![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
200 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Apical Ectodermal Ridge
|
Ectoderm on most distal aspect of limb buds
|
|
|
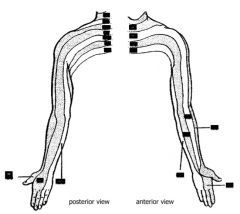
Veins on preaxial border of limbs
|
Cephalic and greater saphenous
|
|
|
Veins on postaxial border of limbs
|
basilic and lesser saphenous
|
|
|
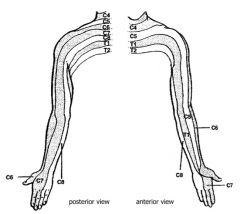
Innervation of preaxial muscle mass
|
C5, 6, 7 ventral rami
|
|
|
Innervation of postaxial muscle mass
|
C7, 8, T1 ventral rami
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Anterior compartment innervation
|
Arm: musculocutaneous
forearm: median thigh: femoral Leg: Peroneal |
|
|
Posterior compartment innervation
|
Arm: radial
Forearm: radial Thigh: Tibial Leg: Tibial |
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that innervate shoulder joint
|
C5, C6 (they generally innervate muscles originating from scapula)
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that innervate elbow joint
|
C6, C7
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that innervate wrist joint
|
C7, C8
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that innervate Intrinsic muscles of the hand
|
C8, T1
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that innervate flexors of hip joing
|
L2, L3
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that innervate Extensors of knee joint
|
L3, L4
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that dorsiflex ankle joint
|
L4, L5
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that extend the hip joint
|
L4, L5
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that Flex the knee joint
|
L5, S1
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that plantarflex the ankle joint
|
S1, S2
|
|
|
Spinal Cord Levels that innervate intrinsic muscles of plantar foot
|
S2, S3
|
|
|
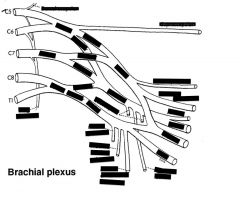
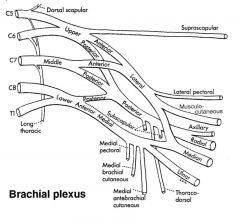
Cervoaxillary canal
|
Apex of the axilla. Formed by clavicle on the anterior side, first rib medially, scapula posteriorly.
|
|
|
Branches of 1st part of axillary artery
|
Superior (supreme) thoracic: supplies first few intercostal spaces
|
|
|
Branches of 2nd part of axillary artery
|
Thoroacromial trunk (clavicular, pectoral, acromial, deltoid) and lateral thoracic artery
|
|
|
Branches of 3rd part of axillary artery
|
Subscapular a. (circumflex scapular and thoracodorsal a.), anteriohumeral circumflex a., posterior humeral circumflex a.
|
|
|
Axillary artery collaterals
|
Suprascapular a. from thyrocervical trunk anastomoses with circumflex scapular.
Transverse cervical from thyrocervical trunk anastomoses w/subscapular a. Internal thoracic --> anterior intercostal --> lateral thoracic a --> axillary |
|
|
5 elements of a synovial joint
|
1) 2 or more rigid skeletal elements
2) Articular cartilage (hyaline or fibrocartilage) 3) Joint capsule (continuous with periosteum) 4) Synovial membrane (vascular CT) 5) Synovial fluid |
|
|
3 types of ligaments
|
Capsular: most common, thickening of joint capsule
Extracapsular: outside capsule, ex: coracoclavicular lig. Intracapsular: Least common, intracapsular but extrasinovial. ex: cruciate ligament |
|
|
Movements of the pectoral (shoulder) girdle
|
Vertical axis: protraction and retraction
AP axis: Elevation and depression Oblique axis: Medial and lateral rotation |
|
|
Glenohumeral joint movements
|
Horizontal axis: flex and extend
AP axis: abduct/adduct Vertical Axis: rotate medially and laterally |
|
|
Sternoclavicular joint movement
|
Multiaxial
Vertical axis: protraction/retraction AP axis: elevation/depression Oblique Axis: lateral/medial rotation |
|
|
acromioclavicular joint movement
|
Almost no movement, moves only slightly to allow smooth movement.
