![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
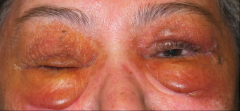
What is this?
What doe it indicate? |
Peri-orbital edema, VERY RARE
SPECIFIC sign for amyloidosis Yellow-brown skin discoloration |
|
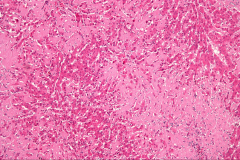
What is shown here?
What physical examination finding correlates with this? |
Deposition of eosinophilic amyloid protein in the sinusoids of the liver.
HEPATOMEGALY (enlarged liver) |
|
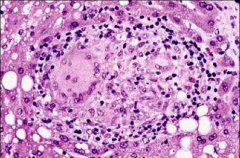
What is shown here?
What will you see high concentrations of in the blood? |
A granuloma (hepatic space occupying disease)
ALP |
|
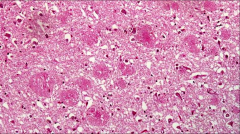
What is the abnormality in this brain tissue?
|
Plaques of eosinophilic material (neuritic processes around a core of AB amyloid)
|
|
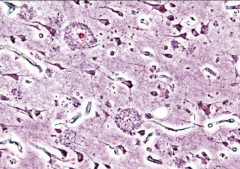
What is shown here?
What symptoms would you see? |
A-beta amyloid in blood vessels of the brain.
Cognitive impairment (dementia) |
|
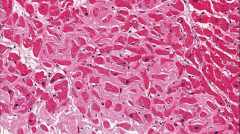
What is shown here?
What is the negative process here? |
Acellular smooth "hyaline" dense eosinophilic INTERSTITIAL deposits in the heart
Pressure atrophy that squeezes the myocytes inhibiting proper contraction of the heart (affects electrical impulses) |
|
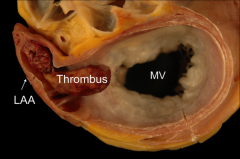
What problems do you see here?
|
1. Abnormal color of heart muscle (characteristic of severe cardiac amyloidosis)
2. Thrombus SYSTEMIC THROMBOEMBOLISM |
|
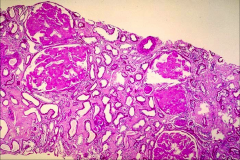
What do you see here?
|
Hyaline deposits in the GLOMERULI (MOSTLY) with some interstitium. Will see them predominantly in the glomeruli.
|
|
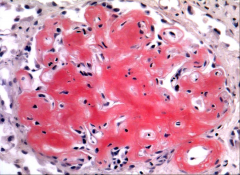
What is this?
|
Congo red stain of amyloid kidney
|
|
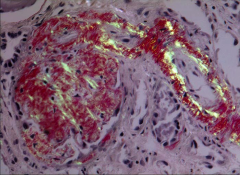
What is this?
|
Congo red stain under polarized light:
APPLE GREEN BIREFRINGENCE |
|
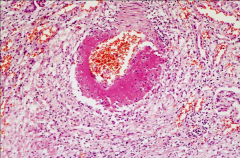
What do you see here?
What can this not be and why? |
Lots of neutrophils, eosinophilic material in an artery possibly
Cannot be amyloidosis because there is inflammation involved. |
|
|
What happens when the frequency of a symptom increases?
|
The specificity of that symptom decreases.
|
|
|
What could peri-orbital edema with BRUISING be a diagnostic tool for?
|
Basal skull fracture
RARELY with amyloidosis because the blood vessels are the first site of amyloid deposits, weakening them, and making them prone to rupture. |
|
|
In what patient population will you predominantly see amyloidosis?
|
Late middle-aged and elderly
|
|
|
What are the two major types of amyloidosis?
|
Primary (MOST COMMON) = AL
Reactive systemic (must be secondary to another chronic disease) = AA |
|
|
What is amyloidosis?
|
Abnormal folding of proteins
All folded into beta-pleated sheets |
|
|
Where is amyloid deposited?
|
BLOOD VESSELS!!!!
glomeruli and interstitium |
|
|
Hepatic amyloidosis (or any other space occupying problem such as neoplasm or granulomas) is most likely to correlate with elevation of serum...?
|
ALP
|
|
|
What are some initial symptoms of amyloidosis?
|
Nonspecific = weakness, weight loss
|
|
|
What are some later symptoms of amyloidosis?
|
Dyspnea, light-headedness, syncope (heart) or edema (kidneys)
|
|
|
What are some presentations of amyloidosis?
|
Heart failure
Renal failure Dementia Peripheral neuropathy --depending on where the deposits are |
|
|
What is cardiac amyloidosis most often due to? What patient population is this often seen in?
How do patients present? |
Transthyretin deposition
Elderly African-American males Sudden death and dyspnea |
|
|
What is the chronic inflammatory disease most likely to cause amyloidosis?
|
Rheumatoid arthritis
|
|
|
What is AL amyloidosis due to?
|
Free immunoglobulin light chains (BENCE JONES) due to proliferation of plasma cells
|
|
|
What are common features associated with AL amyloidosis?
|
Peripheral edema due to renal disease (nephrotic syndrome), weight gain from fluid retention, preceded by nonspecific symptoms like fatigue
|
|
|
What predmoninant microscopic pathology would you see in a patient with AL amyloidosis?
|
GLOMERULAR HYALINE DEPOSITS
|
|
|
What is the diagnosis of amyloidosis?
|
Biopsy
|
|
|
What is the treatment of amyloidosis?
|
Transplantation (potential cure)
Chemotherapy (AL amyloidosis) Eprodisate (soon, AA amyloidosis) PROGNOSIS IS POOR! |

