![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
136 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Human Anatomy |
The study of structures |
|
|
Human Physiology |
The study of functions |
|
|
Gross Anatomy |
Structures visible with the naked eye. Studied with cadavers (dead bodies) or corps. |
|
|
Morphology |
Study of forms and shapes. Can refer to whole organisms or cells. |
|
|
Regional Anatomy |
Confined to a body segment (head, pelvis, and limbs) |
|
|
Systematic/ Stemic Anatomy |
Structures that are involved in a common function. Study by system. |
|
|
Development Anatomy |
Study of how humans develops from time of conception until aging process and death occurs. |
|
|
Comparative Anatomy |
Study of diffrent species. |
|
|
Neuroanatomy |
Study of the Nervous System |
|
|
Structural Levels |
1. Chemicals (Amino Acids, Glucose, DNA, and 99% H2O) 2. Organelles 3. Cells 4. Tissues (Histology) 5. Organ 6. Organ Systems 7. Organisms |
|
|
The Integument |
The surface of the body which consists of skin, hair and nails |
|
|
Skin |
Principal function is to prevent bodily invasion by harmful microorganisms. It also produces sweat and sebum (oil) that contain antimicrobial substances for further protection. Aids in temperature regulation and exertion. |
|
|
The Skeletal System |
Form a solid framework, consists of bones, cartilage, and ligaments, provides support and protection for the softer parts of the body, and provide points of attachment for muscles which act as levers when muscles contract (makes movement possible). |
|
|
The Muscle System |
Composed of muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Functions: Allow body movement, posture and produces body heat |
|
|
Tendons attatch |
muscle to bone and ligaments |
|
|
Ligaments attatch |
muscle to mucle |
|
|
The Nervous System |
(Most important) Composed of the Central Nervous System (CNS) and Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Functions: Regulates and coordinates all lifes activities. |
|
|
Central Nervous System (CNS) |
The brain and spinal cord |
|
|
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) |
Prephiral nerves and recepters |
|
|
Cardiovascular System or Circulatory System |
Composed of the heart (Myocardium) and blood vessels. Functions: transport minerals, waste products, and oxygen. Plays a role in the immune system and regulates body temperature. |
|
|
Myocardium |
Heart |
|
|
Myo |
Muscle |
|
|
Cardium |
Heart |
|
|
Largest artery |
Arota |
|
|
Largest veire |
Inferior Vena Cava |
|
|
The Lymphatic System |
Composed of Lymph vessels, and Lymph nodes. Functions: removing foreign substances from the blood. |
|
|
The Respetory System |
Composed of the lungs, respiratory passages, and alveoli (where gas exchange takes place). Function: the exchange of gases between the blood and air. |
|
|
The Digestive System |
Composed of the mouth esophagus, stomach, small intestines, large intestines and rectum. Functions: perform both mechanical and chemical digestion, and elimination of wastes. |
|
|
Urinary System |
Composed of kidneys, ureters and urinary bladder, and urethra. Functions: excretion and removing cellular wastes. Regulates PH, ions, and water balance. |
|
|
Reproductive System |
Composed of gonads (testes and ovaries), accessory structures, and genitals. Functions: Perform the process of reproduction and to control sexual behaviors. |
|
|
Anatomical Position |
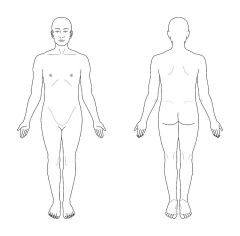
The body is erect or standing with the arms at the side and palms turned forward. The head and feet are also pointing forward. |
