![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
137 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Strengthening which muscles can help to correct lordosis? a. Muscles that retract the scapula
b. Muscles that tilt the pelvis backwards
c. Muscles that protract the scapula
d. Muscles that tilt the pelvis forwards |
b. Muscles that tilt the pelvis backwards |
|
|
Which of the following developmental postural adaptations has the greatest impact upon normal breathing patterns? a. Kyphosis
b. Flat back
c. Lordosis
d. Scoliosis |
a. Kyphosis |
|
|
Which of the following describes the joint between the humerus and ulna? a. A gliding joint allowing supination and pronation
b. A hinge joint allowing flexion and extension
c. A condyloid joint allowing abduction and adduction
d. A pivot joint allowing internal and external rotation |
b. A hinge joint allowing flexion and extension |
|
|
Which of the following is the deepest layer of connective tissue within skeletal muscle?
a. Periosteum
b. Perimysium
c. Epimysium
d. Endomysium |
d. Endomysium |
|
|
Which of the following describes the articulation at the pubis symphysis? a. A cartilaginous joint with limited movement
b. A fixed joint with no movement
c. A synovial joint with excessive movement
d. A saddle joint with free movement |
a. A cartilaginous joint with limited movement |
|
|
Which exercise uses movement in the transverse plane? a. Torso rotation
b. Knee extension
c. Side leg raise
d. Bicep curl |
a. Torso rotation |
|
|
Which of the following best describes the process of motor unit recruitment? a. An efferent nerve impulse triggers some of the fibres in the motor unit to contract
b. An afferent nerve impulse triggers all of the fibres in the motor unit to contract
c. An afferent nerve impulse triggers some of the fibres in the motor unit to contract
d. An efferent nerve impulse triggers all of the fibres in the motor unit to contract |
d. An efferent nerve impulse triggers all of the fibres in the motor unit to contract |
|
|
Which by-product of the energy systems can cause muscle fatigue? a. Hydrogen ions
b. Water
c. Creatine phosphate
d. Oxygen |
a. Hydrogen ions |
|
|
Which of the following is a ‘global’ stabilising muscle of the spine? a. Transverse abdominis
b. External oblique
c. Multifidus
d. Pelvic floor |
b. External oblique |
|
|
What structure forms the junction between a neuron and a target cell? a. Synapse
b. Cell nucleus
c. Axon
d. Cell body |
c. Axon |
|
|
Excessive abdominal adiposity is most associated with what type of postural deviation?
a. Kyphosis
b. Spondylosis
c. Scoliosis
d. Lordosis |
d. Lordosis |
|
|
Which of the following can cause the valsalva effect? a. Dynamic stretching
b. Long duration aerobic training
c. Exercising immediately after a meal
d. Holding breath during exertion |
d. Holding breath during exertion |
|
|
Increased heart rate during exercise is brought about by which of the following? a. Sympathetic action of the somatic nervous system
b. Parasympathetic action of the autonomic nervous system
c. Sympathetic action of the autonomic nervous system
d. Parasympathetic action of the somatic nervous system |
c. Sympathetic action of the autonomic nervous system |
|
|
What common muscle imbalance can develop, leading to insufficient core stabilisation?