|
|
|
Glenoid cavity
|
Cavity on scapula to allow room for humerus at the glenohumeral joint
|
|
|
Shoulder separation vs shoulder dislocation
|
Shoulder separation: acromioclavicular joint
Shoulder dislocation: glenohumeral joint, usually through weak spot on inferior aspect of glenohumeral joint |
|
|
Elbow Ligaments
|
Collateral ligaments limit ab/adduction. Look like thickened areas of joint capsule
Annular ligament: Holds the radius in position against the ulna. Does not fit as tightly in children, easy to pull out. |
|
|
Radioulnar Joints
|
Supination/pronation
Proximal, middle and distal radioulnar joints, each are uniaxial. |
|
|
Muscles of the Sternoclavicular Joint
|
All attach to the scapula
Anterior: Pectoralis minor and serratus anterior Posterior: Trapezius, Levator Scapulae, Rhomboids |
|
|
2 muscles that laterally rotate scapula
|
serratus anterior and trapezius
|
|
|
Serratus Anterior movements and innervation
|
protraction, depresses, laterally rotates scapula
Also holds scapula along posterior thoracic wall, if nerve is cut get "winged scapula" protruding on back Long Thoracic nerve (from C5, 6, 7 roots) |
|
|
Pectoralis Minor movements and innervation
|
depression, protraction, medial rotation
medial and lateral pectoral nerves |
|
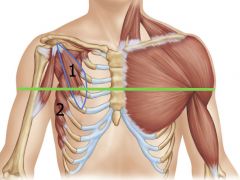
|
1: Pectoralis minor
2: Serratus Anterior |
|
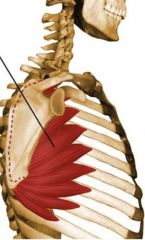
|
Serratus Anterior
|
|
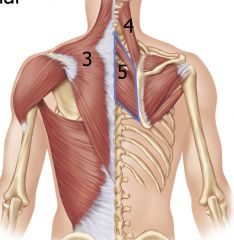
|
3: Trapezius
4: Levator Scapulae 5: Rhomboids |
|
|
Levator Scapulae Movement
|
Elevation
|
|
|
Rhomboids movement
|
Elevation, retraction, medial rotation
|
|
|
Trapezius Movements
|
Superior Fibers: elevation, lateral rotation
Middle Fibers: Retraction Inferior Fibers: depression, lateral rotation |
|
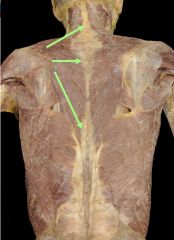
|
Trapezius
|
|
|
Muscles of Glenohumeral Joint
|
Anterior: Pectoralis major, coracobrachialis, biceps brachii, deltoid
Posterior: Latissimus dorsi, teres major, triceps brachii, deltoid Rotator Cuff: Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, subscapularis |
|
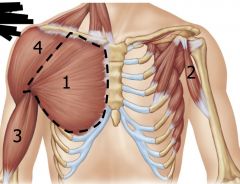
|
1: Pectoralis Major
2: Coracobrachialis 3: Biceps brachii 4: Deltoid All Flex glenohumoral joint |
|
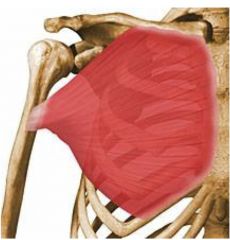
|
Pectoralis Major
Flexion, adduction, medial rotation "hugging muscle" |
|
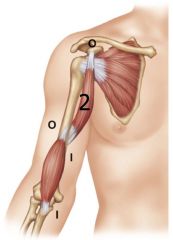
|
Coracobrachialis
Mostly flexor |
|
|
Musculocutaneous Nerve
|
Motor to muscles of the anterior arm, cutaneous to the lateral forearm.
Usually pierces coracobrachialis. |
|
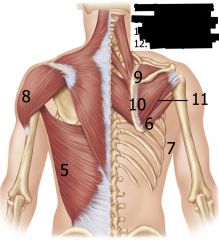
|
5: Latissimus Dorsi
6: Teres Major 7: Triceps brachii 8: Deltoid 9: Supraspinatous 10: Infraspinatous 11: Teres Minor 12: Subscapularis |
|
|
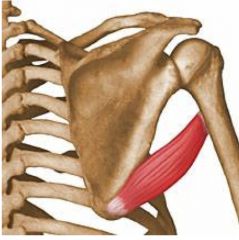
Teres Major
Extension, adduction, medial rotation |
|
|
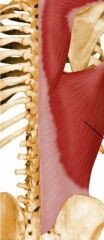
Latissimus Dorsi
Extension, adduction, medial rotation |
|
|
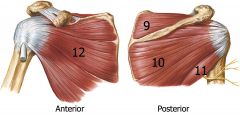
Rotator Cuff Muscles: SITS
9: Supraspinatous 10: Infraspinatous 11: Teres Minor 12: Subscapularis Each muscle has one action |
|
|
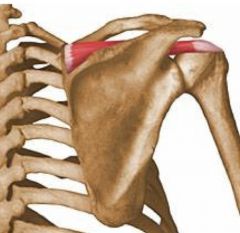
Supraspinatous Muscle
Abbduction |
|
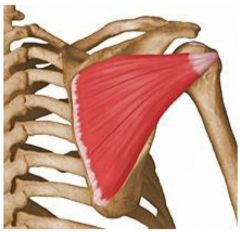
|
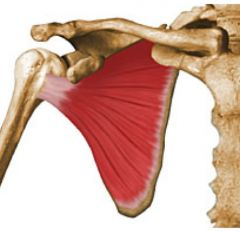
Infraspinatous
Lateral rotation |
|
|
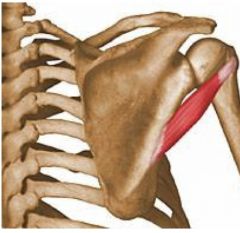
Teres Minor
Lateral rotation |
|
|
Subscapularis
Medial Rotation |
|
|
Brachial artery terminal branches
|
Deep brachial, radial, ulnar
|
|
|
Relationship between nerve and artery in scapular notch
|
suprascapular artery and nerve
|
|
|
Relationship between nerve and artery in surgical neck
|
posterior circumflex humeral artery and axillary nerve
|
|
|
Relationship between nerve and artery in shaft of humerus
|
deep brachial artery and radial nerve
|
|
|
Long thoracic nerve runs with which artery
|
lateral thoracic a
|
|
|
long head of triceps goes where?
