![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
6 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
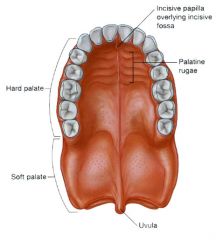
Palate (distinguish maxillary from palatine contributions)
What muscle uses the hamulus as a pulley?
What attaches to the pharyngeal tubercle? |
The tensor veli palatini uses the pterygoid hamulus of the sphenoid bone as a pulley.
The superior pharyngeal constrictor attaches to the pharyngeal tubercle. |
|
|
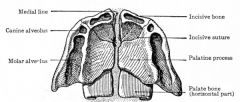
Several areas of the head have common bony walls. Fill in the blanks below:
The floor of the orbit is also the roof of the _________.
The floor of the nasal cavity is also the roof of the _________.
The roof of the nasal cavity is the _________.
The roof of the sphenoid sinus is also the floor of the _________. |
The floor of the orbit is also the roof of the maxillary sinus.
The floor of the sphenoid sinus is also the roof of the nasopharynx.
|
|
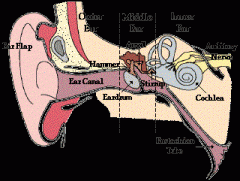
Ear Model:
-Internal acoustic meatus -External acoustic meatus cells (aditus) -Internal ear – cochlea, semicircular canals -Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) -Groove for sigmoid sinus |
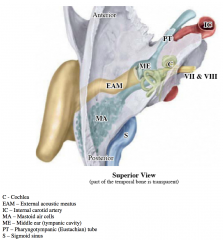
-Internal acoustic meatus -External acoustic meatus cells (aditus) -Internal ear – cochlea, semicircular canals -Vestibulocochlear nerve (VIII) -Groove for sigmoid sinus |
|
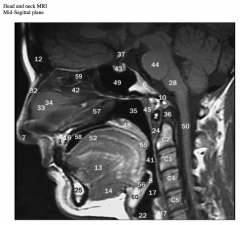
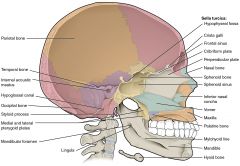
Identify the nasal septum and tongue. Which bones do #42 and 57 indicate?
What muscles are #13 and 14?
Identify the clivus and pituitary gland (hypophysis).
What air sinus (#49) is inferior to the pituitary (hypophyseal) fossa?
What part of what bone is this air sinus within?
What air sinuses (#59) are anterior to the air sinus indicated by #49?
What region is lateral to air sinus #59 and what space is medial to it?
Identify the hard and soft palate, the epiglottis and hyoid bone.
Why is the inferior part of the laryngopharynx not seen as a space? |
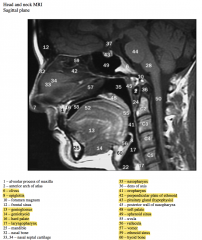
There are two sphenoid sinuses (right and left) that are within the body of the sphenoid bone.
On occasion they may extend into the wings of the sphenoid bone.
The orbits are lateral to the ethmoid sinuses while the nasal cavity is medial to them.
|
|
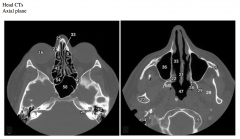
The images above are from two different levels. Which is more superior? What clues did you use to determine this?
Which air spaces are present in the two images (#5, 34, 36, 43, 47, 54, 58)?
What air filled space (#42) is anterior to #34?
What foramen does #26 indicate and what is contained within it?
What bones do #21, 25 and 27 indicate? |
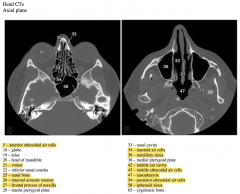
The image on the left is through the orbits and mastoid processes and is superior to the image on the right that is through the maxillary sinuses and atlas.
Ethmoid air cells are also apparent in the image on the left.
The mastoid air cells are within the mastoid process of the temporal bone.
|
|
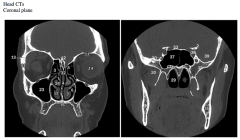
The images above are from two different coronal planes. Which is more anterior? What clues did you use to determine this?
#17 and 24 and nasal conchae. Which two are they?
Why isn’t the third one seen?
Which air spaces are present in the two images (#1, 3, 6, 23, 29, 37)?
What suture does #13 indicate?
|
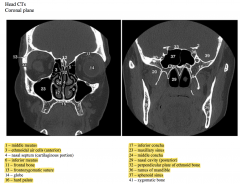
The image on the left is through the orbits, maxillary sinuses and conchae, and is anterior to the image on the right that is through the sphenoid air sinuses, choanae and ramus of the mandible.
The superior nasal concha is not seen in the image on the left because it is too anterior. This concha is superior to the posterior portion of the middle concha.
The superior nasal concha is also anterior to the sphenoid sinus, which is why it is not seen in the more posterior image on the right.
The continuity between spaces #1 and #23 is the foramen through which the maxillary sinus drains (called the maxillary ostium).
Note that the maxillary sinus drains into the middle meatus. |

