![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
24 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a gene?
|
A small packet of information that controls a characteristic. It is a section of DNA.
|
|
|
What is an allele?
|
Different forms of the same gene.
|
|
|
Describe the process of mitosis.
|
A cell produces new identical copies of the chromosomes in the nucleus then the cell divides to form two genetically identical cells.
|
|
|
What are stem cells?
|
Unspecialised cells which can become any type of cell that is needed.
|
|
|
What are specialised cells?
|
Cells that do a particular job that have differentiated. Some cells cannot divide so stem cells replace the dead or damaged cells.
|
|
|
How is differentiation different in plants?
|
Plant cells don't differentiate until they are at their final position in the plant. They can also differentiate all through their lives. The differentiation is not permanent, they can redifferentiate to become a completely different type of cell.
|
|
|
Why is it difficult to clone animals?
|
Animal cells differentiate permanently.
|
|
|
Describe the process of meiosis.
|
Gametes are formed by meiosis. All chromosomes in a cell are copied once. The cell divides twice in quick succession to form four gametes, which have half the chromosome count as a normal cell.
|
|
|
What are the differences between sexual and asexual reproduction?
|
In asexual reproduction the offspring are genetically identical to the parents. There is no variation, unlike sexual reproduction, where each gamete is different and one gamete comes from each parent so the offspring is different from both parents, but has characteristics from both.
|
|
|
What are the problems with using stem cells?
|
Most come from aborted embryos. Others come from spare embryos in fertility treatment. Some people feel that this is wrong since the embryo cannot give permission and therefore it is violating its human rights. There is also concern that embryonic stem cells may cause cancer if they are used to treat sick people. Making stem cells is slow, difficult, expensive, and hard to control.
|
|
|
What are the disadvantages of adult stem cells?
|
They can only develop into a limited range of cell types.
|
|
|
What is the cell cycle of a healthy cell?
|
It divides via mitosis and doesn't divide for a long period (interphase) so the cell can get bigger, carry out normal activities, and replicate their DNA ready for the next division.
|
|
|
How do tumour cells form?
|
A mutation causes tumour cells. They divide rapidly with very little non dividing time for growth.
|
|
|
What are the differences between benign and malignant tumours.
|
Benign tumours grow in one place and don't invade other tissues.
Malignant tumours spread around the body, they are often referred to as cancer. The initial tumour may split up, releasing small clumps into the bloodstream or lymph system, where they lodge in another organ and continue to divide. |
|
|
What are some causes of cancer?
|
Mutations. Chemicals such as asbestos and the tar in tobacco smoke can cause these mutations. These chemicals are known as carcinogens.
Ionising radiation such as UV light and X-rays. Virus infections. |
|
|
What is a tissue?
|
A group of cells with similar structure and formation working together.
|
|
|
What does muscular tissue do?
|
Contracts and brings about movement.
|
|
|
What does glandular tissue do?
|
Contains secretory cells that produce and release substances like enzymes and hormones.
|
|
|
What does epithelial tissue do?
|
Covers the outside of your body as well as your internal organs.
|
|
|
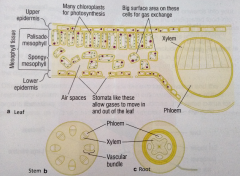
What does epidermal tissue do?
|
Cover the surfaces of plants and protects them.
|
|
|
What does palisade mesophyll do?
|
Contains lots of chloroplasts and carries out photosynthesis.
|
|
|
What does spongy mesophyll do?
|
Has big air spaces and a large surface area to make the diffusion of gases easier.
|
|
|
What are organs made from?
|
They are made up of several tissues which all work together to carry out functions in the organism.
|
|

|
|

