![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Thermodynamics
|
The study of the flow of heat and thermal energy
|
|
|
Total Energy
|

Total Energy = Internal + Kinetic + Potential
|
|
|
Temperature
|
Measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of a substance.
|
|
|
Heat
|
Internal energy exchanged by two bodies in contact.
|
|
|
Ideal Gas Law
|
PV=nRT
|
|
|
Average Kinetic Energy of a Gas
|
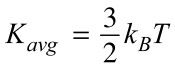
K=3/2(boltzman's constant)*Temperature (K)
|
|
|
Internal Energy of a System (U)
|
The sum of all kinetic energies of all the molecules of a system.
U=NK(ave) U=N*3/2*(Boltzman's constant)(Temperature) |
|
|
First Law of Thermodynamics
|
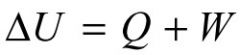
Change in energy = heat flow into system + work done on the system
|
|
|
Directions of Heat and Work
|
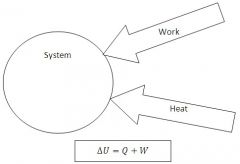
Heat flowing from the environment to the system is positive heat.
Work done by the surrondings on the system is positive work. |
|
|
Thermodynamic State
|
The state of a gas defined by its pressure, volume, and temperature.
|
|
|
Isothermal Process
|
A process in which the temperature (and therefore the internal energy of the system) remains constant.
|
|
|
Isobaric Process
|
A process in which the pressure is constant.
|
|
|
Isometric Process
|
Constant volume. Also known as isochoric process. Since there is not change in volume, no work is done on the gas.
|
|
|
Adiabatic Process
|
A process that happens with no change in heat with the outside surroundings. Since Q = is zero, then
delta-U=W |
|
|
Work done on a gas
|
W=-P*(delta)V
|
|
|
When a gas completes a cycle
|
There is no change in temperature or internal energy of the system.
|
|
|
Heat Engines
|
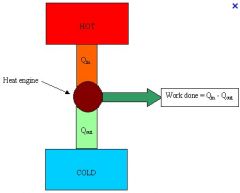
Convert heat into work. This process is never 100% efficient.
Heat flows from a region to Qh to a region of lower temperature Ql. The work is Qh-Ql. |
|
|
Efficiency of a heat engine.
|
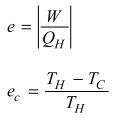
e=Work/Qh
or e= (Th-Tl)/Th |