|
|
Trunk |
Subdivided into two pectoral, two groin, and the abdominal regions. |
|
|
Abdominal Regions |
(not covered by ribs) Anterior torso below the diaphragm. |
|
|
Caliac |
Area of the Abdomen |
|
|
Pelvic |
The lower portion of the torso (hip bone) |
|
|
Dorsum of trunk (posterior) |
Costal (ribs) |
|
|
Costal |
Ribs |
|
|
Lumbar (Loin) |
Area between the ribs and hips |
|
|
Lumbar |
Loin |
|
|
Buttocks |
Gluteal |
|
|
Perineal Area |
Between the anus and the genitals |
|
|
Flank |
Side of the trunk which adjoins the lumbar region |
|
|
Axilla |
Armpit area |
|
|
Brachium |
Upper arm |
|
|
Antebrachium |
Forearm (between the elbow and wrist) |
|
|
Cubital Area |
Elbow |
|
|
Antecubital |
The opposite side of the elbow |
|
|
Carpal |
The wrist |
|
|
Digital |
Fingers |
|
|
Palmar |
The palm of the hand |
|
|
Femur |
Thigh; the upper portion of the leg |
|
|
Calf |
Lower posterior fleshy portion |
|
|
Ham or Popliteal |
Between the thigh and calf on the posterior surface, opposite of the knee (hamstring) |
|
|
Popiteal |
Depression between the thigh and calf on the posterior surface. |
|
|
Plantar Surface |
Sole of the foot |
|
|
Crural |
The leg (between the knee and ankle) |
|
|
Pedal |
The foot |
|
|
Tarsal |
The ankle |
|
|
Volar |
Refers to the palms of the hands and the soles of the feet. |
|
|
Frontal (Facial) |
Forehead |
|
|
Oral or Buccal Cavity |
Mouth |
|
|
Orbital or Ophthalmic |
Eyes |
|
|
Nasal |
Nose |
|
|
Vestubular |
Open area at base of nose |
|
|
Zygomatic |
The cheek |
|
|
Mastoid |
The area of the skull just below and behind the ears |
|
|
Occipital |
The back of the skull |
|
|
Temporal |
The side of the skull |
|
|
Cephalic |
The head |
|
|
Cranial |
The skull |
|
|
Cervical |
The neck |
|
|
Axial Skeleton |
1. Head 2. Neck 3. Trunk (Torso) |
|
|
Appendicular Skeleton |
1. Upper Extremities 2. Lower Extremities |
|
|
Abdominal Region |
1. Right Hypochondriac 2. Epigastric 3. Left Hypochondriac 4. Right Lumbar 5. Umbilical 6. Right Iliac 7. Left Lumbar 8. Hypogastric 9. Left Iliac |
|
|
Right Hypochondriac |
Right lobe of liver, gallblader |
|
|
Epigastric |
Right and left lobes of liver, large portion of the stomach |
|
|
Left Hypochondriac |
Small portion of the stomach, left colic (splenic) flexure of L.I |
|
|
Right Lumbar |
Ascending colon, the right colic (hepatic) flexure of the L.I and part of the S.I |
|
|
Umbilical |
Portion of transverse colon and S.I |
|
|
Right Iliac |
Appendix, cecum, parts of S.I |
|
|
Left Lumbar |
S.I and descending colon |
|
|
Hypogastric |
S.I and urinary bladder |
|
|
Left Iliac |
Descending colon, sigmoid colon, S.I |
|
|
Transpyloric Plane |
The upper horizontal plane which would pass though the lower portion of the stomach |
|
|
Transtubercular Plane |
The other horizontal plane which touches the top surfaces of the hipbones (iliac crests) |
|
|
Right and Left Lateral Planes |
Approximately halfway between the midsagittal line and the crests of the hips. |
|
|
The umbilical region lies |
in the center, includes the navel, and is bordered by the two horizontal and to vertical planes. |
|
|
The epigastric region lies |
immediately above the umbilical region and covers much of the stomach |
|
|
The hypogastric region lies |
below the umbilical zone (pubic area) |
|
|
The right and left hypochondriac zones lie |
on each side of the epigastric area |
|
|
The right and left lumbar areas lie |
beneath the hypochondriac areas (on each side of the umbilical zone) |
|
|
The right and left iliac areas lie |
on each side of the hypogastric area |
|
|
Pectoral or Mammary |