|
between teres major and minor
|
|
|
Median nerve runs with which artery
|
brachial a
|
|
|
Lower subscapular nerve runs with which artery
|
circumflex scapular artery
|
|
|
Axillary nerve runs with
|
posterior humeral circumflex artery
|
|
|
radial nerve runs with
|
deep brachial artery
|
|
|
Movement of wrist joint and components
|
biaxial: flexion/extension and adduction/abduction
Radiocarpal joint and midcarpal joint |
|
|
Readiocarpal joint
|
between distal end of radius, the radioulnar disc and the proximal row of carpal bomes
|
|
|
Radial nerve innervates
|
All posterior forearm muscles, there are no posterior hand muscles
3 muscles that move the elbow o Triceps brachii, (anconeus), brachioradialis n 3 muscles that move the wrist o ECRL, ECRB, ECU 3 muscles that move the fingers o ED, EI, EDM 3 muscles that move the thumb o EPL, EPB, APL |
|
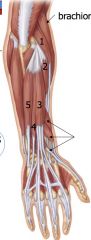
|
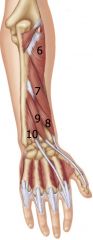
Superficial extensors originate from/near lateral epicondyle
1: extensor carpi radialis longus 2: extensor carpi radialis brevis 3: Extensor digitorum 4: extensor digit minimi 5: extensor carpi ulnaris |
|
|
Extensor digitorum tendon
|
Flares out to form extensor hood, and continues to the DIP joint.
|
|
|
Deep extensor Muscles
6. Supinator 7: Abductor pollicis longus 8: extensor pollicis brevis 9: extensor pollicis longus 10: extensor indicis |
|
|
Muscles of Thumb
|
Form the anatomical snuffbox
Staring dorsally: Extensor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis longus. |
|
|
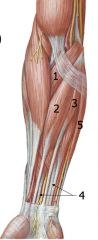
Anterior Forearm Superficial muscles originate from medial epicondyle via common flexor tendon
1. Pronator teres 2. Flexor carpi radialis 3. Palmaris longus 4. Flexor digitorum superficialis 5. Flexor carpi ulnaris |
|
|
Anterior Forearm Deep
6. Flexor digitorum profundus 7. Flexor pollicis longus 8. Pronator quadratus |
|
|
Flexor digitorum muscles superficial vs deep
|
Flexor digitorum superficialis tendons attach to middle phalanges
Flexor digitorum profundus tendons attach to distal phalange, can move DIP joints |
|
|
Pronators and supinators
|
Pronators: brachiradialis (half-way), pronator teres, pronator quadratus
Supinators: Brachioradialis (half-way), supinator, biceps brachii |
|
|
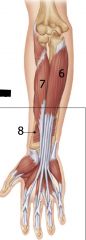
What travels through carpal tunnel?
|
FDS, FDP, FPL, median nerve
Ulnar nerve and artery are outside of it. |
|
|
Symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome
|
Numbness of lateral 3.5 digits, pain of lateral 3.5 digits.
Atrophy of median nerve target muscles. |
|
|
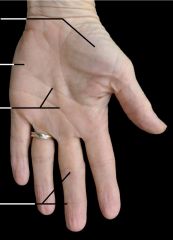
From top to bottom:
Thenar eminence, hypothenar eminence, flexion creases, flexion creases |
|
|
Thenar muscles
|
Opponens pollicis, abductor pollicis brevis, flexor pollicis brevis.