a. Dominant and weaker muscles both lengthen
b. Dominant and weaker muscles both tighten
c. Dominant muscles lengthen and weaker muscles tighten
d. Dominant muscles tighten and weaker muscles lengthen |
d. Dominant muscles tighten and weaker muscles lengthen |
|
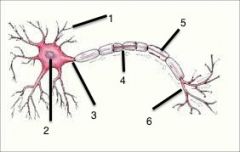
Name the Nerve cell parts |
1. Dendrites- takes stimulus in afferent nerves 2. Nucleus- control centre of the nerves 3. Axon- takes stimulus away efferent nerves 4. Nodes of ranvire- carries waste nutrients 5 myelin sheath, covers axon 6 Axon terminal holds neurotransmitters and chemicle |
|
|
As the agonist contracts, the antagonist muscle relaxes to allow movement. What is this occurrence known as? a. Reciprocal inhibition
b. Golgi tendon organ
c. Passive resistance
d. Inverse stretch reflex |
a. Reciprocal inhibition |
|
|
During the eccentric phase of a press up, what movement occurs at the scapula? a. Protraction
b. Elevation
c. Depression
d. Retraction |
d. Retraction |
|
|
What is the function of muscle spindle cells? a. They respond to excessive lengthening of the muscle
b. They respond to excessive contraction of the muscle
c. They respond to excessive heat within the muscle
d. They respond to excessive lactic acid within the muscle |
a. They respond to excessive lengthening of the muscle |
|
|
What is the role of a motor unit? a. To contract a single muscle in response to a nerve impulse
b. To relax a group of muscle fibres in response to a nerve impulse
c. To contract a group of muscle fibres in response to a nerve impulse
d. To relax a single muscle fibre in response to a nerve impulse |
c. To contract a group of muscle fibres in response to a nerve impulse |
|
|
Where are catecholamines produced? a. Pancreas
b. Adrenal glands
c. Thyroid gland
d. Ovaries |
b. Adrenal glands |
|
|
Improved neuromuscular efficiency can lead to which of the following benefits? a. Better cardiovascular fitness
b. Reduced risk of coronary heart disease
c. Increased bone density
d. Faster reaction times |
d. Faster reaction times |
|
|
Which of the following is a neuromuscular adaptation associated with training? a. Reduced frequency of nerve impulses to motor units
b. Increased need for conscious control of movement
c. Better inter-muscular coordination during movement
d. Unsynchronised recruitment of motor units |
c. Better inter-muscular coordination during movement |
|
|
Which hormone causes the conversion of glycogen to glucose to raise blood sugar level?
a. Testosterone
b. Oestrogen
c. Glucagon
d. Insulin |
c. Glucagon |
|
|
Which of the following best describes onset of blood lactate accumulation (OBLA)? a. The intensity at which lactic acid in the muscles reduces and the aerobic system starts to contribute energy.
b. The intensity at which the lactic acid system provides all of the energy being used.
c. The intensity at which lactate is first produced in the muscles.
d. The intensity at which lactate is being produced in the muscles faster than it can be cleared. |
d. The intensity at which lactate is being produced in the muscles faster than it can be cleared |
|
|
What structures within skeletal muscle tissue bring about contraction? a. Actin and myosin filaments
b. Epimysium and perimysium
c. Tendon and fascia
d. Regular collagen fibres |
a. Actin and myosin filaments |
|
|
What Movement takes place in the Saggital Plane?
|
Flexion & Extension |
|
|
What Movement takes place in the Transverse Plane? |
Rotation |
|
|
What Movement takes place in the Frontal Plane? |
Abduction/ Adduction |
|
|
Which exercise uses movement in the Saggital plane?
a. Bicep Curl B. torso rotation c. abduct the leg d. chest press |
a. Bicep Curl |
|
|
Flexion
a. increases the angle at the joint and occurs in the sagittal plane
B. decreases the angle at the joint and occurs at the sagittal plane
C increases the angle at the joint and occurs in the transverse plane
d. decreases the angle at the joint and occurs in the transverse plane |
B. decreases the angle at the joint and occurs at the sagittal plane |
|
|
Extension
a. increases the angle at the joint and occurs in the sagittal plane
B. decreases the angle at the joint and occurs at the sagittal plane
C increases the angle at the joint and occurs in the transverse plane
d. decreases the angle at the joint and occurs in the transverse plane |
a. increases the angle at the joint and occurs in the sagittal plane |
|
|
What type of joint is a sternoclavicular joint
A.Hinge joint B. Synovial gliding joint with cartilaginous disc C. Synovial saddle joint with cartilaginous disc D. Ball and socket joint |
C. Synovial saddle joint with cartilaginous disc |
|
|
The spine of the scapula, ends in a large bony process called the …..
