![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Otitis externa |
Swimmer's ear |
|
|
|
Constant involuntary eye movement |
Nystagmus |
|
|
|
Aminoglycoside antibiotics |
Very ototoxic |
|
|
|
Conductive hearing loss occurs at the |
Outter ear |
|
|
|
Type of diplopia woth worst prognosis |
Binocular |
Bi or monocular |
|
|
Progressive hearing loss due to age |
Presbycusis |
|
|
|
"Organ of hearing" |
Cochlea |
|
|
|
Most common cause of conjuctivitus |
Viruses |
|
|
|
Inflamation of eye lid |
Conjuctivitus |
|
|
|
Damage to cranial nerve VII (Vestibulocochlear) causes _______ hearing loss |
Sensorineural |
|
|
|
Condition of unequal pupils |
Anisocoria |
|
|
|
Substance or entity that poisons the ear |
Otoxic |
|
|
|
Gelatinous substance in athe back of the eye |
Vitreous humor |
|
|
|
Waxy substance in the external auditory canal that helps filter dust and bacteria from entering the ear |
Cerumen |
Saruman |
|
|
Pupil dilation |
Mydriasis |
|
|
|
Infection of eyelid caused by "ingrown eyelash" A stye |
Hordeolum |
|
|
|
Pupil constriction |
Miosis |
|
|
|
Mechanism of eye where pupils work together |
Consensual |
|
|
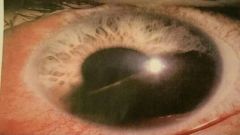
Hyphemaactive bleeding into anterior lense of the eye caused by trauma |
Hyphema |
|
|
|
Normal eyesight |
Emmetropia |
|
|
|
The measure of the intra occular pressure |
Tonometry |
|
|
|
The lens of the eyebends to increase or decrease curvature to focus near and far objects |
Accomodation |
|
|
|
The inability to focus near. The focal point of the eye is behind the retina. Farsighted |
Hyperopia |
|
|
|
Outer edge of the cornea |
Limbus |
|
|
|
Hard benign nodule that develops on eyelid, not painful or infectious |
Chalazion |
|
|
|
Upward drift of eyeball often due to weak muscles |
Hypertropia |
|
|
|
Ventilating tube for inner ear connecting to the parynx. Keeps pressure and drains excess fluid |
Eustacian tube |
|
|
|
Tympanic membrane |
"Eardrum" |
|
|
|
Tube that connects meatus to the tempanic membrane |
External auditory canal |
|
|
|
External pinna |
Part of the ear that is visible |
|
|
|
Normal near vision with distance vision impaired Nearsighted |
Myopia |
|
|
|
Visual defect with multiple focal points |
Astigmatism |
|
|
|
Hard fibrous covering of the eye, gives it shape |
Sclera |
|
|

Most common medical condition that blinds prople 50+. Cannot see centrally or in detail |
Macular degeneration |
|
|
|
Ringing, roaring, or rushing sound in ears |
Tinnitus |
|
|

A form of lazy eye that turns inward toward the nose |
Esophoria |
|
|
|
A group of conditions where there is an overproduction or inadequate outflow of aqueous humor increasing intraoccular pressure |
Glaucoma |
|
|
|
A clouding of the anterior lens of the eye |
Cataract |
|
|
|
Form of lazy eye where the eye turns outward toward the ear |
Exophoria |
|
|
|
A fatty growth over the lateral aspect of the eye |
Pterygium |
|
|
|
A sense of position of the body or body part and equilibrium |
Proprioception |
|
|
|
The area of the retina where most clear distinct vision occurs. Has the most concentration of cones |
Macular fovia |
|
|
|
The blind spot in the eye where blood vessels and the optic nerve enters the eyeball |
Optic disc |
|
|
|
Palpebral fissure |
The part of the eye that make up the corners of the eye opening |
|
|
|
Inner lining of posterior of the eyeball |
Retina |
|
|
|
Enzyme in tears that has antibacterial agents |
Lyozyme |
|
|
|
Rods |
Light receptor for night vision Black and white |
|
|
|
Color vision and daylight vision |
Cones |
|
|
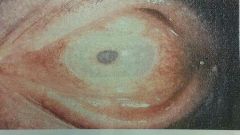
Puss in the anterior of the eye |
Hypopyon |
|
|

|
Retinal detachment |
|
|

|
Diabetic retinopathy |
|

