![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
15 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back

|
|
|
|
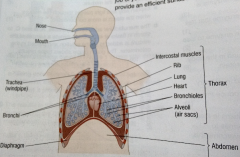
What happens to your lungs when you breathe in?
|
Your intercostal muscles contract, and this pulls your ribs upward and outward. At the same time, your diaphragm muscles contract, which flattens your diaphragm.
These two movements increase the volume of your thorax, dropping the pressure so it's lower than the air outside. This forces air into your lungs, pushed in by atmospheric pressure. |
|
|
What happens to the air you breathe in?
|
Oxygen rich air moves to your lungs, maintaining a steep concentration gradient with the lungs. Oxygen continually diffuses into your bloodstream through the alveoli. Breathing out removes carbon dioxide rich air from the lungs which maintains a concentration gradient so carbon dioxide can continually diffuse out of the bloodstream into the air in the lungs.
|
|
|
What adaptations do the alveoli have?
|
There are clusters of alveoli to provide a very large surface area.
They have a rich supply of capillaries to maintain a concentration gradient in both directions. |
|
|
What are negative pressure ventilators?
|
They cause air to be drawn into the lungs then exhaled passively as the chest collapses down.
The iron lung pumped air out of its chamber to form a vacuum, which caused the chest wall of the patient to move up. This made them breathe in due to the pressure. Then the vacuum switched off automatically, forcing air out of the lungs. |
|
|
What are positive pressure ventilators?
|
They force a breath of air into the lungs under a positive pressure. Then the air pressure stops, waiting for the lungs to deflate.
|
|
|
What are the advantages of positive pressure ventilators?
|
It can be given using a face mask or tube going into the trachea. Temporary ones can be used in emergency treatments.
Full scale machines can keep patients alive through major surgery. Patients do not have to be inside an iron lung, they can be at home and move about. They also have control over the machine. |
|
|
What is the formula for aerobic respiration?
|
Glucose + Oxygen --> Carbon Dioxide + Water (+ Energy)
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O (+ Energy) |
|
|
What adaptations do mitochondria have?
|
They have a folded inner membrane that provides a large surface area for the enzymes involved in aerobic respiration.
|
|
|
Why do we need to respire?
|
It releases energy from food so our cells can use it. Living cells need energy to carry out the basic functions of life, building large molecules from smaller ones and making new cell material (synthesis reactions).
Making muscles contract. All muscular activity uses energy. Maintaining a constant internal body temperature (in mammals and birds). In plants, energy moves mineral ions from the soil into root hair cells. It also converts nutrients into amino acids, which are built up into proteins. |
|
|
What happens to your body when you exercise?
|
Your heart rate increases and the arteries supplying food to your muscles dilate, increasing the blood flow to your exercising muscles and the rate CO2 is removed more quickly from the body.
You breathe faster and more deeply. This means you bring more air into your lungs each time you breathe in. This also means CO2 is removed more quickly. Glycogen stored in the muscles is converted back to glucose to supply the cells with the fuel they need for increased cellular respiration. |
|
|
What is the formula for anaerobic respiration in humans?
|
Glucose --> Lactic Acid (+ Energy)
C6H12O6 --> 2C3H6O3 (+ Energy) |
|
|
What causes muscle fatigue?
|
The build up of lactic acid. Eventually blood flowing through the muscles removes the lactic acid.
|
|
|
Why is less energy released during anaerobic respiration?
|
The breakdown of glucose is incomplete.
|
|
|
What is oxygen debt?
|
The amount of oxygen needed to break down the lactic acid to carbon dioxide and water.
|