A. acromion process b. condyloid C. cuneform D. glenoid process |
A. acromion process |
|
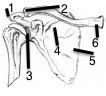
Name the joints |
1 Acromion Process 2 Acromioclavicular Joint 3 Glenhumeral joint 4 Spine of scapula 5 Scapula 6 Sternoclavicular joint |
|
|
Which bone is longer the Radius or Ulna? |
Ulna |
|
|
during extension the head of the humerus hits the trochlear notch preventing
A. hypertension B. Hyperextension C. Hypoplasia D. Hypertrophy |
B. Hyperextension |
|
|
The Radius and the Ulna are connected to each other, both at the proximal and distal ends by a:
A. Hinge joint B. gliding synovial joint C. Synovial pivot joint D Condyloid synovial joint |
C. Synovial pivot joint |
|
|
The radius articulates with two carpel bones to form a A. Hinge joint B. gliding synovial joint C. Synovial pivot joint D Condyloid synovial joint |
D Condyloid synovial joint |
|
|
Condyloid synovial joint allows which movements
A. flexion, extension, abduction, adduction B. Flexion and extension C. abduction, Adduction D. Rotation flexion, extension, abduction, adduction |
A. flexion, extension, abduction, adduction |
|
|
What sort of bones are the vertebrae
A. irregular bones b. Flat bones C long bones D. sesamoid bones |
A. irregular bones |
|
|
The rotator cuff muscles hold the head of the humorous in the glenoid cavity true false |
True |
|
|
The sacrum articulates with;
a. the ischium and pubis b. the fifth lumbar vertebra, and the coccyx c. illium and ischium d. pubis and coccyx |
b. the fifth lumbar vertebra, and the coccyx |
|
|
what sort of joint is the pubis symphysis; a. cartilaginous joint with limited movement b. synovial joint with large range of movement c. inmovable joint, no movement d. cartilaginous joint with large movement |
a. cartilaginous joint with limited movement |
|
|
Hip abductor muscles attach to?
a. Acetabulum b. the lesser trochanter of the femur c. the greater trochanter of the femur |
c. the greater trochanter of the femur |
|
|
The longitudinal arch runs from heel to ball of the foot.
True false |
True |
|
|
Name the local abdominal muscle a. Multifidus, transverse abdominis, internal obliques
b. Rectus abdominis, external obliques, erector spinae
c. Rectus abdominis, Transvers abdominis Exteranl obliques
D pelvic floor, transverse abdominis, Quadratus lumborum |
a. Multifidus, transverse abdominis, internal obliques |
|
|
Name the Global abdominal muscle a. Multifidus, transverse abdominis, internal obliques
b. Rectus abdominis, external obliques, erector spinae
c. Rectus abdominis, Transvers abdominis Exteranl obliques
D pelvic floor, transverse abdominis, Quadratus lumborum |
b. Rectus abdominis, external obliques, erector spinae |
|
|
What muscles originate from Thoraco Lumbar Fascia?
A. external obliques, lattisimus Dorsi, gluteus maximus B. Lattisimus Dorsi, internal obliques, glutus maximus c. Rectus abdominus, lattisimus dorsi, glutus minimus d. rhomboids, internal obliques, glutus maximus |
B. Lattisimus Dorsi, internal obliques, glutus maximus |
|
|
what is lordosis?
A. exaggerated curve in thoracic region b. sideways curvature of the spine C. exaggerated curve of the lumbar spine |
C. exaggerated curve of the lumbar spine |
|
|
what is Kyphosis?
A. exaggerated curve in thoracic region b. sideways curvature of the spine C. curve of the lumbar spine |
A. exaggerated curve in thoracic region |
|
|
what is Scoliosis?
A. exaggerated curve in thoracic region b. sideways curvature of the spine C. curve of the lumbar spine |
b. sideways curvature of the spine |
|
|
which is a complaint of kyphosis?
a. reduced thoracic cavity makes breathing less efficient
b. to much pressure on inter vertebral discs compressing them, low back pain, pelvic imbalance
c. Muscle imbalance
d. Hypertrophy of hamstring weak glutes |
a. reduced thoracic cavity makes breathing less efficient |
|
|
which is a complaint of Lordosis?
a. reduced thoracic cavity makes breathing less efficient
b. to much pressure on inter vertebral discs compressing them, low back pain, pelvic imbalance tilts forwards to much
c. Muscle imbalance
d. headaches tight muscles at the front of the torso weekend muscles in the upper back |
b. to much pressure on inter vertebral discs compressing them, low back pain, pelvic imbalance |
|
|
which is a complaint of Lordosis?
a. reduced thoracic cavity makes breathing less efficient
b. headaches tight muscles at the front of the torso weekend muscles in the upper back
c. Muscle imbalance
d. Hypertrophy of hamstring weak glutes |
d. Hypertrophy of hamstring weak glutes |
|
|
which is a complaint of Kyphosis?
a. Hypertrophy of hamstring weak glutes
b. to much pressure on inter vertebral discs compressing them, low back pain, pelvic imbalance
c. Muscle imbalance
d. headaches tight muscles at the front of the torso weekend muscles in the upper back |
d. headaches tight muscles at the front of the torso weekend muscles in the upper back |
|
|
How would you address strengthening an individual with Lordosis?
