![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
antiseptics |
- a germicide applied to living tissue - are agents used externally on man and animals to kill or prevent multiplication of ineffective agents and therefore, they are bactericidal or bacteriostatics |
|
|
disinfectant
|
- a germicide applied to inanimate objects - Actually disinfectants are agents which are too toxic to apply to the body but useful in destroying pathogens
|
|
|
Classification |
- Detergents |
|
|
Detergents |
Detergents are emulsifying and cleansing surface acting agents (surfactants) used to remove dirt and contaminated organisms by solubilization and physical means. There are 2 main detergents: |
|
|
Oxidizing agents |
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) - Antiseptic and deodorant action |
|
|
Potassium permanganate (PPM) |
- Antiseptic and deodorant action Mode of action is destruction of toxic substances by oxidation. Solution of 1:1000 (0.1%) used as wound and mouth lotions Antidote (1:5000) for animals swallowed morphine, strychnine and aconite. Antidotal effect against snakebite |
|
|
Halogens (chlorine and Iodine)
|
Iodine: Weak solution of iodine- common tincture iodine contains 2.5% iodine in an alcoholic solution of an equal amount of potassium iodine. Tincture iodine- skin sterilization prior to surgery |
|
|
Iodine |
Aqueous solution of iodine (Lugol’s iodine solution) mainly for intra-uterine vaginal irrigation(0.2%) |
|
|
Iodophors |
Iodine with non-ionic surface acting agents for surface antisepsis and disinfection. Antibacterial, antiviral and antifungal activity and recommended for FMD, foot-rot and ringworm in cattle and also treatment of wounds and for preoperative skin preparations. |
|
|
chlorine disinfectants |
Hypochlorites are the most widely used. The most common chlorine products in are aqueous solutions of 4 to 6% sodium hypochlorite, which are readily available as “household bleach”. |
|
|
Reducing agents |
Sulphur dioxide Formaldehyde solution |
|
|
Metallic compounds |
mercury, silver and copper -antiseptic and disinfectants |
|
|
Silver nitrate |
Solution, 0.5%
|
|
|
Copper sulphate |
Copper sulfate is used as a fungicide not only in agriculture, but also as an antiseptic and germicide against fungal infections in humans. Helps in preventing athlete's foot in tropical countries. |
|
|
Acids and alkalies |
Boric acid: weak acid-used as antiseptic for irrigating the conjunctival sac. limited antibacterial activity. |
|
|
Alcohol |
Ethyl alcohol (70%) Less volatile than ethyl alcohol |
|
|
Phenol and cresol |
Carbolic acid: is caustic, antiseptic, disinfectant and parasiticidal. Qualitrol is a triple phenolic disinfectant
|
|
|
Phenol |
commonly found in mouthwashes, scrub soaps and surface disinfectants, in household disinfectants (e.g. Lysol, Pine Sol). -effective against bacteria and enveloped viruses. They are not effective against nonenveloped viruses and spores. |
|
|
Dye compounds |
Azo-dyes: used for stimulating epithelial growth in clean, dry but static, wounds and ulceration |
|
|
Teat antisepsis |
Chlorhexidine/glycerine (0.35%) A 0.5% iodophore-containing gel – reduce mastitis |
|
|
weight/volume scale |
1g/100ml = 1%
1g/1000ml = 0.1%
1g/5000ml = 0.5% |
|
|
Emulsify |
To emulsify means to bind two things together that don't naturally bind, like oil and vinegar |
|
|
Convert |
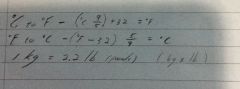
|

