![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
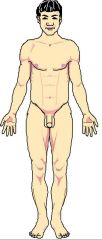
Name the appropriate directional terms. |
Anterior (towards the front, or head) , or Ventral (belly side). |
Front |
|
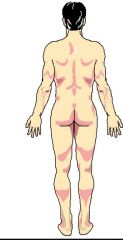
Name the appropriate correctional terms. |
Posterior (towards the back side, tail), or Dorsal (back side). |
Back. |
|
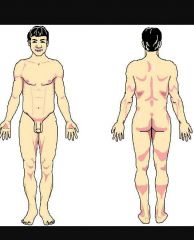
What is this? |
Standard Anatomical Position *The body is erect with feet slightly apart. Palms are facing forward with thumbs away from the body. |
"Standing at attention" |
|
|
Anatomy |
The structure of body parts and their relationship to one another. |
|
|
|
Physiology |
How body parts work and carry out life-sustaining activities. |
|
|
|
Gross/Macroscopic Anatomy |
The study of large body parts visible to the naked eye. |
Heart, lungs, kidneys. |
|
|
Regional Anatomy |
All of the structures in a specific region being examined at the same time. |
|
|
|
Surface Anatomy |
The study of internal strictures as they relate to the skin surface. |
Bulging muscles on a body builder. |
|
|
Microscopic Anatomy |
Structures too small to be seen by the naked eye. |
|
|
|
Cytology |
Study of cells. |
|
|
|
Histology |
Study of tissues. |
|
|
|
Development Anatomy |
Structural changes throughout the life span. |
|
|
|
Embryology |
The delevlopment changes that occur before birth. |
|
|
|
Survival Needs |
Nutrients (food), oxygen, water, appropriate temperature, appropriate atmospheric pressure. |
|
|
|
Integumemtary System |
Skin *Forms external body covering *Protects deeper tissues from injurys. *Synthesizes vitamin D. *Houses cutaneous receptors, sweat, and oil glands. |
|
|
|
Skeletal System |
Bones and joints *Protects *Supports *Provides framework for movement **Blood cells are made in bones **Bones store minerals |
|
|
|
Muscular system |
Smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, skeleteal muscle. *Allows motion *Maintains posture *Produces heat |
|
|
|
Nervous System |
Brain, spinal cord and nerves. *Control system of the body *Responds to changes in the body by activating specific things. |
|
|
|
Endocrine System |
Pineal gland, pituitary gland, thyroid gland, thymus, adrenal gland, pancreas, ovary, testis. *Secrete hormones that regulate growth, reproduction, and nutrient use by body cells. |
|
|
|
Cardiovascular System |
Heart, arteries, and blood vessels. *Blood vessels transport blood carrying oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and wastes. *Heart pumps the blood |
|
|
|
Lymphatic System/Immunity |
Red bone marrow, thymus, lymphatic vessels, thoracic duct, spleen, and lymph nodes. *Houses white blood cells *Attacks foreign substances in the body |
|
|
|
Respiratory System |
Nasal cavity, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchus, lungs. *Keeps blood supplied with oxygen *Removes carbon dioxide |
|
|
|
Digestive System |
Oral cavity, esophagus, liver, stomach, intestines, rectum, and anus. *Breaks down food for nutrients *Removes wastes |
|
|
|
Urinary System |
Kidney, ureter, urinary bladder, and urethra. *Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body *Regulates water, electrolyte and acid-base balance of blood. |
|
|
|
Male Reproductive System |
Prostate, penis, testis, scrotum, and ductus deferens. *Aid in delivery of sperm for reproduction |
|
|
|
Female Reproductive System |
Mammary glands, ovary, uterine tube, uterus, and vagina. *Produce eggs for reproduction *Mammary glands produce milk for newborns |
|
|
|
Homeostasis |
Maintaining stable conditions internally despite external conditions. |
Thermostat |
|
|
Negative Feedback Mechanism |
*Most homeostatitc control mechanisms are this. The output shuts off the original effect of stimulus or reduces it's intensity. They cause the variable to change in a direction opposite of the initial change returning to it's ideal value. |
It gets colder than the set temperature in the house, so the thermostat turns the heat on until it's back to normal then it turns off. |