a. Strengthern Pectorials, neck flexors, middle and lower trapezious
B. isolateral work, dumbbell and resistance work practice correct alignment
C. focus on tilt of pelvis to find neutral, strengthen external obliques, transverse abdominis, Internal obliques and gluteus
|
C. focus on tilt of pelvis to find neutral, strengthen external obliques, transverse abdominis, Internal obliques and gluteus |
|
|
How would you address strengthening an individual with Kyphosis?
a. Strengthern Pectorials, neck flexors, middle and lower trapezious
B. isolateral work, dumbbell and resistance work practice correct alignment
C. focus on tilt of pelvis to find neutral, strengthen external obliques, transverse abdominis, Internal obliques and gluteus |
a. Strengthern Pectorials, neck flexors, middle and lower trapezious |
|
|
How would you address strengthening an individual with Scoliosis?
a. Strengthern Pectorials, neck flexors, middle and lower trapezious
B. isolateral work, dumbbell and resistance work practice correct alignment
C. focus on tilt of pelvis to find neutral, strengthen external obliques, transverse abdominis, Internal obliques and gluteus |
B. isolateral work, dumbbell and resistance work practice correct alignment |
|
|
Core stability is provided by which systems
a. Passive system, Active system, Neural control
b. Anerobic system, neural control, active system
c. Aerobic system, passive system, neural control
D. Peripheral system, passive system, active system
|
a. Passive system -the spinal column and spinal ligaments |
|
|
What is the passive system? a. uses the structure and arrangement of the vertebrae and discs along with the spinal ligaments to provide stability
b. made up of muscles of the core, that are divided into local and global muscles
c.Proprioceptors play an important role in the sequence that muscles contract in order to prevent unwanted contraction of muscles |
a. uses the structure and arrangement of the vertebrae and discs along with the spinal ligaments to provide stability |
|
|
What is the Active system? a. uses the structure and arrangement of the vertebrae and discs along with the spinal ligaments to provide stability
b. made up of muscles of the core, that are divided into local and global muscles
c.Proprioceptors play an important role in the sequence that muscles contract in order to prevent unwanted contraction of muscles |
b. made up of muscles of the core, that are divided into local and global muscles |
|
|
What is the Neural control? a. uses the structure and arrangement of the vertebrae and discs along with the spinal ligaments to provide stability
b. made up of muscles of the core, that are divided into local and global muscles
c.Proprioceptors play an important role in the sequence that muscles contract in order to prevent unwanted contraction of muscles |
c.Proprioceptors play an important role in the sequence that muscles contract in order to prevent unwanted contraction of muscles |
|
|
What proprioceptors are involved in core stability?
a. stretch reflex, Golgi tendon organs b. muscle spindles of the belly of the muscles, Golgi tendon organs c.muscle spindles of the belly of the muscles, stretch reflex
|
muscle spindles of the belly of the muscles, Golgi tendon organs
|
|
|
What is intra abdominal pressure (IAP)?
a.broard sling of muscles from the pubic bone
b. supporting the spine in flexion by forming an abdominal balloon, by contracting the abdominal muscles and holding the breath
c.a sheet of ligaments tissue covering the lumbar spine and SI joint for core stabilising muscles to attach to
D. pull in the abdominal wall or engage the TVA for the purpose of increasing spine stability
|
b. supporting the spine in flexion by forming an abdominal balloon, by contracting the abdominal muscles and holding the breath |
|
|
What is Thoracolumbar Fascia (TLF) ?
a.broard sling of muscles from the pubic bone
b. supporting the spine in flexion by forming an abdominal balloon, by contracting the abdominal muscles and holding the breath
c.a sheet of ligaments tissue covering the lumbar spine and SI joint for core stabilising muscles to attach to
D. pull in the abdominal wall or engage the TVA for the purpose of increasing spine stability |
c.a sheet of ligaments tissue covering the lumbar spine and SI joint for core stabilising muscles to attach to |
|
|
What is Abdominal Bracing ?
