![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is a tissue? |
a group of similar cells that perform a particular function |
|
|
Four primary tissue types found in the human body? |
Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Neural |
|
|
Primary purpose of epithelial tissue |
Provides protection, transport, sensation, and secretion |
|
|
Basic characteristics that epithelial tissue share |
covers all body surfaces, always has a "free" side, no blood vessels, and reproduce rapidly/heal quickly |
|
|
Three basic epithelial cell shapes |
squamous, cuboidal, columnar |
|
|
Describe and name the two types of layering |
Simple, simple layer of cells covering the basement membrane Stratified, several layer of cells covering the basement membrane |
|
|
Where in the body would simple epithelum be found and why |
Inside of cornea, so light can pass through |
|
|
How about stratified epithelium? |
Skin, for protection and to withstand stress |
|
|
What type of epithelium lines the air sacs of the lungs? Why? |
simple squamous, allows oxygen to go through cells. |
|
|
What are microvilli for? how about cilia |
Microvilli increase surface area for absorption and cilia help move materials (sex cells, mucus) |
|
|
Why is pseudostatified epithelium thus named? |
Looks like it is layered but all cells contact basement membrane |
|
|
What are the three basic components of all types of connective tissue? |
Specialized cells, protein fibers(collagen and elastin), and fluid |
|
|
What are the basic characteristics that connective tissue share |
makes up membrane in the body, not tightly packed, and never exposed to the outside enviroment |
|
|
What are the various functions of connective tissues? |
Support, protection, transport, storage, and defense |
|
|
Difference between tendon and ligament |
Tendons connect muscle to bone and ligaments connect bone to bone |
|
|
What type of connective tissue are tendons and ligaments |
Fibrous connective or dense connective tissue |
|
|
What are fibroblasts, macrophages, and mast cells |
Fibroblast make collagen and elastin, macrophages clean out unwanted particles, and mast cells respond to injury/infection |
|
|
What is collagen? what is elastin? |
Collagen are white fibers and elastin are yellow fibers |
|
|
What are chondrocytes and osteocytes |
Chondrocytes are cartilage cells and osteocytes are bone cells |
|
|
What is the major factor that influences how fast a connective tissue heals? |
blood supply |
|
|
What are the three types of cartilage in the body? |
Hyaline, elastin, and fibro |
|
|
Which type makes up the external ear? the pads between vertabre |
elastin and fibro |
|
|
Which cell is most abundant in blood |
red blood cell |
|
|
