![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
134 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomical position |
Body erect with arms at side, palms forward |
|
|
Supine |
Lying down, face up, palms up |
|
|
Prone |
Lying down, face down, palms down |
|
|
Cephalic |
Head |
|
|
Cervical |
Neck |
|
|
Axillary |
Armpit |
|
|
Brachial |
Arms |
|
|
Thoracic |
Chest |
|
|
Abdominal |
Abs |
|
|
Dorsal |
Back |
|
|
Lumbar |
Lower back |
|
|
Pelvic |
Pelvic region |
|
|
Three sectional planes |
Transverse, frontal, sagittal |
|
|
Frontal or coronal sectional plane |
Divides into anterior and posterior portions |
|
|
Transverse or cross sectional plane |
Divides into superior and inferior portions |
|
|
Sagittal sectional plane |
Divides into right and left portions |
|
|
Anterior, ventral |
Front |
|
|
Posterior, dorsal |
Back |
|
|
Inferior |
Down, below |
|
|
Superior |
Up, above |
|
|
Medial |
Towards midline |
|
|
Cranial, cephalic |
Towards head |
|
|
Lateral |
Away midline |
|
|
Caudal |
Towards tail |
|
|
Proximal |
Close to attachment |
|
|
Distal |
Far from attachment |
|
|
Four tissue types |
Epithelial, connective, muscle, neural |
|
|
Superficial |
Close to surface |
|
|
Deep |
Away from surface |
|
|
Epithelial tissue |
Protective layer -lines most of body -glands form -apical and basal surfaces |
|
|
Apical |
Exposed surface of cells |
|
|
Basal |
Attachment point of cells |
|
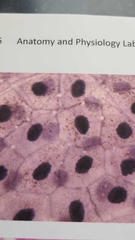
What is this? |
Simple squamous epithelium -layer of flat cells |
|
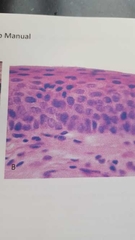
What is this? |
Stratified squamous epithelium -multiple layers of flat cells |
|
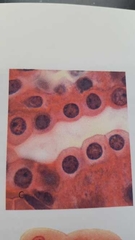
What is this? |
Simple cuboidal epithelium -layer of cube cells |
|
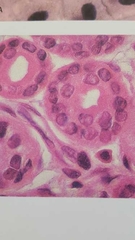
What is this? |
Stratified cuboidal epithelium -multiple layers of cube cells |
|

What is this? |
Transitional (stretched) epithelium |
|
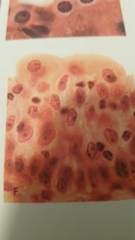
What is this? |
Transitional (relaxed) epithelium |
|
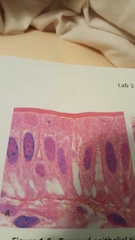
What is this? |
Simple columnar epithelium -hairs on top |
|

What is this? |
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium |
|
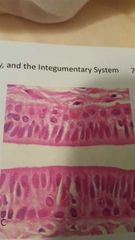
What is this? |
Stratified columnar epithelium |
|
|
Where are cilia located |
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium |
|
|
Endocrine glands |
Releases products into interstitial fluid |
|
|
Exocrine glands |
Releases products through ducts directly onto epithelial surfaces |
|
|
Three features of connective tissue |
Specialized cells Extracellular protein fibers Ground substance |
|
|
Matrix |
Protein fibers + ground substamce |
|
|
Types of connective tissue |
Areolar, adipose, reticular, dense regular, dense irregular |
|
What is this? |
Areolar connective tissue Papillary layer of dermis, open space, loose fibers |
|
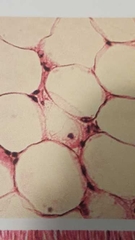
What is this? |
Adipose connective tissue Fatty tissue |
|

What is this? |
Reticular connective tissue Reticular fibers, messy - spleen, liver, bone marrow |
|

What is this? |
Dense irregular connective tissue -Collagen fibers, irregular |
|

