![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
138 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Petrarch,Poet(1304-1374) |
New conception of history: Clear division between two periods: Classical history (historiae antiquae) = light Recent history (historiae novae) = darkness |
|
|
|
Petrarch |
-return to the light of the past,return to the original sources (Greek andLatin texts), as oppose to medievalcommentaries. -Central role of politics andLanguage |
|
|
|
Humanism |
-Cultural and educational mission -Role of citizen central in society -Revival of cultural legacy of -Antiquity, esp. literature |
|
|
|
3 Phases of renaissance |
1. Brunelleschi, Alberti 2.Leonardo, Bramante 3. Micheal angelo, Palladio |
|
|
|
Filippo Brunelleschi Ospedale degli Innocenti (The Foundling Hospital) Location: Florence, Italy Date: Begun 1419 -Arcade -Loggia -Portico |

|
|
|
|
Filippo Brunelleschi -Column -Pilaster Pazzi Chapel, Church of Santa Croce,Florence, Italy Date: 1430 |

|
|
|
|
Filippo Bruneeschi Ospedale degli innocenti |

|
|
|
|
foundling Hospital- men's and women's |
|
|
|
|
Filippo Brunelleschi -Column -Pilaster Pazzi Chapel, Church of santa Croce, Date: 1430 |
|
|
|
|
Filippo Brunelleschi Pazzi Chapel, Church of santa Croce, Date: 1430 |

|

|
|
|
Filippo Brunelleschi San Lorenzo, Church and Old Sacristy, Florence, Italy Date: begun 1421 |
|
|
|
|
Palazzo Medici Riccardi Florence, Italy Date: Begun between 1445 and 1460 Architect: Michelozzo di Bartolomeo -Piano Nobile -Palazzo -Rusticato |
|
|
|
|
Palazzo Medici Riccardi Florence, Italy Date: Begun between 1445 and 1460 Architect: Michelozzo di Bartolomeo -Courtyard |
|
|
|
|
Beauty= “the harmony andconcords of all parts achieved insuch a manner that nothing could beadded or taken away except for theworst” |
Leon Battista Alberti -From 10 Books on architecture |
|
|
|
Ornament= “a kind of additional brightness and improvement on beauty. Beauty is something lively which is proper and innate and diffused throughout the whole, whilst ornament is something added and fastened on, rather then proper and innate.” |
Leon Battista Alberti -From 10 Books on architecture |
|
|
|
Who used Pilaster and arch? |
Alberti |
|
|
|
Who used Column and Arch? |
Brunelleschi |
|
|
|
Leon Battista Alberti Palazzo Rucellai Florence, Italy Date: 1456 |

|
|
|
|
Leon Battista Alberti Santa Maria Novella Facade, Florence, Italy Date: 1458-1466 |

|
|
|
|
Leon Battista Alberti San Fancesco Church, Rimini, c. 1450 |

|
|
|
|
Leon Battista Alberti San Sabastiano church, Mantua Begun in 1460
|

|
|
|
|
Leon Battista Alberti The Basilica di Sant'Andrea Location: Mantua, Italy Date: Begun 1472 |

|
|
|
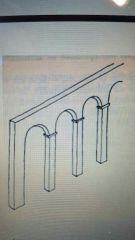
|
Pilaster and Arch |
|
|
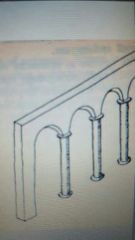
|
Column and Arch |
|
|
|
Who was the father of Humanism? |
Petrarch |
|
|
|
System of proportion |
Alberti |
|
|
|
Flat column on wall |
Pilaaters |
|
|
|
Covered porch with a succession of arches |
Arcade |
|
|
|
Loggia |
Covered exterior gallery or corridor |
|
|
|
Recent history |
Darkness |
|
|
|
Classical history |
Light |
|
|
|
5 basic principles |
1. Unit 2. Walls 3. Orders 4. Space 5. Light |
|
|
|
Unit |
Module - organized |
|
|
|
Walls |
Flat |
|
|
|
Orders |
Vitruvius, Greek orders of columns. To order space visually |
|
|
|
Space |
Clearing, arch opening |
|
|
|
Light |
Clear story windows |
|
|
|
Cornice |
Over hang of roof |
|
|
|
Bottom band |
Retail, offices, ground floor |
|
|
|
Middle band |
Piano Nobel Where the family lives. |
|
|
|
Top band |
Sleeping quarters |
|
|
|
Rusticato |
Rough system |
|
|
|
Enfilad |
Series of openings, space unfolds in sequences |
|
|
|
Political leader, safe keeper of culture |
Alberti |
|
|