Adductor pollicis is not technically a thenar muscle, but is in similar area |
|
|
Hypothenar muscles
|
Opponens digiti minimi, abductor digiti minimi, flexor digiti minimi
|
|
|
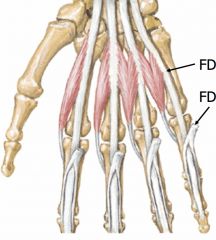
lumbrical muscles
Originate from flexor digitorum profundus tendons, insert into extensor hoods. Along with interosseous muscles flex MP joints and extend IP joints. 2 get medial innervation, 2 get ulnar innervation (on ulnar side) |
|
|
Interosseous muscles
|
Dorsal and Palmar muscles. Originate from metacarpals, insert onto extensor hoods. Innervated by ulnar nerve
Along with lumbrical muscles flex the MP joint and extend the IP joint. Palmar: adducts Dorsal: abbducts |
|
|
Blood supply in hand
|
Ulnar artery superficial to carpal tunnel, forms superficial palmar arch and continue to common digital arteries and proper digital arteries.
Radial artery passes through anatomical snuffbox to form deep palmar arch. |
|
|
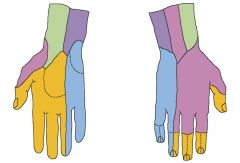
Cutaneous innervation
Blue: Ulnar nerve Yellow: Median nerve Pink: Radial nerve Purple: ??? |
|
|
Median nerve motor and cutaneous targets
|
Motor:
Anterior forearm: everything but flexor carpi ulnaris, half of flexor digitorum profundus) Anterior hand: thenar compartment, half the lumbricals Cutaneous: 3.5 digits, with only tips on dorsal side |
|
|
Ulnar nerve motor and cutaneous targets
|
Motor:
Anterior forearm: flexor carpi ulnaris, half of flexor digitorum profundus Anterior hand: all muscles except thenar compartment and half the lumbricals Cutaneous: 1.5 digits |
|
|
Radial Nerve Motor and Cutaneous targets
|
Motor: all muscles of posterior arm and forearm
Cutaneous: 3.5 digits on dorsal surface |
|
|
Radial Nerve Palsy Symptom
|
Wrist drop due to loss of extensors.
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hip Joint
|
Transverse: Flexion/extension
AP: Abduction/adduction Vertical: Medial/lateral rotation |
|
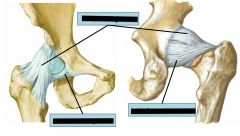
|
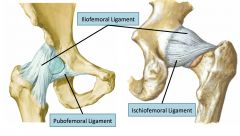
Spiral arrangement of collagen fibers loosen during flexion and tighten during extension ~15 degrees.
|
|
|
Knee joint
|
Transverse: flexion/extension
Vertical: medial/lateral rotation |
|
|
Ligaments of knee joint
|
Lateral and medial collateral ligaments.
Anterior cruciate ligament: ACL prevent tibia from moving out anteriorly Posterior cruciate ligament: prevents posterior movement of the tibia. |
|
|
Purpose of medial and lateral mensisci
|
Deepen articular surfaces on tibia, act as shock absorbers, protect articular cartilage of tibia and femur.
|
|
|
what structures would be torn with a lateral hit to the knee
|
ACL, MCL, MM (ACL is attached to MM)
|
|
|
What structures would be damaged with a medial hit to the knee
|
PCL, LCL
|
|
|
Compartment Syndrome
|
A bleed within a facial compartment in the leg (probably arm too), there is no room to expand so it compresses the muscle and is very painful.
|
|
|
Lumbar plexus Branches
|
Superior: Subcostal, iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal, genitofemoral
Posterior Division: Lateral femoral cutaneous, nerves to iliopsoas, femoral nerve Anterior Division: obturator nerve |
|
|
Sacral Plexus
|
Posterior Division: Gluteal nerves, nerve to piriformis, common fibular nerve
Anterior division: tibial nerve, nerves to lateral rotators. (Sciatic nerve has both anterior and posterior divisions, here they are named common fibular and tibial) |
|
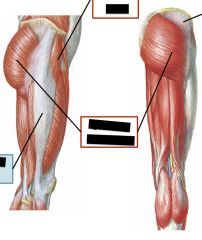
|
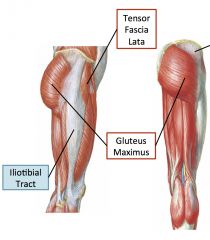
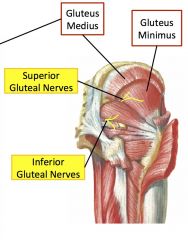
Top right is gluteus medius
|
|
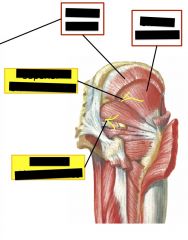
|
|
|
|
Hip Flexors and extensors
|
Extensors: Gluteus maximus and gluteus medius
Flexors: TFL and gluteus minimus |
|
|
Hip rotators
|
Lateral: gluteus maximus and medius
Medial: TFL and gluteus minimus |
|
|
Main abductors of the hip
|
Gluteus medius and gluteus minimus
|
|
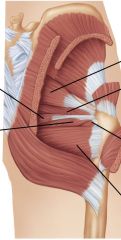
and innervation
|
Lateral Rotators
All innervated by "nerve to _____" except for "obturator nerve" |
|
|
Anterior Thigh muscles and their innervation
|
flexors to hip: Psoas major, iliacus, iliopsoas. Nerves to iliopsoas innervates
Flexion and adduction: pectineus, femoral nerve OR obturator nerve |
|
|
Sartorius
Insertion/attachment Innervation Action |
Attaches proximally to anterior superior iliac spine, and attaches to medial surface of the tibia.