What are the three types of muscle tissue found in the body? Where are they found? |
Skeletal-attached to bone, smooth-organs, urinary tract, and blood vessels Cardiac- found in heart |
|
|
What muscle tissue is voluntary? |
skeletal |
|
|
What muscle tissue has striations |
Skeletal and cardiac |
|
|
What muscle tissue has intercalated disks |
Cardiac |
|
|
Number of Nuclei in skeletal? how about smooth and cardiac? |
Skeletal has multiple nuclei and smooth and cardiac both have only one |
|
|
What two fibers make up muscle tissue |
collagen and elastin |
|
|
What is neural tissue for |
Collect stimuli, transmit impulses, and coordinate responses |
|
|
In what order does the impulse pass through the neurons? |
dendrites, cell body, axon, and end brush |
|
|
What are the four signs of inflammation? What causes this? |
Swelling, redness, heat, and pain. Caused by impact, abrasion, chemicals, pathogens, or extreme temperatures |
|
|
How do tissues change as they age? what causes these changes? |
Tissues repair more slowly and there is a thinning of cells |
|
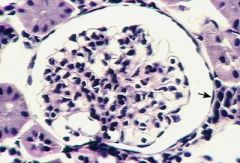
What is this? |
Simple squamous Epithelium |
|
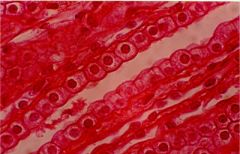
What is this? |
Simple cubiodal epithelium |
|
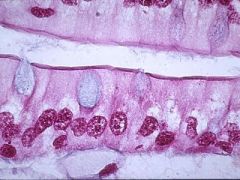
What is this? |
simple columnar epithelium |
|
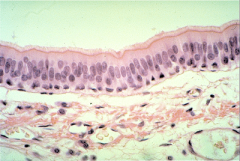
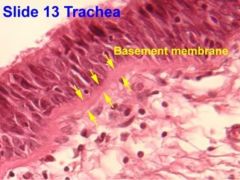
What is this? |
Pseudostratified epithelium |
|
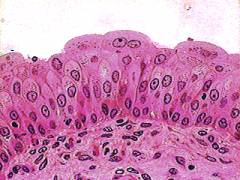
What is this? |
Transitional Epithelium |
|
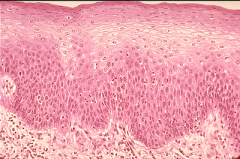
What is this? |
Stratified squamous epithelium |
|
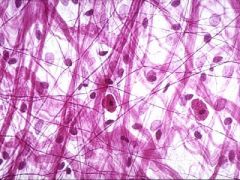
What is this? |
Aerolar tissue |
|
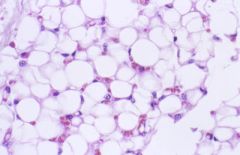
What is this? |
Adipose tissue |
|
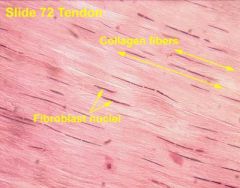
What is this? |
Dense connective tissue |
|
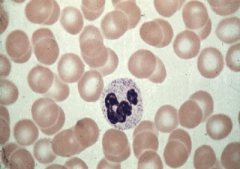
What is this? |
Blood |
|
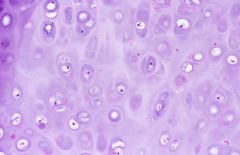
What is this? |
Hyaline cartilage |
|
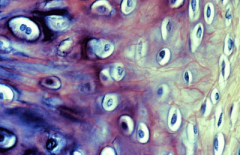
What is this? |
Elastic cartilage |
|
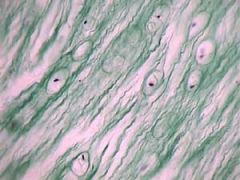
What is this? |
fibro cartilage |
|
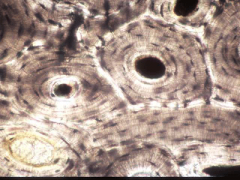
What is this? |
Bone tissue |
|

What is this? |
skeletal muscle |
|
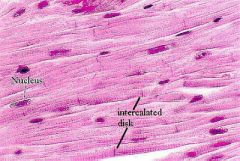
What is this? |
Cardiac muscle |
|
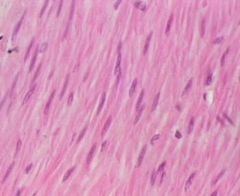
What is this? |
Smooth muscle |
|
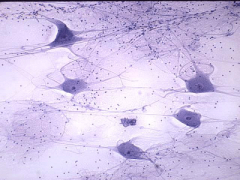
What is this? |
Neural Tissue |
|
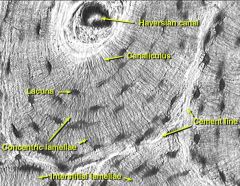
|
Identify structures on a diagram |
|
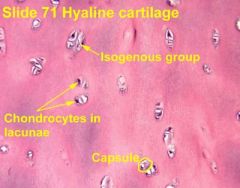
|
Identify structures on a diagram |
|
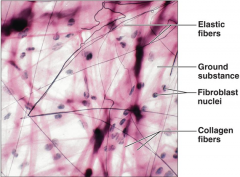
|
Identify structures on a diagram |
|
|
Identify structures on a diagram |