|
One point perspective |
|
|
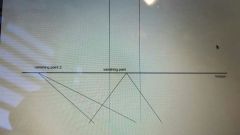
|
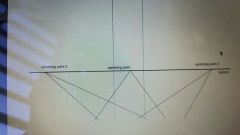
2 point perspective |
|
|
|
3 point perspective |
|
|
|
Lines in space to refer |
Dattum |
|
|
|
Shows one point perspective |
Grid |
|
|
|
Preparatory sketch |
Before you draw |
|
|

|
Masaccio "The Trinity" Painter: Masaccio |
|
|

|
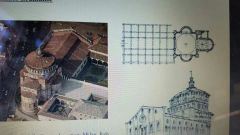
Basilica di Santa Maria del Fiore Filippo brunelleschi |
|
|
|
Birthplace of the Renaissance |
Florence |
|
|
|
Centralized church, cube, carved away, facade dome |
Bramante |
|
|
|
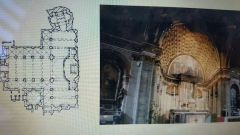
Tromp I'Oeil |
Trick of the eye Illusion of a barrel vault |
|
|
|
Donato Bramante Santa Maria delle Grazie Milan, Italy 1492-97 |
|
|

|
Donato Bramante Santa Maria delle Grazie Milan, Italy |
|
|

|
Santa Maria delle Grazie Milan, Italy |
|
|

|
Donato Bramante Santa Maria Presso S Satiro, Milan, Italy 1482-92 |
|
|
|
Trompe I'Oeil |
|
|
|
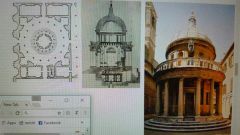
Donato Bramante Tempietto in S. Pietro in Montorio Rome, Italy 1506 |
|
|

|
Cola da Caprarola S. Maria delle Consolazione Todi, Italy 1508-1607 |
|
|

|
Cola da Caprarola S. Maria delle Consolazione Todi, Italy 1508-1607 |
|
|

|
Donato Bramante Cortile del Belvedere, Rome, Italy 1505-13 |
|
|

|
Donato Bramante Design for St.Peters |
|
|

|
St. Peter's Built by Michelangelo |
|
|
|
Who took Italy over, durring this time |
French |
|
|
|
Higher elevation to have an uninterrupted view of the garden |
Belvedere |
|
|
|
First landscaped urban space |
Cortile del Belvedere |
|
|
|
What was built for Pope Julius and has a retaining wall system? |
Cortile del Belvedere |
|
|
|
When did Bramante begin to redesign St. Peter's? |
1505 |
|
|
|
Modeled after an Italian church |
Château de Blois |
|
|
|
Large country house, palace, country estate |
Château / Villa |
|
|
|
What is the tallest tower called? |
Keep |
|
|
|
The garden of France/ last Renaissance Château |
The Louvre |
|
|
|
When did Paris become the capital of France? |
1526 |
|
|
|
Who attacked Milan? |
Louis XII |
|
|
|
-Rules start to be broken -Scale is oversized -Compositional dynamism -more reaction |
Late Renaissance |
|
|
|
-Verticality -stone work/ carving -Moves beyond the rules |
Michelangelo |
|
|

|
Château de Blois Hybrid style Loire Valley, France 13th century -17th |
|
|

|
Château de Chambord Philibert de I'Orme, Jean Bullant. Chenonceaux, France 1515 |
|
|

|
The Louvre Sequence of building over hundreds of years Pierre Lescot Paris, France 1546-1878 |
|
|

|
Place des Vosges Paris, France 1605-1612 (Residence of Henry IV) |
|
|

|
Filippo Brunelleschi San Lorenzo, Church and old sacristy Florence, Italy 1421 |
|
|
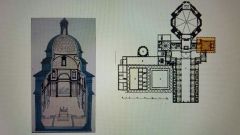
|
Michelangelo The New Sacristy of San Lorenzo 1520 |
|
|

|
Michelangelo Laurentian Library within the larger plan of San. Lorenzo Florence, Italy 1525 |
|
|

