
|
|
Cancer risk in epidermodysplacia verruciformis? |
SCCs found in 30-60% of patients aged 20-40 |
|
|
What is WHIM syndrome? |
warts, hypogammaglobulinemia, infections, myelokathexis (retention of mature neutrophils in bone marrow) |
|
|
Condyloma acuminata (genital warts) are caused by what HPV types? |
90% are types 6, 11
**remember that these lesions SPARE the scrot* |
|
|
Genital warts in children... work up? |
<1yo, most likely vertical transmission, autoinoculation, social non sexual contact, if >3 years old, work up for sexual abuse |
|
|
Bowenoid papulosis HPV types? |
16, 18
risk of progression to SCC |
|
|
Erythroplasia of Queyrat HPV types? |
16, 18 induced SCC |
|
|
HPV associated with giant condyloma of Buschke-Lowenstein? |
HPV 6 > 11 (unlike other HPV induced genital carconimas)
6 and elevenstein = lowenstein |
|
|
Epithelioma cuniculatum is an HPV associated verrucous carcinoma involving the: |
SOLE (HPV 11) |
|
|
What is an Ackerman tumor? Viral type? |
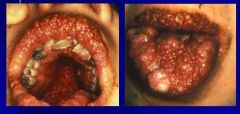
oral florid papillomatosis --> verrucous carcinoma in the mouth!!!
associated with smoking, irradiation, chronic inflammation
a/w HPV 6, 11
|
|
|
Which HPV is implicated in papillomatosis cutis carcinoides di Gottron? |
HPV 11 |
|
|
Hecks disease is associated with which HPV? |
HPV 13, 32 |
|
|
PICTURE OF HECKS DISEASE |
Hecks disease
'focal epithelial hyperplasia'
HPV 13, 32
small white to pink papules diffusely in oral cavity
Native Americans, Greenland, Turnkey |
|
|
Warty keratoses at the angle of the mouth, bilateral, are manifestations of which type of HPV in what subtype of patients? |
HPV 2
HIV patients |
|
|
Imiquimod has been proven beneficial in the treatment of all of the following lesions exceps:
a. erythroplasia of queyrat b. superficial BCC c. AK d. SCC e. extramammary paget's disease |
SCC |
|
|
What temperature do keratinocytes need to be frozen at to destroy them? Benign lesions? Malignant lesions? |
Keratinocytes: -25C Benign: -25C Malignant: -50C Melanocytes: -5C |
|
|
Which strains are covered by the HPV vaccine? |
6, 11, 16, 18 |
|
|
Cutaneous warts in renal transplant recipients show increased expression of which keratin? |
K13 |
|
|
What is the most common cause of focal epithelial hyperplasia? |
HPV |
|
|
Cutaneous warts in renal transplant recipients show increased expression of which keratin? |
K13 |
|
|
Which virus is the most common cause of focal epithelial hyperplasia (Heck's disease)? |
HPV |

