![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
8 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
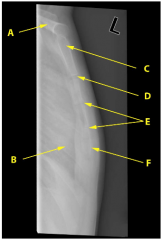
On the lateral chest radiograph, identify the labelled structures A-F of the chest wall and upper limb.
|
A) Clavicle.
E) Fracture of the sternum body. C) Manubrium. F) Sternal body. B) Rib. D) Sternomanubrial angle. |
|
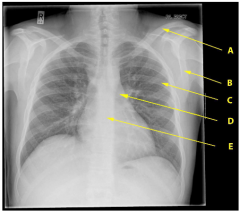
On the A-P chest radiograph, identify the labelled features A-E of the thorax and upper limb.
|
C) Rib.
B) Scapula. D) Rib cartilage. E) Thoracic vertebra. A) Clavicle. |
|
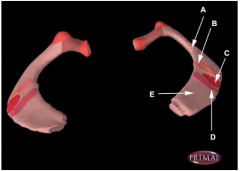
Which one of the following regions A-E of a first rib marks the tubercle produced by the insertion of scalene muscles?
Select one: A) E) B) D) C) |
C) Scalene tubercle.
|
|
|
Which one of the following statements applies best to the ribs and/or intercostal muscles?
Select one: A) The first rib articulates with the transverse process of C7. B) The fibres of the internal intercostal muscles run antero-inferiorly from the rib above to that below. C) The first rib is crossed on its superior surface by the subclavian vein. D) The intercostal vein, artery and nerve lie between the external and internal intercostal muscles. E) The intercostal muscles are innervated by the internal thoracic nerves. |
C) The first rib is crossed on its superior surface by the subclavian vein.
|
|
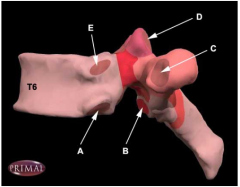
Which one of the following thoracic vertebral structures A-E articulates with the rib tubercle (left lateral view on T6 shown)?
|
C. Costotubercular facet, articulates with rib facet on rib tubercle.
D is the superior articular facet for synovial joint between two neighbouring vertebrae (in this case articulating with the inferior articular facet of T5). |
|
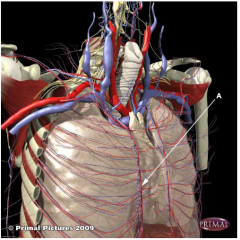
Which one of the following are blood vessels supplying the thorax wall and arising from blood vessel "A" (right antero-lateral view of thorax and thorax wall)?
Select one: A) Thoracodorsal arteries. B) Posterior intercostal arteries. C) Internal thoracic arteries. D) Lateral cutaneous arteries. E) Anterior intercostal arteries. |
E) Anterior intercostal arteries.
|
|
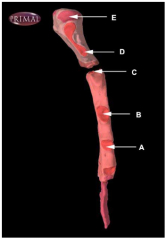
Identify the sternal facet at which the cartilage of rib 3 articulates with the sternum (sternum shown in right lateral view).
|
B.
C is articular facet for rib 2. |
|
|
Which one of the following statements applies best to the fourth intercostal nerve?
Select one: A) It runs above its corresponding artery and vein in an intercostal space. B) It carries sensory nerve fibres from an area of skin on the upper anterior abdominal wall. C) It conveys parasympathetic axons to the mammary glands. D) It contains fibres which are secreto-motor to sweat glands. E) It carries parasympathetic fibres. |
D
|