|
Michelangelo Dawn and Dusk |
|
|

|
Michelangelo Night and Day |
|
|

|
Michelangelo Palazzo Farnese Rome, Italy 1534 |
|
|

|
Michelangelo Piazza del Campidoglio Rome, Italy 1538-1650 |
|
|
|
What was Palladio? |
Traditionalist |
|
|
|
Who took Palladio under his belt? |
Giangiorgio |
|
|
|
Painter of Villa Barbaro |
Veronese |
|
|
|
Fundamentals of the orders |
Book I |
|
|
|
Domestic Design |
Book II |
|
|
|
Public and Urban Design and Engineering |
Book III |
|
|
|
Temples |
Book IV |
|
|

|
Andrea Palladio |
|
|

|
Giangiorgio Trissino |
|
|

|
Andrea Palladio Villa Trissino, Near Vicenza 1538 |
|
|

|
Andrea Palladio Villa Godi, Lonedo 1540 |
|
|
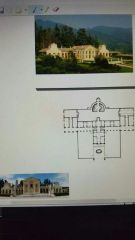
|
Andrea Palladio Villa Barbaro Maser, Italy 1560 |
|
|

|
Andrea Palladio Villa Foscari Malcontenta, Italy 1549-1563 |
|
|

|
Andrea Palladio Villa Rotunda Vicenza, Italy 1566-1571 |
|
|

|
Andrea Palladio S. Giorgio Maggiore Venice, Italy 1570 |
|
|

|
Andrea Palladio Redentore (the Redeemer) Venice, Italy 1570 |
|
|

|
Andrea Palladio Teatro Olimpico (Proscenium) Vicenza, Italy 1579-80 |
|
|
|
A row of columns supporting a roof |
Colonade |
|
|
|
Who wrote the 4 books of Architecture? |
Palladio |
|
|
|
Who wrote the 10 books of Architecture? |
Alberti |
|
|
|
Main stylistic features of the Baroque |
-Classical language extended -Inter relationships -Theatricality |
|
|

|
Giacomo della Porta Il Gesù Rome, Italy 1568 |
|
|

|
Giacomo della Porta Il Gesù Rome, Italy 1568 |
|
|
|
Who took part in St.Peters? |
-Bramante -Michelangelo -Bernini -Fontana -Maderno |
|
|

|
Gianlorenzo Bernini and Francesco Borromini Piazza Navona Rome, Italy 1644 |
|
|
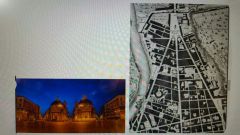
|
Gianlorenzo Bernini S. Maria dei Miracoli S. Maria Montesanto Rome, Italy 1662-79 |
|
|

|
Gianlorenzo Bernini Sant 'Andrea al Quirinale Rome, Italy 1658-70 |
|
|

|
Francesco Borromini San Carlo alle Quattro Fontane Rome, Italy 1638 |
|
|
|
Period of time NOT described by Circle and Square |
Baroque |
|
|
|
Inter-Relationship |
Inside and Outside |
|
|
|
Theatricality |
-Action, drama -dynamic walls/ facade |
|
|
|
What did the Catholic Church use architecture for? |
To fight Protestant Reformation |
|
|
|
Where is the center of the Baroque? |
Rome |
|
|
|
Sixtus V was important in? |
Infrastructure Drinking water |
|
|
|
Strados |
Large streets cut into rome -Breathing room, eased movement -Prevented disease |
|
|
|
Who built the Colonnade of St. Peter's? |
Bernini |
|
|
|
Who built the Nave and Facade of St. Peter's? |
Maderno |
|
|
|
Who placed the Obelisk in St. Peter's? |
Fontana |
|
|
|
Architects in the Early Renaissance |
-Brunelleschi -Alberti |
|
|
|
Architects in the High of Renaissance |
-Leonardo -Bramante |
|
|
|
Architects in the Late Renaissance |
-Michelangelo -Palladio |
|
|
|
Palazzo |
Inner Courtyard |
|
|
|
Piazza |
Surrounded courtyard |
|
|
|
Classical Orders |
-Doric -Ionic -Corinthian |
|
|
|
Michelangelo was a pre-curser to? |
Baroque Plasticity |
|
|
|
Lives of the Artists |
Vasari |
|
|

|
Ideal city paintings |
|
|
|
Who ordered for rebuilding St. Peters? |
Nicholas V |
|