a.broard sling of muscles from the pubic bone
b. supporting the spine in flexion by forming an abdominal balloon, by contracting the abdominal muscles and holding the breath
c.a sheet of ligaments tissue covering the lumbar spine and SI joint for core stabilising muscles to attach to
D. pull in the abdominal wall or engage the TVA for the purpose of increasing spine stability |
D. pull in the abdominal wall or engage the TVA for the purpose of increasing spine stability |
|
|
which statement best describes Proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation (PNF)?
a. a controlled contraction of the muscles immediately prior to it being stretched
b.the individual moves slowly into position until a stretch is felt
c.performed with controlled movements communing range of movement work and muscle warming |
a. a controlled contraction of the muscles immediately prior to it being stretched |
|
|
What nervous system is responsible for controlling involuntary muscles?
a. somatic system b. autonomic system c. sympathetic system d. parasympathetic system |
b. autonomic system |
|
|
The parasympathetic system is a part of?
a. peripheral autonomic system b. peripheral somatic system c. central nervous system d Autonomic sympathetic system
|
a. peripheral autonomic system |
|
|
what are the three functions of the nervous system?
a. Sensory input, interpretation, Motor output b. sensory input, hormone control, motor output c. sensory output, interpretation, motor input |
a. Sensory input, interpretation, Motor output |
|
|
What are the two branches of the nervous system?
a. Sympathetic system and central nervous system b. somatic system and peripheral nervous system c. Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system d. autonomic system and central nervous system |
c. Central nervous system and peripheral nervous system |
|
|
The peripheral nervous system is sub divided in to two further sections.
a. Somatic system and Autonomic system b. somatic system and sympathetic system c. autonomic system and parasympathetic system d. somatic system and parasympathetic system |
a. Somatic system and Autonomic system |
|
|
What are the two branches of the autonomic system?
a. Somatic system and parsympathetic system b. somatic system and sympathetic system c. peripheral system and parasympathetic system d.sympathetic system and parasympathetic system |
d.sympathetic system and parasympathetic system |
|
|
What is the peripheral system responsibility?
a. made up of the brain and spinal cord recies information and interprets and collates information
b. all the incoming nerves which carry sensory information to the CNS via afferent nerves and carry responses to muscles and organs via efferent nerves
c.concerend with changes in the external environment, regulates voluntary body movement through skeletal muscles
d. concerned with changes internal environment, senses hormonal status, controls cardiac and smooth involuntary muscle not under conscious control
e. controls efferent nerves and divided into two divisions
f. increase activity and play a vital role in fight or flight response speeds things up and release a chemical called neurotransmitters adrenaline/ noradrenaline
g. decreasing activity more active during relaxation, slow things down, release a neurotransmitter called acetylchlorine |
b. all the incoming nerves which carry sensory information to the CNS via afferent nerves and carry responses to muscles and organs via efferent nerves |
|
|
What is the Central nervous system responsibility?
a. made up of the brain and spinal cord recies information and interprets and collates information
b. all the incoming nerves which carry sensory information to the CNS via afferent nerves and carry responses to muscles and organs via efferent nerves
c.concerend with changes in the external environment, regulates voluntary body movement through skeletal muscles
d. concerned with changes internal environment, senses hormonal status, controls cardiac and smooth involuntary muscle not under conscious control
e. controls efferent nerves and divided into two divisions
f. increase activity and play a vital role in fight or flight response speeds things up and release a chemical called neurotransmitters adrenaline/ noradrenaline
g. decreasing activity more active during relaxation, slow things down, release a neurotransmitter called acetylchlorine |
a. made up of the brain and spinal cord recies information and interprets and collates information |
|
|
What is the Somatic nervous system responsibility?
a. made up of the brain and spinal cord recies information and interprets and collates information
b. all the incoming nerves which carry sensory information to the CNS via afferent nerves and carry responses to muscles and organs via efferent nerves
c.concerend with changes in the external environment, regulates voluntary body movement through skeletal muscles
d. concerned with changes internal environment, senses hormonal status, controls cardiac and smooth involuntary muscle not under conscious control
e. controls efferent nerves and divided into two divisions
f. increase activity and play a vital role in fight or flight response speeds things up and release a chemical called neurotransmitters adrenaline/ noradrenaline
g. decreasing activity more active during relaxation, slow things down, release a neurotransmitter called acetylchlorine |
c.concerend with changes in the external environment, regulates voluntary body movement through skeletal muscles |
|
|
What is the Autonomic nervous system responsibility?
