![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the shp output |
1679 AEO 1872 OEI |
|
|
How are the engines connected to the MGB? |
Directly via a torquetube and a crosshead device. The crosshead device absorps axial and radial loads |
|
|
How are the engines mounted |
Reverseflow so the inlet is aft, the output is direct to the MGB. Two mounts on the airframe Third mount on the MGB via torquetube and crosshead |
|
|
How is the EEC powered? |
Below 40% Ng ON side ESS Above 40% Ng Via the Permanent Magnet Alternator |
|
|
How is the Ng picked up? |
By an Ng sensor on the AGB using the starter generator gearshaft teeth as reference. Top left part |
|
|
What does the fuel heater do? |
Uses oil to heat fuel. Prevents ice build up and filter clogging. Low temp operations without additives |
|
|
Explain the DCU |
Stores engine data through interface with EEC Exceedances, cycled, running time, fault codes. Has trim data and eng ID on it. |
|
|
Explain the bleed valve and the pre swirl |
At low compressor speeds P2.8 opens bleedvalve and allows air from the compressor to be recirculated. It passes piccolo holes to improve the angle of attack. P3 air, when pressure gets higher is tapped and via outside routed to the bleedvalve to close it. The EEC can close it with a torquemotor |
|
|
What is the devision of air used for the engine? |
25 for combustion 60 for cooling 15 for pressurizing, cooling the hot section and provide cabin heating etc. |
|
|
Explain the amount and type of fuelnozzles |
7 simplex and 7 duplex. Duplex used for starting, and running Simplex used for running |
|
|
Explain the NF/TQ sensors |
A dual coil type to pick up the magnetic field. Bottom of bearing 5 LH is nr 1 / coil 1 to EEC / coil 2 to mau (cockpit) RH is nr 2 / coil 1 to backup mau (cockpit) / coil 2 to EEC LH has a temp compensation sensor. |
|
|
How is ITT derived? |
T5-T1 |
|
|
Describe the ignition system |
28 VDC exciter into two ignitors Onside ESS bus |
|
|
Describe the EEC |
Main purpose to maintain 100% Nr It has a control subsystem: adjusting fuelflow in the Fuel Management Module FMM A limiter subsystem. Independend hardware NF limiter. At 111% the overspeed valve closes to Idle fuel flow. At 109% it re opens. EEC is single channel and crosstalks to other EEC (load share) In case the EEC fails, manual control is obtained by the ECL and the beep trim sw on collective EEC has a PMA for independend power above 40% Ng |
|
|
What are the bearings? |
1,2,3,4,5 1,5 ball for axial and radial loads 2,3,4 rollers radial loads and thermal expansion |
|
|
Eplain the engine oil system |
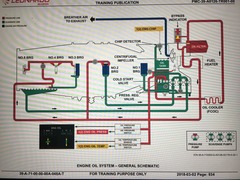
From tank to Pump (coldstart valve) Oil cooler FCOC Filter (with bypass) Fuel heater To the bearings Via sumps Three scavenge pumps Via chip detector on top of tank Back in the tank |
|
|
Where and when is the ENG OIL TEMP caution generated? |
Sensed after the filter, sent to MAU. Above 140gr |
|
|
How can the engine be started manually? |
Only after the first engine is started in Auto. |
|
|
How many times may the 2,5 min range be used? |
Cumulative 15 minutes. |
|
|
Exain the PI |
It is a translation to percentage TQ from the first limit to be reached by ITT, Ng or Tq. |
|
|
Explain the engine fuel system |
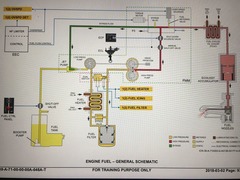
From the tank Jet pump Low press EDP Fuel heater Fuel filter (bypass) Dual switch (FUEL HEATER , FUEL ICING, FUEL FILTER) High pressure EDP Manual SOV (ECL driven) Shut down SOV (ECP selection) Metering valve (tq motor controlled by EEC) FCOC Ecology accumulator Nozzle Excess fuel from metering valve to jetpump. |
|
|
What does the FMM provide? |
Pressure build up in fuel, SOV in auto and manual Metering and overspeed solenoid |
|
|
Explain the ECL |
ECLs are a back up means of manual control. When EEC fail, or for emergency shut off. Normally the ECL is in FLT to ensure full engine control (travel) ECL pos caution appears when ECL is not in FLT. |
|
|
ENG GOV to manual can only be selected on .... collective |
Pilot |
|
|
How is a miscompare in engine data discovered? |
The MAU receives Ng Nf Tq and ITT direct from the engine (RAW) It compares this with the EEC data. |
|
|
What is the auto start sequence |
EEC controls fmm and commands engine relay box Commands GCU to start Activates ignition Present start legend on NG Terminates at 49% |
|
|
What should be done to obtain a higher power output regarding load share? |
ITT share |
|
|
How is the NR tripple coil pick up devided |
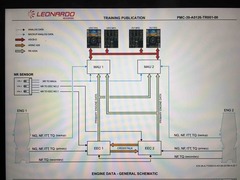
1 MAU 2 EEC 2 3 EEC 1 |
|
|
What means the CAS “EEC DATA” |
Data between EEC amd MAU is lost. Raw data is on MFD. |
|
|
What are rhe 2,5 min ranges of PI, TQ, ITT and Ng |
PI and TW: 140-160 ITT 775-835 Ng 102.4-106 |

