![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
a) How are ions formed?
b) Why do they attract each other? |
a) Electrons are transferred from metals to non-metals.
b) Through electrostatic attraction as they are oppositely charged. |
|
|
Define ionic bonding.
|
A chemical bond in which an electron or electrons are transferred from one atom to another, resulting in the formation of oppositely charged ions held together in a crystal lattice by electrostatic attraction.
|
|
|
What are the five properties of ionically bonded compounds?
|
>Solid at room temperature
>Have giant structures, therefore high melting and boiling temperatures >Do not conduct electricity unless molten or dissolved in water (free ions) >Brittle >Dissolve in water |
|
|
Define covalent bonding?
|
A shared pair of electrons, one electron being supplied by each atom either side of bond.
|
|
|
Define co-ordinate/dative covalent bonding?
|
A shared pair of electrons, both electrons being supplied by one atom in the bond, and the other atom having an empty orbital.
|
|
|
What are the three properties of covalently bonded molecules?
|
>Low melting and boiling temperatures due to bonds only being between atoms and no attraction between atoms
>Poor conductors - no charged particle >Dissolve in organic solvents |
|
|
How many electrons are shared in
a) a single covalent bond? b) a double covalent bond? |
a) 2
b) 4 |
|
|
What is meant by the term electronegativity?
|
The ability of an atom to attract the pair of electrons in a covalent bond towards itself.
|
|

|

|
|
|
What three things define an atoms electronegativity?
|
>Nuclear charge
>Distance between nucleus and outer shell electrons >Shielding of nuclear charge by electrons in inner shells |
|
|
What is the nature of bonding in a metal?
|
Lots of delocalised electron spread over a lattice of positive ions.
|
|
|
What are the properties of metals?
|
>Good conductors of electricity and heat
>Strong >Malleable >Ductile >High melting and boiling points |
|
|
What are the three types of intermolecular force?
|
>van der Waals forces - act between all atoms and molecules
>Dipole-dipole forces - act only between certain types of molecules >Hydrogen bonding - acts only between certain types of molecules |
|
|
How do dipole-dipole forces arise?
|
Dipole-dipole forces act between molecules with permanent dipoles.
|
|
|
How do van der Waals forces arise?
|
Caused by the changing position of the electron cloud.
|
|
|
How do dipole moments arise?
|
In certain molecules some of the atoms are more electronegative than others pulling the electrons towards themselves.
|
|
|
What is needed for hydrogen bonding to occur?
|
A hydrogen atom that is bonded to a very electronegative atom.
|
|
|
What elements are electronegative enough for hydrogen bonding to occur?
|
FON.
|
|
|
What energy changes occur when solids melt?
|
Energy is needed to weaken forces holding particles in solid state. No temperature change, heat is turned to kinetic energy.
|
|
|
What energy changes occur when liquids vaporise?
|
Energy is needed to break all the intermolecular forces between particles. No temperature change, thermal to kinetic.
|
|
|
How are the values of enthalpies of fusion and vaporisation explained?
|
The heat measured under constant pressure. The temperature depends on the average kinetic energy of particles so is related to their speed, the greater the energy the faster they go.
|
|
|
What are the physical properties of macromolecular solids?
|
>Covalent
>Strong bonds >High melting point |
|
|
What are the physical properties of molecular solids in terms of their detailed structures and bonding?
|
>Molecules held in regular arrays by one or more of the three types of intermolecular forces
>Covalent bonds within molecules hold atoms together but do not act between molecules >Low melting points >Weaker than covalent, ionic and metallic bonding |
|
|
What are the three types of strong bonding?
|
>Ionic - metal and non-metal
>Covalent - non-metal atoms only >Metallic - metal atoms only |
|
|
How is electrical conductivity related to bonding?
|
>Metallic - good conductor due to delocalised electrons
>Ionic - conducts only in liquid state or dissolved in water >Covalent - Does not generally conduct, (no charged particles) unless reacted to form ions. Ifffy, graphite!!! |
|
|
What is the shape of an atom with two pairs of electrons in outer shell?
|
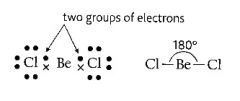
>Linear
>180 degrees (furthest away they can get) |
|
|
What is the shape of an atom with three pairs of electrons in outer shell?
|
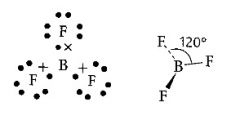
>120 degrees
>Flat >Trigonal planar |
|
|
What is the shape of an atom with four pairs of electrons in outer shell?
|
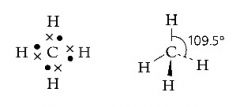
>Tetrahedral
>109.5 degrees >Three dimensional (sum of angle can be more than 360) |
|
|
What is the shape of an atom with five pairs of electrons in outer shell?
|
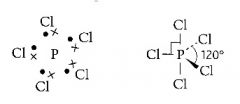
>Trigonal bipyramid
>120 degrees |
|
|
What is the shape of an atom with six pairs of electrons in outer shell?
|
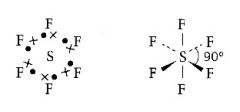
>Octahedral
>90 degrees |
|
|
What rules govern the shapes of simple molecules?
|
The number of pairs of electrons on the outer shell. Each pair will repel every other pair as far away as possible.
|
|
|
What is the shape of an atom with lone pairs of electrons in outer shell?
|

>Pyramidal
>107 degrees |
|
|
What is the shape of an atom with two lone pairs of electrons in outer shell of negative ion?
|

>Square planar
90 degrees |
|
|
What happens to the shape of a molecule when a bonding pair of electrons is replaced with a non-bonding pair?
|
It squeeze the angle between each of the bonded pairs closer by approx 2.5 degrees.
|
|
|
Define the term macromolecular.
|
Many atoms joined together in a regular array by a large number of covalent bonds.
|
|
|
Define the term polar bond.
|
A covalent bond where the shared pair of electrons is displaced to one end.
|
|
|
What groups of elements are ionically bonded?
|
1-2 and 6-7
|