What is this? |
Dense regular connective tissue More aligned, regular Can be seen as tendon, ligament |
|
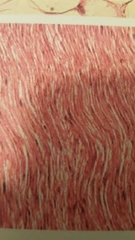
What is this? |
Elastic connective tissue Type of dense regular tissue Straightest, elastic bundles |
|
|
Fluid connective tissue |
Blood and lymph |
|
|
Blood |
Common to all parts of body |
|
|
Lymph |
Fluid collected from extracellular space and circulated in body by lymph system |
|
|
Plasma |
Water, proteins, etc. |
|
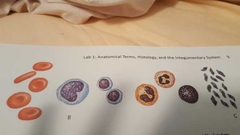
What makes blood? |
Erythrocytes, leukocytes, platelets |
|
|
Cartilage |
An avascular substance -receives nutrients form blood supply |
|
|
Chondrocytes |
Specialized cells in cartilage |
|
|
Bone |
Osseous tissue Calcuim salts and collagen fibers Bone can be hard and flexible |
|
|
Supporting connective tissue |
Bone and cartilage |
|
|
Three types of cartilage |
Hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage |
|
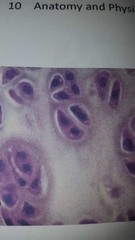
What is this? |
Hyaline cartilage Contains chondrocytes, elastic fibers in lacuna |
|

What is this? |
Elastic cartilage Elastic fibers, chondrocytes in lacuna |
|
|
Osteocytes |
Specialized cell in bone |
|
|
Osteoblasts |
Produce fibers and matrix of bone |
|
|
Canaliculi |
Channels between osteocytes |
|
|
Periosteum |
Outermost layer of bone |
|
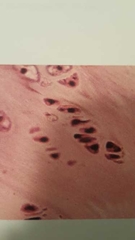
What is this? |
Fibrocartilage, fibrous cartilage Collagen fibers, chondrocytes in lacuna |
|
|
Osteoclats |
Dissolves fibers and matrix of bone |
|

What is this? |
Bone tissue |
|
|
Compact bone |
Hard, outer bone |
|
|
Muscle tissue |
Produces movement in body Contraction can be voluntary or involuntary |
|
|
Three types of muscle tissue |
Skeletal, cardiac, smooth muscle tissue |
|
|
Spongy bone |
Porous, inner bone |
|

What is this? |
Skeletal muscle tissue Controlled movement, strided Voluntary |
|

What is this? |
Cardiac muscle tissue Involuntary movement, strided |
|

What is this? |
Smooth muscle tissue Nonstrided, involuntary movement |
|
|
Neural tissue |
Wires body for communication of messages by stimuli |
|
|
Two types of neural tissue |
Neurons Glial cells (neuroglia) |
|
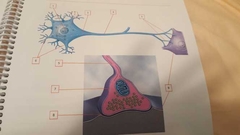
What is 1? |
Nucleus |
|
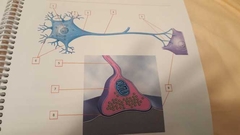
What is 2 |
Perikaryon Fluid matrix in cell body (cytoplasm) |
|
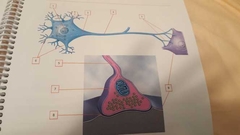
What is 3 |
Axon hillock Connects cell body and axon |
|
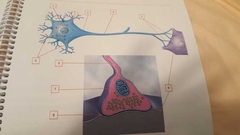
What is 4 |
Axon |
|
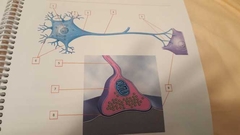
What is 5 |
Telodendria (terminal branches) |
|
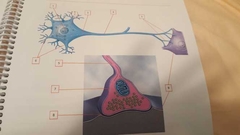
What is 6 |
Dendrites |
|
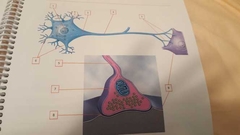
What is 7 |
Synaptic knob Bell-shaped end |
|
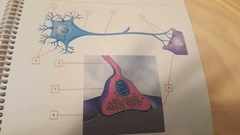
What is 8 |
Synaptic cleft Space between synaptic terminal and postsynaptic cell |
|
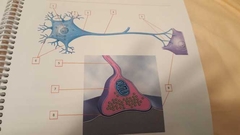
What is 9 |
Postsynaptic cell Cell after synaptic terminal |
|
|
Glial cells |
Support cells |
|
|
Oligodendrocyte |
Glial cells in CNS |
|
|
Schwann cells |
Glial cells of PNS |
|
|
Internode (region) |
Myelinated portion of axon |
|
|
Nodes of Ranvier (region) |
Unmyelinated portion of axon |
|
|
Myelin sheath (structure) |
Layer that surrounds an axon |
|
|
Integumentary system |
Compsed of cutaneous membrane (skin) and accessory structures |
|
|
What is cutaneous membrane made of |
Epidermis and dermis |
|
|
Epidermis |
Stratified squamous epithelium Avascular Contains keratinocytes (four layers) |
|
|
What are the two layers of dermis |
Papillary layer and reticular layer |
|
|
Papillary layer |
Formed by dermal papillae Aerolar connective tissue |
|
|
Reticular layer |
Deep irregular connective tissue Contains most accessory structures |
|
|
Which layers are not part of the epidermis |
Basal lamina and dermal papillae |
|