Femoral nerve flex, lateral rotation, abduction of hip. Flexion and medial rotation of knee. |
|
|
Anterior thigh muscles and innervation
|
Sartorius, rectus femoris, quadriceps femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, vastus medialis.
Femoral nerve |
|
|
Muscles that attach to quadriceps tendon and their action.
|
rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, vastus medialis.
Rectus femoris flexes hip All 4 extend the knee The quadriceps tendon becomes the patellar ligament when crossing knee. |
|
|
Adductors/Medial Thigh Muscles
|
Gracilis, adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus
|
|
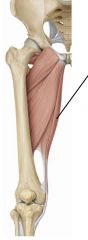
|
Gracilis muscle
Hip: adduction, flexion Knee: flexion, medial rotation Obturator nerve |
|

plus underlying muscle
|
Adductor Longus, superficial to adductor brevis
Adduction, flexion of hip Obturator nerve |
|
|
Adductor Magnus
|
Anterior fibers: Adduction, flexion of hip. Obturator nerve.
Posterior fibers: adduction, extension of hip. Tibial nerve. |
|
|
Posterior Thigh Muscles
|
Semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris
|
|
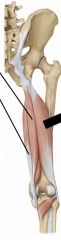
|
Semitendinosus superior, semimembranosus inferior.
Hip: extend Knee: flexion, medial rotation Tibial nerve |
|
|
Biceps Femoris
|
long head: Tibial nerve
Hip: extend Knee: flexion, lateral rotation Short head: Common fibular nerve knee: flexion, lateral rotation |
|
|
Pes Anserinus
|
"goose foot" made up of tendons from gracilis, sartorius, semitendinosus. Medial aspect of knee, contributions from all three compartments.
|
|
|
Femoral Triangle
|
Borders: inguinal ligament, sartorius, adductor longus. Pectineus runs through it.
Includes femoral nerve, femoral artery, femoral vein and lymphatics |
|
|
Blood supply to hip and thigh
|
Deep femoral artery, circumflex femoral arteries to femoral head and neck, perforating branches to thigh.
|
|
|
Cruciate anastomosis
|
Medial femoral circumflex, lateral femoral circumflex, first perforating branch of deep femoral, inferior gluteal artery all anastomose around hip.
|
|
|
Adductor hiatus
|
In popliteal fossa the femoral artery changes into the popliteal artery. Sciatic nerve often splits into tibial nerve and common fibular nerve here as well.
|
|
|
synovial tendon sheaths
|
surround tendons that are bound in palce by retinacula. Wraps all the way around, except at mesotendon where vessels and nerves can pass through to tendon.
|
|
|
Deep palmar space
|
Fascial space bound by the long flexor tendons and the muscles on the floor of the palm.
|
|
|
Where can median nerve injury occur? Symptoms?
|
At elbow after a supracondylar fracture of the humerus.
Most commonly at the wrist where it lies just under the skin and investing fascia. Implicated in carpal tunnel syndrome. "ape hand" - de-rotation of the thumb to lie in same plane as other fingers due to loss of opponens pollicis |
|
|
Where can ulnar nerve injury occur? Symptoms?
|
The ulnar nerve superficial and against bone in elbow, near medial epicondyle.
"claw hand" Sensory loss in hand, ring and little fingers are flexed at proximal and distal interphalangeal joints. |
|
|
Where can radial nerve injury occur? Symptoms?
|
Fracture of the midshaft of the humerus or crompression with crutches. Also vulnerable near the lateral supracondylar ridge.
Damage results in "wrist drop": inability to extend wrist. Inability to grip firmly. Only have sensory loss in a small area because of overlap. |
|
|
Gluteus Maximus
Insertion/attachment Innervation Action |
Originates from sacrotuberous ligament, ilium, sacrum and coccyx, attaches to luteal tuberosity of the femur and iliotibial tract (a thickened lateral portion of the fascia lata)
Inferior gluteal nerve Hip extension, lateral rotation |
|
|
Tensor Fasciae latae (TFL)
Insertion/attachment Innervation Action |
Originates from iliac creast and inserts into iliotibial tract with gluteus maximus.
