![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
58 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Skeletal muscle develop mainly from this germ layer in the embryo
|
Mesoderm
|
|
|
The mesoderm differentiate into these three parts:
|
paraxial mesoderm
intermediate mesoderm lateral mesoderm |
|
|
In the paraxial mesoderm, paired blocks of _____ that are supplied by its own _____
|
somites
pair of spinal nerves |
|
|
The somite differentiates into the _____ which contributes to the vertebral column
|
ventromedial sclerotome
|
|
|
The epimere is the _____ portion of the myotome
|
dorsomedial
|
|
|
The hypomere is the ____ portion of the myotome
|
dorsolater
|
|
|
The hypomere forms these muscles
|
limbs
extrinsic back muscles muscles of the body wall |
|
|
The dorsal roots are mainly (sensory/motor), (afferent/efferent), and contain a _____
|
sensory
afferent dorsal root ganglion |
|
|
The ventral roots are mainly (sensory/motor), (afferent/efferent)
|
motor
efferent |
|
|
Ventral rami form _____ or _____
|
plexuses
intercostal nerves |
|
|
This layer of the intrinsic back muscles are mainly found in the neck
|
superficial layer (spinotransversales)
|
|
|
This layer of the intrinsic back muscles are associated with the vertebral column of the back
|
Intermediate (erector spinae)
Deep layer (transversospinales) |
|
|
The segmental muscles of the intrinsic back muscles are mainly for:
|
proprioreception
|
|
|
This is enclosed between to layers of facia and is attached to the nuchal ligament, spines of the thoracic, limbar, and sacral vertebrae, supraspinous ligament, iliac crest ischial tuberosity, and sacrum
|
thoracolumbar facia
|
|
|
The superficial layer of the intrinsic back muscles are formed by muscle(s), attaching to this portion of the spine
|
splenius capitus
splenius cervicis transverse process |
|
|
The splenius capitus and the splenius cervicis is also known as ____
|
spinotransversales
|
|
|
Splenius capitis:
Attachements: |
Spinous process
Ligamentum nuchae Superior nuchal line Mastoid process |
|
|
Splenius capitis and splenius cervicis is innervated by this nerve(s)
|
C4-C8
|
|
|
Splenius capitis and splenius cervicis action(s)
|
Rotates head
Extends/hyperextends head *ipsilateral* |
|
|
Splenius cervicis
Attatchments: |
O: Spinous process
I: Transverse process |
|
|
Name the three muscles of the erector spinae: from medial to lateral
|
Spinalis > longissimus > iliocostalis
|
|
|
The erector spinae muscles and the deep layer of the intrinsic back muscles are supplied blood through this artery
|
Posterior intercostal arteries
|
|
|
The iliocostalis is innervated by nerve(s)
|
Thoracic and lumbar nerves
|
|
|
The spinalis is innervated by nerve(s)
|
cervical and thoracic spinal nerves
|
|
|
The deep layer of the intrinsic back muscles are also called ____
|
transversospinalis muscles
|
|
|
The three deep layer of the back muscles are:
And they each span how many segments: |
Semispinalis (upper half - span 4-6 segments)
Multifidius (span 2-4) Rotatares (span 1-2) |
|
|
The only deep layer of the intrinsic back muscle that has an action on the ipsilateral side is the
|
Semispinalis capitis
|
|
|
The rotatores is best developed in the _____
|
thoracis region
|
|
|
The semispinalis is innervated by nerve(s)
|
dorsal rami of cervical, thoracic, and lumbar nerves
|
|
|
The segmental muscles can be divided into these three parts:
|
interspinalis
intertransversarii levatores costarum |
|
|
This segmental muscle is innervated by both ventral and dorsal nerves:
|
intertransversarii
|
|
|
This segmental muscle is innervated by the dorsal rami of C8-T11:
|
Levatores costarum
|
|
|
Damage to the dorsal ramus of C2 will cause loss of function of muscle(s)
|
Oblique capitis inferior
|
|
|
Damage to the dorsal ramus of C3 will also cause damage to nerve(s)
|
Third occipital nerve
|
|
|
Lying next to the occipital artery is nerve(s):
|
Greater occipital nerve
|
|
|
These muscles make up the sub-occipital triangle
|
rectus capitis posterior major
oblique capitis inferior oblique capitis superior |
|
|
This muscles lies medial to the tirangle
|
rectus capitis posterior minor
|
|
|
The suboccipital nerve (Dorsal rami of C1) innervates what muscle(s)
|
Rectus capitis posterior major
Oblique capitis inferior Oblique capitis superior Rectus capitis posterior minor |
|
|
Damage to the occipital artery will lead to loss of blood supply to what muscle(s)
|
Rectus capitis posterior major
Oblique capitis inferior Oblique capitis superior Rectus capitis posterior minor |
|
|
Attachments of the rectus capitis posterior major are:
|
Spinous process of axis (C2)
Inferior nuchal line |
|
|
Attachments of the oblique capitis superior are:
|
Transverse process of atlas (C1)
Between superior and inferior nuchal lines |
|
|
Attachments of the oblique capitis inferior are:
|
Spinous process of axis (C2)
Transverse process of atlas (C1) |
|
|
Attachments of the rectus capitis posterior minor are:
|
Posterior tubercle of atlas (C1)
Inferior nuchal line |
|
|
What nerve enters from the suboccipital triangle?
|
Suboccipital nerve (Dorsal rami of C1)
|
|
|
What nerve lies under or caudal to the oblique capitis inferior muscle?
|
Greater occipital nerve (Dorsal rami of C2)
|
|
|
What nerve pierces the trapezius and ends in the skin of the lower occipital region?
|
Third occipital nerve (Dorsal rami of C3)
|
|
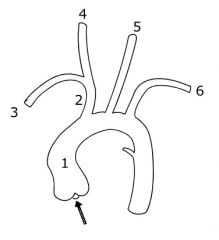
Give the names of the structures 2-6
|
2 - Right Brachiocephalic trunk
3 - Right subclavian artery 4 - Right common carotid artery 5 - Left common carotid artery 6 - Left subclavian artery |
|
|
The common carotid artery divides and becomes:
|
External carotid - occipital artery (supplies neck and face)
Internal carotid artery (supplies brain) |
|
|
The Subclavian artery divides becomes:
|
Vertebral artery
Internal thoracic artery Thyrocervical artery Costocervical artery |
|
|
What artery branches from the first part of the subclavian and ascends through the transverse foramina of C6-C1
|
Vertebral Artery
|
|
|
The vertebral artery comes from where?
|
First branch of subclavian
|
|
|
Describe the path the vertebral artery takes to make the basilar artery
|
Branches off subclavian > ascends transverse foramina > bends 90 degrees above atlas > enters cranial cavity
|
|
|
The vertebral artery supplies what and contributes to what?
|
Main supply to the brainstem
Also supplies brain and spinal cord Contributes to the Circle of Willis |
|
|
Vertebral artery divides into the:
|
anterior spinal artery
posterior spinal artery |
|
|
The iliocostalis, multifidus, and the rotatores attach in these locations and are therefore named:
|
cervicis
thoracis lumborum |
|
|
the longissimus, spinalis, and semispinalis attach in these location and are therefore named:
|
capitis
cervicis thoracis |
|
|
The deep and intermediate intrinsic back muscles that are divided into the capitis, cervices, and thoracis are:
|
longissimus
spinalis semispinalis |
|
|
The deep and intermediate intrinsic back muscles that are divided into the cervices, thoracis, and lumborum are:
|
multifidus
iliocoastalis rotatores |

