![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
35 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is conus arteriosus? Gives rise to ? |
Outflow portion of right ventricle; from which pulmonary trunk arises
~part of the right ventricle that sticks out |
|
|
Paraconal interventricular groove is on which side?
|
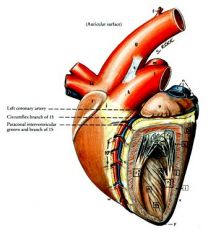
Left side
|
|
|
lymph nodes at base of HEART?
|
middle mediastinal nodes
|
|
|
define basal border of the lung
|
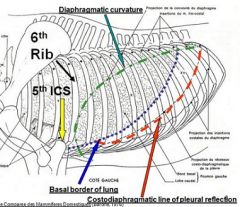
caudoventral border (base slants upwards gently) |
|
|
L.N. embedded in lungs called _____, they drain into ____ lymph nodes, which located _______.
|
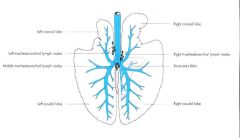
pulmonary lymph nodes drain into tracheobronchial nodes located near tracheal bifurcation (and primary bronchi)
|
|
|
Describe equine lung (lobes):
|
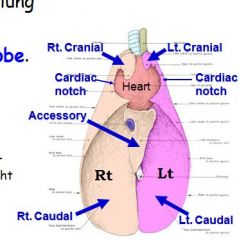
technically non-lobated (no interlobar fissures), but cranial to CARDIAC NOTCH is cranial lobe; caudal portion is caudal lobe;
right lung has Accessory lobe where which caudal vena cava goes through |
|
|
On which side does cardiac notch extend farther? borders?
|
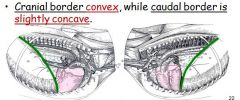
3rd to 6th intercostal spaces (left lung),
|
|
|
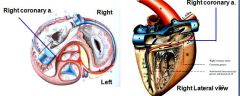
Major coronary artery is which side of heart? It supplies?
|
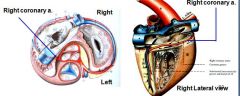
RIGHT coronary artery is dominant over left coronary artery, (is switched in dog/ruminants)
Supplies interventricular septum (in subsinuosal groove) and part of left ventricle |
|
|
What is coronary sinus?
Opening of the coronary sinus is ? |
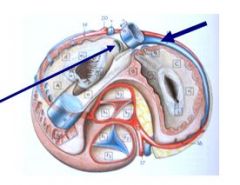
collection of veins draining myocardium, empties into right atrium, which also collects deoxygenated blood from rest of body
subsinosal! |
|
|
Only vein in body that carries oxygenated blood, empties where?
|
pulmonary vein empties into left atrium
|
|
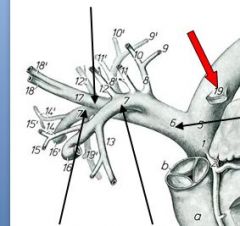
identify
|
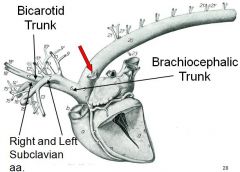
|
|
|
First sound - ?
Second heart sound ? |
First sound - ventricular systole
Second - ventricular diastole. "Cardiac notch" area used. |
|
|
1. What is name for line on which parietal pleura reflects from thoracic wall to the cranial surface of the diaphragm?
(translation: name for caudal edge of parietal pleura, where diaphragm meets thoracic wall) 2. How is it clinically significant? |
1. Costodiaphragmatic line of pleural reflection
2. Diaphragm attaches to wall, caudal to this line; and peritoneal cavity can be punctured behind here w/o entering pleural cavity. |
|
|
Which azygous vein found in dog?
|
Right azygous vein (same in dog)
No left azygous vein, as present in ruminants and pig. |
|
|
where is thymus in adult
|
ventral part of the cranial mediastinum
|
|
|
nerve ass w/ laryngeal hemiplegia (causing roaring).
|
left recurrent laryngeal n.
unrelated note: this is nerve that wraps around aorta |
|
|
Caudal mediastinal nodes in horse?
|
(associated with the oesophagus and the aorta); poorly developed or absent.
|
|
|
Thoracocentesis
-boundaries for procedure? |
invasive procedure to remove fluid or air from the pleural space for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes
- – in standing position; mid/lower of 7th intercostal space; 5 cm dorsal to olecranon, or just dorsal to superficial thoracic vein. |
|
|
Pericardiocentesis
-boundaries for procedure? |
-- procedure where fluid is aspirated from the pericardium (the sac enveloping the heart).
- 4th intercostal space level of costochondral junction |
|
|
How can enlarged lymph nodes cause roaring?
|
Enlarged lymph nodes
Left tracheobronchial ln.: when enlarged, may place pressure on LRL nerve, pressed against pulsating aorta. May cause nerve degen., and paralysis of most intrinsic muscles of larynx, including cricoarytenoideus dorsalis muscle (dilator of larynx). Causes roaring. |
|
|
Which side of mediastinum does caudal vena cava extend from?
|
on right side along w/right phrenic nerve (inside "caudal fold")
|
|
|
What is space betw. caval fold and caudal mediastinum?
What is housed here? |
mediastinal recess - houses accessory lobe of right lung
|
|
|
Horse has how many pairs of ribs ?
describe width of equine ribs compared to other species (like ox)? |
18 ribs; lumbar area, therefore, appears quite short. |
|
|
sternum tilts ?
effect of this ? |
cranio-dorsally,
- helps stream-line the thoracic cage, but diminishes area and volume of the cranial thoracic cage. |
|
|
The diaphragm shape? slope? cranial border at which incostal space?
|
Diaphragm is dome-shaped, gentle cranioventral slope. The vertex is at the lower part of the 6th intercostal space or 7th rib. |
|
|
first five ribs are covered by the ?
|
triceps brachii M. (as well as the scapula and humerus, partly).
|
|
|
right crus of Diaphragm attaches?
|
to first four or five lumbar vertebrae, via ventral longitudinal ligament, and left to first two lumbar vertebrae.
|
|
|
sternal part of Diaphragm attaches to _____ ;
|
xiphoid cartilage
|
|
|
comb-like muscle filaments in right (and left) atrium?
|
pectinate muscles
|
|
|
Name this structure or space:
Extends beyond the first rib (about 3 cm) only on the right, as in the ox Consists of two sacs – dorsal (about 30mm deep) and ventral (about 25 mm deep). |
The Cupula Pleurae
|
|
|
costodiaphragmatic recess
|
costodiaphragmatic recess (the narrow space bordered immediately by the diaphragm and thoracic wall) is within the thoracic cage, narrow and extensive.
|
|
|
The Lung Field
|
Topographical boundaries of triangular area of contact between the thoracic wall and the lung: |
|
|
attaches sternum to heart?
|
sternopericardiac ligament
|
|
|
annulus fibrosus
|
Fibrous skeleton
|
|
|
From KL's notes:
Identify septomarginal band? function? |
* Septomarginal band: goes from wall of ventricle to parainterventricular septum
o Serves 2 functions: + Passage of the purkinjie fibers: for contraction/ pacemaker + Supports right ventricle |