Superior gluteal nerve Abducts, medially rotates and flexes the hip joint. |
|
|
Gluteus Medius
Insertion/attachment Innervation Action |
arises from ilium and inserts into greater trochanter.
Superior gluteal nerve Main action is abduction of hip, can also extend and laterally rotate the hip. |
|
|
Gluteus minimus
Insertion/attachment Innervation Action |
Deep to gluteus maximus, same attachments, ilium and greater trochanter.
Superior gluteal nerve Medially rotates and flexes the hip, as well as abducting it. |
|
|
Inferior vs superior gluteal nerves
|
Inferior supplies maximus, superior supplies medius, minimus and tensor fasciae latae
|
|
|
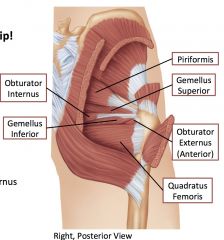
Piriformis
Insertion/attachment Innervation Action |
Originates from the internal (anterior) surface of sacrum, emerges through greater sciatic foramen, and attaches to greater trochanter.
the nerve to the piriformis (ventral rami of S1-S2) Lateral rotation of hip joint |
|
|
Obturator internus
Insertion/attachment Innervation Action |
Arises from internal surface of obturator membrane and surrounding bone, fibers converge to a tendon that passes lesser sciatic foramen and attaches to greater trochanter
Nerve to the obturator internus lateral rotator of hip joint |
|
|
Superior gemellus and inferior gemellus
|
arise from the ischium and attach to greater trochanter.
Nerve to the superior gemellus and nerve to the inferior gemellus lateral rotator of the hip joint |
|
|
Obturator externus
Insertion/attachment Innervation Action |
Arises from external surface fo the obturator membrane and the surrounding bone, attaches on greater trochanter.
Obturator nerve Lateral rotator of hip joint |
|
|
Quadratus femoris
|
Originates from the ischial tuberosity and inserts into the intertrochanteric creat.
Nerve to the quadratus femoris lateral rotator of hip joint |
|
|
Subcostal Nerve
|
T12
not a lumbar nerve, but joins lumbar plexus. Travels laterally on anterior surface of quadratus lumborum, below 12th rib. |
|
|
Subcostal, iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal innervate
|
cutaneous innervation to T12 and L1 dermatomes, motor fibers to lower abdominal wall muscles.
|
|
|
Genitofemoral nerve
|
L1-2
Runs inferiorly on surface of psoas major muscle. Splits into genital branch that enters deep ring and femoral branch that travels with external iliac artery. Femoral branch sensory to medial aspect of proximal thigh. Genital branch innervates cremaster muscle and sensory to lateral scrotum/labium majus |
|
|
Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
|
L2-3 dermatomes
Sensory to lateral thigh |
|
|
Femoral nerve
|
Posterior division fibers from L2-L4
descends lateral to psoas major muscle Innervates anterior compartment of the thigh: iliacus, sartorius, rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, pectineus |
|
|
Obturator nerve
|
Anterior division fibers of L2-L4
Descends medial to psoas major muscle, though obturator foramen to innervate adductor compartment (medial compartment): gracilis, adductor longus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus (ant. 2/3), obturator externus |
|
|
Lumbosacral trunk
|
branch of L4 and all of L5 that connect to sacral plexus.
|
|
|
Branches of Lumbar Plexus
|
(subcostal), iliohypogastric, ilioinguinal, genitofemoral, lateral femoral cutaneous, obturator, femoral
|
|
|
Branches of sacral plexus
|
Superior and inferior gluteal nerves, sciatic nerve.
|
|
|
Inferior gluteal nerve
|
Posterior division. Gluteus medius, minimus and tensor fasciae latae
|
|
|
Inferior gluteal nerve
|
Posterior division. gluteus maximus
|
|
|
Tibial nerve
|
Anterior division of sciatic nerve, runs down posterior aspect of leg.