a. made up of the brain and spinal cord recies information and interprets and collates information
b. all the incoming nerves which carry sensory information to the CNS via afferent nerves and carry responses to muscles and organs via efferent nerves
c.concerend with changes in the external environment, regulates voluntary body movement through skeletal muscles
d. concerned with changes internal environment, senses hormonal status, controls cardiac and smooth involuntary muscle not under conscious control controls efferent nerves and divided into two divisions
e. increase activity and play a vital role in fight or flight response speeds things up and release a chemical called neurotransmitters adrenaline/ noradrenaline
f. decreasing activity more active during relaxation, slow things down, release a neurotransmitter called acetylchlorine |
d. concerned with changes internal environment, senses hormonal status, controls cardiac and smooth involuntary muscle not under conscious control |
|
|
What is the Sympathetic nervous system responsibility?
a. made up of the brain and spinal cord recies information and interprets and collates information
b. all the incoming nerves which carry sensory information to the CNS via afferent nerves and carry responses to muscles and organs via efferent nerves
c.concerend with changes in the external environment, regulates voluntary body movement through skeletal muscles
d. concerned with changes internal environment, senses hormonal status, controls cardiac and smooth involuntary muscle not under conscious control controls efferent nerves and divided into two divisions
e. increase activity and play a vital role in fight or flight response speeds things up and release a chemical called neurotransmitters adrenaline/ noradrenaline
f. decreasing activity more active during relaxation, slow things down, release a neurotransmitter called acetylchlorine |
e. increase activity and play a vital role in fight or flight response speeds things up and release a chemical called neurotransmitters adrenaline/ noradrenaline |
|
|
What is the parasympathetic nervous system responsibility?
a. made up of the brain and spinal cord recies information and interprets and collates information
b. all the incoming nerves which carry sensory information to the CNS via afferent nerves and carry responses to muscles and organs via efferent nerves
c.concerend with changes in the external environment, regulates voluntary body movement through skeletal muscles
d. concerned with changes internal environment, senses hormonal status, controls cardiac and smooth involuntary muscle not under conscious control controls efferent nerves and divided into two divisions
e. increase activity and play a vital role in fight or flight response speeds things up and release a chemical called neurotransmitters adrenaline/ noradrenaline
f. decreasing activity more active during relaxation, slow things down, release a neurotransmitter called acetylchlorine |
f. decreasing activity more active during relaxation, slow things down, release a neurotransmitter called acetylchlorine |
|
|
What do Afferent Nerves do? a. carry incoming information about changes b.interpret and decision making c. carry outgoing information about a response |
a. carry incoming information about changes |
|
|
What do efferent Nerves do? a. carry incoming information about changes b.interpret and decision making c. carry outgoing information about a response |
c. carry outgoing information about a response |
|
|
explain what the sensory receptor chemoreceptor does
a. present in all tissue to detect temperature change
b. found mainly in the walls of arteries to detect change in blood pressure
c. found in muscles and tendons detect changes in body position
d. throughout the body detect changes in levels of chemicals |
d. throughout the body detect changes in levels of chemicals |
|
|
explain what the sensory receptor thermoreceptor does
a. present in all tissue to detect temperature change
b. found mainly in the walls of arteries to detect change in blood pressure
c. found in muscles and tendons detect changes in body position
d. throughout the body detect changes in levels of chemicals |
a. present in all tissue to detect temperature change |
|
|
explain what the sensory receptor baroreceptor does
a. present in all tissue to detect temperature change
b. found mainly in the walls of arteries to detect change in blood pressure
c. found in muscles and tendons detect changes in body position
d. throughout the body detect changes in levels of chemicals |
b. found mainly in the walls of arteries to detect change in blood pressure |
|
|
explain what the sensory receptor proprioceptor does
a. present in all tissue to detect temperature change
b. found mainly in the walls of arteries to detect change in blood pressure
c. found in muscles and tendons detect changes in body position
d. throughout the body detect changes in levels of chemicals |
c. found in muscles and tendons detect changes in body position |
|
|
Waste products leave a neurone via the?
a. axon b. myelin sheath c. Nodes or ranvier d. dendriutes |
c. Nodes or ranvier |
|
|
The neurotransmitters involved in muscle contraction is called?