What is first and second layer |
Stratum corneum |
|

What is third layer |
Stratum lucidum |
|

What is fourth layer |
Stratum granulosum |
|

What is fifth layer |
Stratum spinosum |
|

What is sixth layer |
Stratum basale or germinativum |
|

What is the seventh layer |
Basal lamina Not part of epidermis |
|

What is eighth layer |
Dermal papillae Not part of epidermis |
|
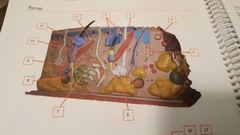
What is 1 |
Papillary plexus Bundles of veins and arteries |
|
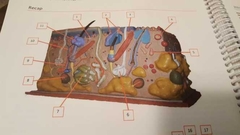
What is 2 |
Papillary layer |
|
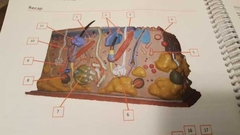
What is 3 |
Arrector pili muscle Controls contraction of hair |
|
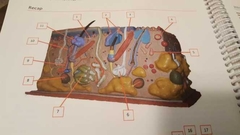
What is 4 |
Tactile, Meissner corpuscules Detect touch |
|
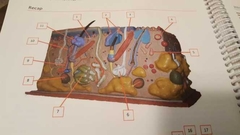
What is 5 |
Ruffini corpuscule |
|
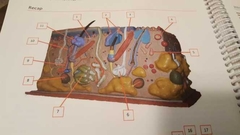
What is 6 |
Meocrine sweat gland Makes sweat |
|
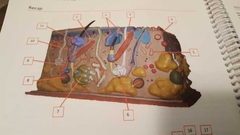
What is 7 |
Apocrine sweat gland Stink sweat |
|
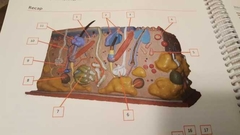
What is 8 |
Lamellated corpuscule |
|
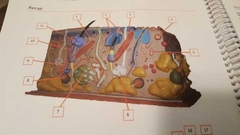
What is 9 |
Artery |
|
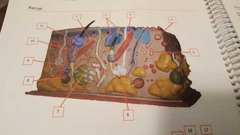
What is 10 |
Vein |
|
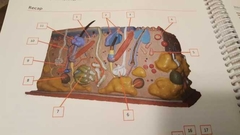
What is 11 |
Sebaceous gland Oils for hair |
|

What is the brown? |
Internal root sheath |
|

What is the yellow |
External rooth sheath |
|

What is the blue |
Glassy membrane |
|

What is the purple |
Connective tissue sheath |
|
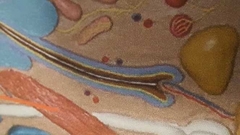
What is blue and red |
Root hair plexus At base of hair |
|
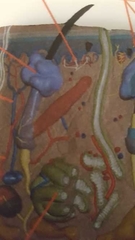
What is area above purple (region) |
Hair shaft Above sebaceous gland |
|
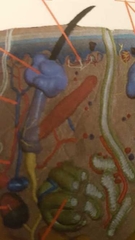
What is area below purple (region) |
Hair root Below sebaceous gland |
|
|
Hair follicle |
Produces hair |
|
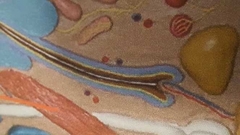
What is blue bell shape |
Hair bulb |
|
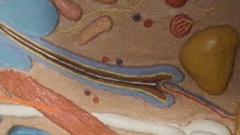
What is the brown arch |
Hair papilla |
|
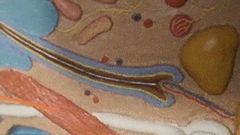
What is white line |
Medulla Center line of hair |
|
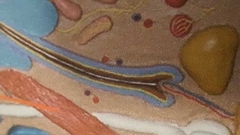
What is dark brown line |
Cortex Middle layer of hair |
|
|
Cuticle |
Clear layer surrounding hair shaft |