Innervates posterior compartment of thigh, adductor magnus (post. 1/3), semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris (long head). Branches into medial and lateral plantar nerves. |
|
|
Blood supply to hip and thigh
|
Internal iliac: gluteal compartment via superior and inferior gluteal arteries. Obturator branch continues into medial compartment
External Iliac: continues as femoral artery in anterior compartment of thigh. Femoral artery supplies leg and foot. Deep femoral artery supplies muscles of thigh. |
|
|
Branches of deep femoral artery
|
Lateral femoral circumflex artery, medial femoral circumflex artery, perforating arteries.
|
|
|
Blood supply to head of femur
|
Medial and lateral femoral circumflex arteries form a ring around neck of femur.
|
|
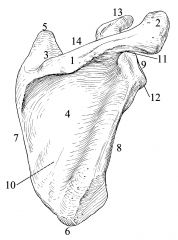
|
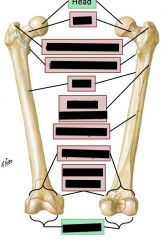
1: Spine
2: Acromion 3: Supraspinatous fossa 4: Infraspinatous fossa 5: Superior angle 6: Inferior angle 7: Vertebral border 8: Axillary border 9: Glenoid fossa 10: Subscapular fossa 11: supraglenoid tubercle 12: Infraglenoid tubercle 13: Coracoid process 14: Scapular/superior notch |
|
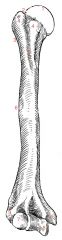
|
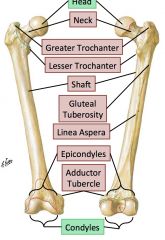
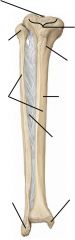
1: head
2: anatomical neck 3: surgical neck 4: greater and lesser tubercles 5: intertubercular groove 6: Deltoid tuberosity 7: Capitulum 8: Trochlea 9: Lateral and medial epicondyles |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
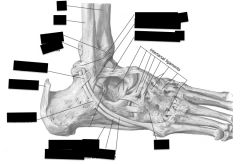
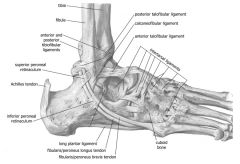
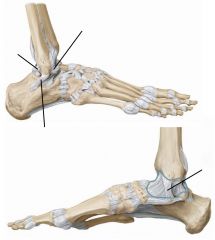
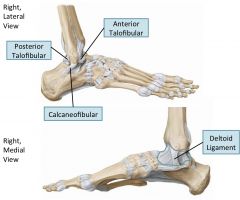
Ankle joint
|
Uniaxial: flexion/extension (dorsiflexion/plantarflexion)
|
|
|
|
|
|
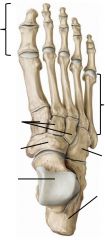
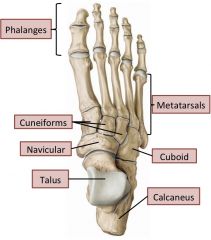
Intertarsal joints
|
Oblique axis: Eversion/Inversion (rolling feet laterally and medially)
"Subtalar joints" Talus articulates with navicular bone and calceneous. |
|
|
Metatarsal and phalangeal joints
|
Transverse: Flexion/extension
Vertical: Abduction/adduction (midline goes throught 2nd digit) |
|
|
Arches of feet
|
2 longitudinal arches, 1 transverse arch.
Supported by long and short plantar ligaments (longitudinal) and calcaneonavicular ligament (transverse), and also some tendons. |
|

|
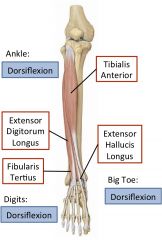
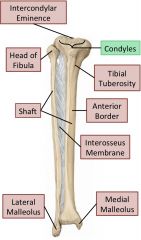
Anterior leg compartment
innervated by deep fibular nerve. |
|
|
common fibular nerve
|
branch of sciatic nerve.
Branches: Superficial fibular (lateral compartment muscles) and deep fibular nerve (anterior compartment muscles) Sensory to lateral leg, dorsum of foot. |
|
|
|
|
|
Eccentric contraction
|
muscle lengthens while doing work
|
|
|
concentric contraction
|
muscle shortens while lengthening
|
|
|
isometric contraction
|
muscle stays same length while working
|
|
|
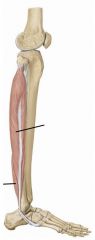
Shin splints
|
Tibialis anterior fibers detach from tibia. Extended overexertion leads to tibial microfractures. Tibialis anterior does concentric, eccentric and isometric contraction.
|
|
|
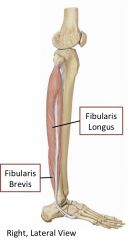
Lateral leg compartment
Ankle: plantarflexion Subtalar joints: eversion Superficial fibular nerve |
|
|
Tibialis anterior
|
Lateral surface of tibia to first cuneiform and first metatarsal.
Dorsiflexor and invertor. |
|
|
Extensor hallucis longus
|
fibula and interosseus membrane to distal phalanx of the big toe.
Extends big toe and dorsiflexes ankle |
|
|
Extensor Digitorum longus
|
Arises from fibula and has four tendons that insert into distal phalanges of lateral toes.
Extends lateral four toes, dorsiflexes ankle |
|
|
Peroneus/Fibularis tertius
|
Belly of extensor digitorum longus muscle to fifth metatarsal.