a. acetylcholline b. andonisine c. glycogen |
a. acetylcholline |
|
|
In order for a nerve impulse to travel along a neurone, the inside of the neurone membrane must be more…… charged than the outside of the neurone membrane
a. positively charged b. negatively charged c. both the same
|
a. positively charged |
|
|
What are synapses? a. gaps between myosin and actin filaments b. gaps between neurones or muscle cells c. the rate or frequency of signals per second
|
b. gaps between neurones or muscle cells |
|
|
Neuron membrane is positively charged inside by?
a. sodium Ions b. potassium Ion c. hydrogen ions |
a. sodium Ions |
|
|
The action potential of a neurone is altered by the passage of sodium and ……. ions in and out of the neurone |
Potassium ions |
|
|
In order for a nerve impulse to travel, the action potential of that neurone must be raise above a certain level called? |
Firing threshold |
|
|
The intensity of a signal received by a muscle is determined by the ….. of the signal |
Frequency |
|
|
Muscle spindles detect the ….. of a muscle |
rate of lengthening |
|
|
You are watching a 400m race the primary energy system being used is?
a. ATP PC system b. Lactic acid system c. Aerobic system |
b. Lactic acid system |
|
|
You are watching a javelin throw the primary energy system being used is?
a. ATP PC system b. Lactic acid system c. Aerobic system |
a. ATP PC system |
|
|
You are watching a marathon the primary energy system being used is?
a. ATP PC system b. Lactic acid system c. Aerobic system |
c. Aerobic system |
|
|
The Lactic acid system lasts
a. 2-3 min b. 10 min c. 3-4 seconds d. 5 min |
a. 2-3 min |
|
|
when strength training you should train at an intensity of around a. 69% b. 75-% c. 95% d. 85% |
c. 95% |
|
|
What does ATP produce when broken down?
a. Energy and Adensoine triphosphate b. energy & lactic acid c. Energy and creatin phosphate
|
a. Energy and Adensoine triphosphate |
|
|
Aerobic training leads to several physiological adaptations such as?
a.increase endurance, increase capilarisation, increase blood volume, stroke volume & increase myoglobin stores
b. Delayed OBLA, tolerate high levels of latic acid, increase muscular strength
c. hypertrophy of muscles, greater storage of ATP, improved motor unit recruitment |
a.increase endurance, increase capilarisation, increase blood volume, stroke volume & increase myoglobin stores |
|
|
Lactic acid system training leads to several physiological adaptations such as?
a.increase endurance, increase capilarisation, increase blood volume, stroke volume & increase myoglobin stores
b. Delayed OBLA, tolerate high levels of latic acid, increase muscular strength
c. hypertrophy of muscles, greater storage of ATP, improved motor unit recruitment |
b. Delayed OBLA, tolerate high levels of latic acid, increase muscular strength |
|
|
ATP pc anaerobic system training leads to several physiological adaptations such as?
a.increase endurance, increase capilarisation, increase blood volume, stroke volume & increase myoglobin stores
b. Delayed OBLA, tolerate high levels of latic acid, increase muscular strength
c. hypertrophy of muscles, greater storage of ATP, improved motor unit recruitment |
c. hypertrophy of muscles, greater storage of ATP, improved motor unit recruitment |
|
|
Pryuvic acid is produced by the …… system
a. ATP PC system b. Aerobic system c. Lactic acid system |
c. Lactic acid system |
|
|
The hormone …… controls growth and development
a. catechoamines b. glucagon c. parathyroid d, Thyroxine |
d, Thyroxine |
|
|
The hormone …… facilitates recovery (parasympathetic activity of the autonomic nervous system)
a. catechoamines b. glucagon c. parathyroid d, Thyroxine |
a. catechoamines |
|
|
The hormone …… regulates levels of calcium in the blood
a. catechoamines b. glucagon c. parathyroid d, Thyroxine |
c. parathyroid |
|
|
The hormone …… responds to falling blood sugar levels
a. catechoamines b. glucagon c. parathyroid d, Thyroxine |
b. glucagon |
|
|
The hormone …… responds to rising blood sugar levels
a. Insulin b. trophic hormone c. Adrenaline d, Corticosteroid |
a. Insulin |
|
|
The hormone …… acts as a messenger and controls other endocrine glands a. Insulin b. trophic hormone c. Adrenaline d, Corticosteroid |
b. trophic hormone |
|
|
The hormone …… prepare the body for fight or flight a. Insulin b. trophic hormone c. Adrenaline d, Corticosteroid |
c. Adrenaline |
|
|
The hormone …… is for every day function levels rise under chronic stress and can have a negative effect on the body a. Insulin b. trophic hormone c. Adrenaline d, Corticosteroid |
d, Corticosteroid |
|
|
The ….. glands are located near the kidneys
a. pituitary b. Adrenal c. parathyroid d.pancreas |
b. Adrenal |
|
|
The ….. glands are located near the hypothalamus in the brain
a. pituitary b. Adrenal c. parathyroid d.pancreas |
a. pituitary |
|
|
The ….. glands are located in the throat on the surface of the thyroid gland
a. pituitary b. Adrenal c. parathyroid d.pancreas |
c. parathyroid |
|
|
The ….. glands are located below the stomach
a. pituitary b. Adrenal c. parathyroid d.pancreas |
d.pancreas |
|
|
Which gland produces hormones that help maintain blood calcium levels?
