![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is the formula for photosynthesis?
|
Carbon Dioxide + Water --(Light Energy)--> Glucose + Oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O --(Light Energy)--> C6H12O6 + 6O2 |
|
|
How do we test for starch?
|
Iodine solution is a yellow brown liquid that turns blue-black when it reacts with starch. You can use this to prove photosynthesis has taken place in a plant.
Take a leaf from a plant and keep it in the dark for 24 hours and one from a plant kept in the light. The leaf must be prepared so the waterproof cuticle doesn't keep the iodine out. The green chlorophyll would mask colour changes so you must boil the leaf to destroy the cuticle and remove the colour. Rinse it in hot water to treat it. Add iodine solution to two leaves, the one kept in the dark stays orange-red but the one kept in the light turns blue-black. |
|
|
What are adaptations in a leaf which help with photosynthesis?
|
Most are broad, giving them a big surface area for light to fall in.
They have chlorophyll in the chloroplasts to absorb the light energy. They have air spaces that allow carbon dioxide to get to the cells and oxygen to leave them by diffusion. They have veins which bring water in the xylem to the cells of the leaves and remove the products of photosynthesis in the phloem. |
|
|
What are limiting factors in photosynthesis?
|
In low light, photosynthesis stops.
As the temperature rises the rate increases but after 40-50°C the enzymes denature and the rate falls. Plants need carbon dioxide to make glucose. Increasing carbon dioxide levels increase the rate. |
|
|
How do plants use glucose?
|
They need it for respiration, the energy released from it builds up smaller molecules into bigger ones.
Some is changed to starch for storage. They build up glucose into more complex carbohydrates like cellulose to strengthen their cell walls. They make amino acids by combining sugars with nitrate ions and other mineral ions. They build up fats and oils to use as an energy store. |
|
|
How are carnivorous plants adapted to live in nutrient-poor soil?
|
They obtain most of their nutrients from the animals such as insects that they catch.
They have special enzymes to digest the insects or animals. |
|
|
How are leaves adapted to only allow carbon dioxide in when it is needed?
|
They are covered with a waxy cuticle which is waterproof and gas-proof.
Stomata are opened when the plant needs to allow air into and out of the leaves. They can be closed by guard cells to limit the loss of water. |
|
|
What is transpiration?
|
The loss of water vapour through the stomata by evaporation and then diffusion. This causes more water to be pulled up through the xylem to take its place.
|
|
|
How does the environment affect the rate of transpiration?
|
If it's sunny more stomata open up and therefore more water is lost by evaporation and then diffusion. Warm, sunny conditions increase the rate.
Hot, dry, windy conditions increase the rate of evaporation and therefore the rate of transpiration. Water evaporates more if the temperature is higher and diffusion happens more quickly. Water vapour diffuses more rapidly into dry air. Windy conditions remove the water vapour straight away as it diffuses out. |
|
|
If a plant loses water faster than it is replaced, what will it do?
|
It will wilt. The leaves collapse and hang down to reduce the surface area available for water loss by evaporation.
The stomata close which stops photosynthesis but risks overheating. This prevents further water loss and wilting. |
|
|
What does the phloem do?
|
It moves dissolved sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plants, also known as translocation. The phloem is alive.
|
|
|
What does the xylem do?
|
It carries water and mineral ions around the plant to the stem and the leaves. Mature xylem cells are dead.
|
|
|
How do plant shoots grow up in the soil?
|
Plants are sensitive to gravity.
|
|
|
What does auxin do?
|
Auxin controls the responses of plants to light and gravity. The top of the shoot is a receptor and detects light. More auxin is put on the side of the shoot facing away from the light, causing the cells there to grow and making the shoot bend to the light. The root grows more where there is less auxin.
|
|
|
How does auxin help commercial horticulturists and farmers?
|
If you take a cutting and dip the end in auxin, roots form there allowing the cutting to grow as its own plant.
Auxin can also send plants into rapid, uncontrolled growth which kills them. This can be used on weeds. Many cereal crops and grass are narrow leaved so they are mostly unaffected. This is an example of a herbicide which kills one type of plant and not another. |
|

|
|
|
|
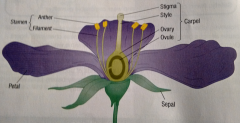
What do the petals do?
|
They attract insects to pollinate the plant.
|
|
|
What do the sepals do?
|
They protect the flower when it's in bud.
|
|
|
What do the stamens do?
|
They are the male parts of the flower. They are made up of the anther, which produces large quantities of small pollen grains containing the male gametes, and the filament, which attaches the anther to the flower.
|
|
|
What does the carpel do?
|
This is the female part of the flower. It is made up of the stigma where pollen grains land during pollination, the style which transports the male sex cell to the ovary, and the ovary, which produces a small number of relatively large ovules. The ovary also forms the fruit once the ovules are fertilised.
|
|
|
How are insect pollinated flowers adapted?
|
They have large, brightly coloured petals to attract insects. They are often scented and have a sugary nectar. The stigma is found inside the petals so insects brush against it on the way to nectar. They have relatively few pollen grains which stick onto the insects that visit.
|
|
|
How are wind pollinated flowers adapted?
|
The petals are small, usually brown or green. The stigma is large and feathery, hanging outside to collect pollen from the air. The anthers hang outside the petals so the pollen is blown away by the wind. There are many, small, light pollen grains that float easily in the wind.
|
|
|
Why are there two nuclei in the ovule of a plant?
|
One forms the embryo in the seed (egg nucleus) and the other forms the food store (endosperm nucleus) for the developing embryo.
|
|
|
How does the pollen grain reach the ovule?
|
It attaches to the top of the stigma. A pollen tube grows from the pollen grain and down the style. It grows into the ovary and into an ovule. The male nuclei then migrate into the ovule to form a zygote. The male and female nuclei fuse. The other male nucleus fuses with two more female nuclei to form the endosperm nucleus. As the seed forms the ovary grows into a fruit which surrounds and protects the seeds.
|