Dorsiflexes and everts. |
|
|
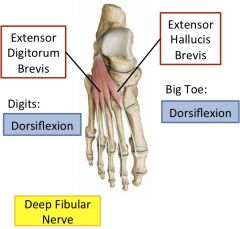
Innervation of anterior leg and foot muscles
|
Deep fibular nerve
Extensor digitorum longus, fibularis tertius, extensor hallucis longus, tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum brevis, extensor hallucis brevis |
|
|
Extensor hallucis brevis
|
attaches to proximal phalanx of big toe, aids extensor hallucis longus
|
|
|
Extensor digitorum brevis
|
attachees to distal phalanges of lateral 3 or 4 toes and aids extensor digitorum longus.
|
|
|
Lateral leg muscles
|
Peroneus/Fibularis longus (superficial) and Peroneus/Fibularis brevis
Evert foot, weak plantarflexion |
|
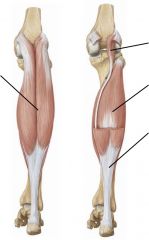
|
Posterior leg muscles: superficial
|
|
|
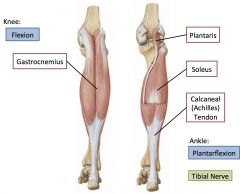
Superficial posterior leg muscles
|
Gastrocnemius, soleus, plantaris, popliteus.
Attach to achilles tendon. Plantarflexion. Tibial nerve |
|
|
Gastrocnemius
|
superficial posterior leg muscle. Plantarflexion, can aid in flexing the knee.
|
|
|
Soleus
|
Superficial posterior leg muscle, deep to gastrocnemius and arises from fibula and tibia. Does not cross knee joint, only dorsalflexion.
|
|
|
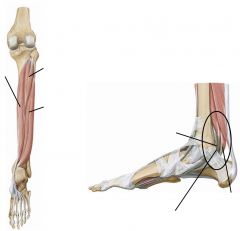
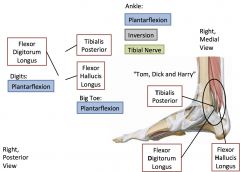
Deep posterior leg muscles
|
Popliteus, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior, flexor hallucis longus, tibialis posterior, flexor digitorum longus, flexor hallucis longus.
Tibial nerve |
|
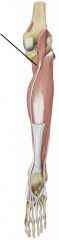
|
Popliteus
Posterior leg muscle deep Tibial nerve Medial rotation of tibia on femur/lateral rotation of femur on tibia |
|
|
|
|
|
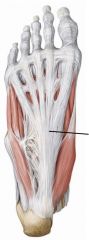
plantar aponeurosis
|
|
|
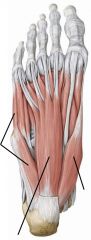
Layer 1 of intrinsic muscles of foot
|
Two abductors and one flexor
Abductor digiti minimi, flexor digitorum brevis, abductor hallucis |
|
|
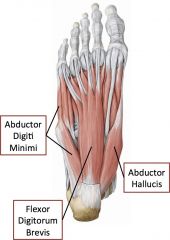
Layer 1 of intrinsic muscles of foot
|
|
|
Layer 2
|
|
|
Layer 3
|
|
|
Layer 4
|
|
|
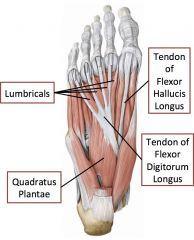
Layer 2 of intrinsic muscles of the foot
|
Tendons and muscles
Lumbricals, tendon of flexor hallucis longus, tendon of flexor digitorum longus |
|
|
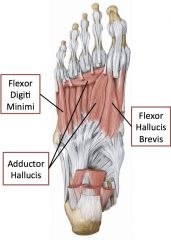
Layer 3 of intrinsic muscles of foot
|
Two flexors and one adductor
Flexor digiti minimi, adductor hallucis, flexor hallucis brevis |
|
|
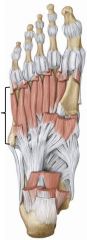
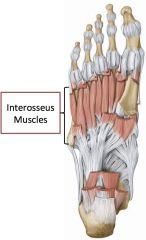
Layer 4 of intrinsic muscles of the foot
|
Bones and muscles
Interosseus muscles (both dorsal and plantar) |
|
|
Innervation of intrinsic muscles of the foot
|
Medial plantar nerve: abductor hallucis, flexor hallucis brevis, flexor digitorum brevis, first lumbrical
Lateral Plantar Nerve: All other intrinsic muscles on plantar surface. |
|
|
Blood supply to leg and foot
|
Femoral --> anterior tibial --> dorsal pedis artery --> dorsal arch
Femoral --> posterior tibial artery --> medial and lateral plantar arteries, also branches to fibular artery. |