a. parathyroid b. thyroid c. pancreas d. adreneal |
a.parathyroid |
|
|
Which gland produces hormones that increase metabolism in the cells of the body and promotes growth in children?
a. parathyroid b. thyroid c. pancreas d. adreneal |
b. thyroid |
|
|
Which gland produces hormones that control blood sugar levels and produce enzymes to break down fats?
a. parathyroid b. thyroid c. pancreas d. adreneal |
c. pancreas |
|
|
Which gland produces hormones that respond to fear and excitement ?
a. parathyroid b. thyroid c. pancreas d. adreneal |
d. adreneal |
|
|
The thyroid and parathyroid gland is located in the
a. throat b. base of the brain c. the abdominal cavity d. below the stomach |
a. throat |
|
|
The hypothalamus and pituitary gland is located in the
a. throat b. base of the brain c. the abdominal cavity d. below the stomach |
b. base of the brain |
|
|
The Adrenal gland is located in the
a. throat b. base of the brain c. the abdominal cavity d. below the stomach |
c. the abdominal cavity |
|
|
The Pancreas gland is located in the
a. throat b. base of the brain c. the abdominal cavity d. below the stomach |
d. below the stomach |
|
|
Growth hormone is produced by which gland?
a. adrenaline b. Pituitary c. parathyroid d. Pancreas |
b. Pituitary |
|
|
The endocrine system consists of …. glands which produce hormones |
ductless |
|
|
Local stabiliser muscles sit closer to the spine than global stabiliser muscles
True False |
True Local muscles are deep, global muscle are surface muscles |
|
|
Which of the following muscles do not pull on the thoraco lumbar fascia to provide support to the back a.latisimus dorsi b. internal obliques c.transverse abdominis d. illiopsoas |
d. illiopsoas |
|
|
because ligaments are unable to contract, they do not support the spine
True False |
False |
|
|
which of the following muscles are involved in contribution to intra abdominal pressure
a. Psoas major b. diaphragm c. Pectoralis major d. bicep femoris
|
b. diaphragm |
|
|
Multifidus is a local stabilising muscle
True False |
True |
|
|
a lumbar spine halfway between a flat lower back and arched lower back is A basic definition of a
|
neutral spine |
|
|
Habit and lifestyle can lead to moderate spinal deviations True false |
True |
|
|
Which muscles should be strengthened to improve kyphotic posture?
a. Thoracic section of the erector spine b. the pelvis and lumber spine c. the hamstrings d cervical spine |
a. Thoracic section of the erector spine |
|
|
Which muscles often become shortened with lordotic posture?
a. Hip flexors b. throacic section of the spine c. the quadriceps
|
a. Hip flexors |
|
|
Which of these is seen in a Kyphotic posture posture?
A. muscle imbalance in one side more than the other use isolateral exercises to bring back in balance stretch one limb at a time
b front of the torso becomes tight and weekend muscles in the upper back
c a weak gluteus, pelvis tilts forward to much, abdominals and gluteus maximus are weekend and lengthened , |
c. front of the torso and weekend muscles in the upper back |
|
|
Which of these is seen in a lordosis posture posture?
A. muscle imbalance in one side more than the other use isolateral exercises to bring back in balance stretch one limb at a time
b front of the torso becomes tight and weekend muscles in the upper back
c a weak gluteus, pelvis tilts forward to much, abdominals and gluteus maximus are weekend and lengthened , |
c a weak gluteus, pelvis tilts forward to much, abdominals and gluteus maximus are weekend and lengthened , |