Upper chest |
|
|
Superior |
A structure that is located above another one |
|
|
Inferior |
Structure that is below or under another |
|
|
Anterior |
In front of |
|
|
Posterior |
In back of |
|
|
Dorsal |
Upper surfaces in fourlegged animals, back |
|
|
Ventral |
Underneath surfaces in fourlegged animals, pertains to abdominal and chest surfaces |
|
|
Proximal |
Nearest to the point of attachment |
|
|
Distal |
Most remote from the point of attachment |
|
|
Medial |
Those surfaces of structures that are closest to the median line |
|
|
Lateral |
Furthest away from the median line |
|
|
Median Line |
an imaginary line on a plane which divided the body into right and left halves |
|
|
Sagittal Sections |
A section divides the body into equal halves |
|
|
Frontal Section or Coronal Section |
Divides the body into front and back portions |
|
|
Transverse Sections or Cross Section |
Cuts through the body in a direction which is perpendicular to the long axis |
|
|
Dorsal Cavity |
Nearest to the dorsal surface, includes the cranial and spinal cavities |
|
|
Cranial Cavity |
The hollow portion of the skull that contains the brain |
|
|
Spinal Cavity |
A long tubular canal within the vertebrae which contains the spinal cord |
|
|
Ventral Cavity |
Largest cavity which encompasses the chest and abdominal regions. |
|
|
Diaphragm |
A dome-shaped thin muscle that separates the upper and lower portions of the ventral cavity |
|
|
Mediastinum |
Contains lungs, heart, trachea, esopagus, and thymus gland |
|
|
Pleural Cavities |
Contains lungs |
|
|
Pericardial Cavity |
Contains the heart |
|
|
Abdominopelvic Cavity |
Inferior to the diaphragm and consists of the abdominal and pelvic cavities |
|
|
Abdomibal Cavity |
Contains the stomach, liver, gall bladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys, and intestines. |
|
|
Pelvic Cavity |
The most inferior portion of the abdominopelvic cavity which contains the urinary bladder, sigmoid colon, rectum, uterus, and ovaries. |
|
|
Serous Membranes |
Line body cavities to provide a smooth surface for the enclosed internal organs |
|
|
Serous Fluid |
Facilitate ease of movement of the viscera against the cavity walls |
|
|
Parietal Pleurae |
The membrane the line the walls of the right and lest thoracic compartments |
|
|
Pleural Cavity |
The potential cavity between the pariental and visceral (what the lungs are covered in) pleurae |
|
|
Visceral Pericardium or Epicardium |
Covers the heart |
|
|
Pariental Pericardium |
Surrounds the heart, double-layered fibroserous sac |
|
|
Pericardial Cavity |
The potential space between the visceral and parietal pericardia |
|
|
Peritoneum |
Most inferior boundary which extends across the abdominal cavity, covers the top portion of the urinary bladder |
|
|
Mesenteries |
Double layered folds in the peritoneum which extends from the body wall to the viscera, holding these organs in place. |
|
|
Parietal Peritoneum |
The part of the peritoneum attached to the body wall |
|
|
Visceral Peritoneum |
The peritoneum that covers the visceral surfaces |
|
|
Peritoneal Cavity |
The potential cavity between the parietal and visceral peritoneums. |
|
|
Retroperitoneal |
Posterior to the parietal peritoneum |
|
|
Homeostasis |
Stable equilibrium |
|
|
Negative Feedback |
Works to correct a deviation from a set point (Tries to get back to the set point/normal) |
|
|
Sweating |
Negative Feedback |
|
|
Positive Feedback |
Changes from the normal point and amplifies it. |
|
|
Milk production (as long as baby is nursing. milk will be produced UNTIL babies done) |
Positive Feedback |

