![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
Atom
|
The smallest particle of an element
|
Any element on the periodic table is an atom. Ex- Ca (calcium)
|
|
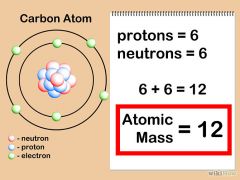
Atomic mass
|
The mass of an atom in atomic mass units; the average mass of the atoms of an element
|
The atomic mass of an element is the number of protons added to the number of neutrons.
|
|
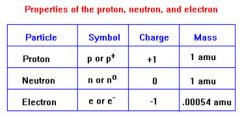
Atomic mass unit
|
One twelfth the mass of the C-12 atom
|
Atomic mass units are the way we measure elements mass. Carbon has 12 atomic mass units (amu).
|
|
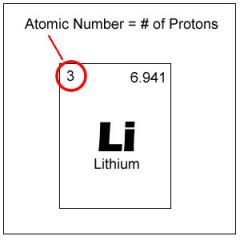
Atomic number
|
The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom
|
Carbon has an atomic number of 6. Therefore, it has 6 protons.
|
|
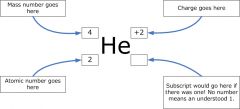
Atomic symbol
|
The mass number, atomic number , and charge is provided.
|
The mass number of carbon is 12 which is on the top and 6 which is the atomic number on the bottom with a C next to it.
|
|
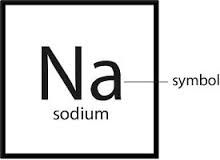
Chemical symbol
|
A notation using one to three letters to represent an element
|
The chemical symbol of carbon is C.
|
|
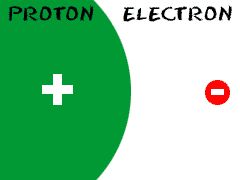
Electron
|
An elementary particle with unit negative charge
|
There is one negatively charged atom in a hydrogen element.
|
|

Group
|
The elements of a vertical column in the periodic table
|
Cobalt, nickel, and copper are all part of the transition metal group on the periodic table.
|
|
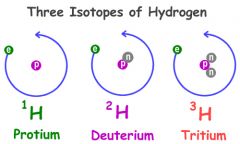
Isotope
|
One of two or more atoms having the same number of Protons but different numbers of neutrons
|
Carbon-12 is a molecule and carbon -14 the isotope has the same number of protons but different number if neutrons.
|
|

Mass number
|
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom
|
The mass number of helium is 4. Which means the protons added to the neutrons would equal 4.
|
|

Metal
|
An element that tends to lose electrons in chemical reactions
|
Aluminum is metal on the periodic table
|
|

Metalloid
|
An element that has properties characteristic of a metal and a nonmetal
|
Silicon and arsenic are both examples of metalloids on the periodic table.
|
|
Neutron
|
A neutral subatomic particle
|
Neutral, uncharged particle in the nucleus of an atom.
|
|
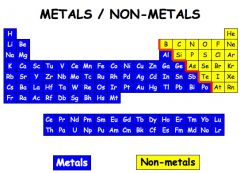
Non metal
|
An element that tends to gain electrons in chemical reactions
|
Carbon, nitrogen, and helium are elements on the periodic table that are non metals.
|
|
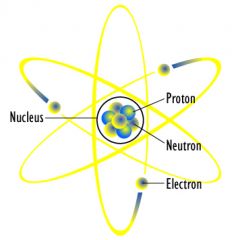
Nucleus
|
Positively charged central core of an atom, consisting of protons and neutrons
|
The nucleus is made up of protons and neutrons.
|
|
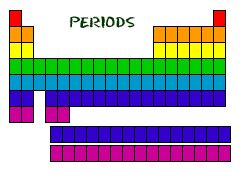
Periods
|
Horizontal row on the periodic table
|
There are seven periods on a periodic table.
|
|
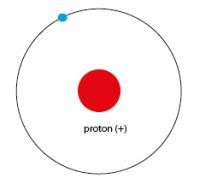
Proton
|
Positive nucleon
|
A proton is a positively charged particle that helps make up the nucleus.
|
|
Subatomic particle
|
A particle smaller than an atom
|
Subatomic particles are usually found when atoms are split.
|

