![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
42 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Anatomical Position |
Standing straight up palms facing forward |
|
|
Supine |
Flat on back |
|
|
Prone |
Patient lying face down |
|
|
Proxmial |
Near the body trunk ( point of reference) |
|
|
Distal |
Further away from body trunk (Point of reference) |
|
|
Inversion |
Turning Inward |
|
|
Eversion |
Turning Outward |
|
|
Anterior |
Front of the body |
|
|
Posterior |
Back of the body |
|
|
Transverse Plane |
Across, seperates superior plane (top) and inferior plane (bottom)
|
|
|
Fowlers Postion |
Lying on back, upper body elevated
|
|
|
Trendlesnberg position |
on back feet elevated
|
|
|
Dorsal |
Toward back or spine |
|
|
Ventral |
Toward front or abdomen |
|
|
Ligament |
Bone to bone |
|
|
Tendon |
Muscle to bone |
|
|
Abduction |
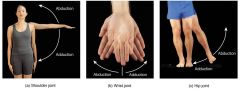
outwards (away from the body)
|
|
|
Adduction |
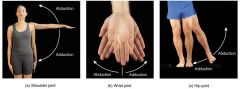
Inwards (towards body)
|
|
|
Synovial Fluid |
Fluid that lubericates joints and prevents friction
|
|
|
Flexion |
Decreasing the angle |
|
|
Extension |
Increasing the angle |
|
|
Medial |
Inwards |
|
|
Lateral |
Outwards |
|
|
Types of Joints |
Freely movable (hip)
Slightly movable (spine)
Immovable (head)
Joints in limbs are either ball and socket (hip)
or hinge (elbow) |
|
|
Types of bones |
Long Bones
Short Bones
Flat bones
Irregular bones |
|
|
Label the main bones in the human body |
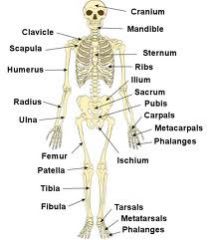
|
|
|
The vertabrea Coloum |
Cervical (neck) 7
Thoratic (rib cage) 12
Lumbar (lower back) 5
Sacrum (pelvis) 5
Coccyx (tailbone) 4 |
|
|
Types of Muscles |
Voluntary (skeletal)
Involuntary (Smooth)
Cardiac |
|
|
Label Respirtaory system |
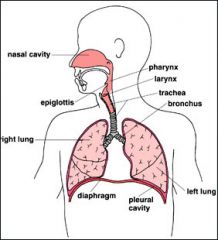
|
|
|
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM, 2 types |
1. motor nerves, carry impulses from the brain
2. sensory nerves, carry impulses to the brain |
|
|
Sympatheic nervous system |
Adreleane "fight or flight"
pupils dilate
inhibits flow of salvia
accels heart beat
dilates bronchi
inhibits bladder contractions
|
|
|
Parasympethic nervous system |
"rest and response" (faint)
Stimulates flow of salvia
slows heartbeat
constricts bronchi
stimulates release of bile
contracts bladder |
|
|
Layers of Skin |
1. Epidermis (top layer) serveral layers of cells
2. Dermis (middle layer) sweat and oil glands sensory nerves blood vessels
3. Subcantoues Tissue (bottom layer) acts as an insulator to retain heat |
|
|
Body Systems (relic n drums) |
Respirtaory system (lungs and treachea that brings air into body)
Excretory system ( Elimates waste from body)
Lympathic system (supplies and drains lympth fluid in support of the cardiovasoular and immune system)
Integumentary system( skin, hair nails sweat)
Cardiovasular system (Circulates blood around the body
Nervous System (collects and processes information)
Digestive system (mechianal and chemical process that provides nutrients via mouth stomach esophagus
Reproductive system ( sex organs)
Urinary system
Muscluar system (enables body to move using muscles)
Sketetal system (bones supporting body and its organs
|
|
|
Organs in digestive system |
R.U.Q
Liver (solid organ): helps food digest, produces a substance called bile, which aids in digestion.
Right Kidney: The primary function of the kidneys is the excretion of waste products resulting from protein metabolism and muscle contraction
Gall Bladder (hollow organ): connected to the underside of the liver, stores bile until required for digestion
Colon (large intenstine, hollow organs) the parts of food that cannot be adsorbed by the body are passed as waste products from the small intenstine to the large intenstine.
Pancreas (solid organ) : produces insulin and pancreatic juices that also aid in digestion
R.L.Q
Appendix
Colon
Small Intestine
Ureter
major vein and artery to right leg
L.U.Q
Stomach (hollow organ) secretes gastric juices that begin to convert food to a form that can be adsorbed by the body
Left Kidney:The primary function of the kidneys is the excretion of waste products resulting from protein metabolism and muscle contraction
Spleen (Solid organ): helps in the production of red blood cells and filtration
Colon
Pancreas (solid organs) produces insulin and pancreatic juices that also aid in digestion
L.L.Q
Colon
Small Intestine
Ureter
major vein and artery to left leg
|
|
|
Intercostals |
contract and open chest cavity
relax and closer chest cavity
|
|
|
Expiration |
Breathing out "positive pressure" active movement of air |
|
|
4 Blood components |
1. Red Blood Cells (erythocytes)
carry oxygen from heart and lungs to other organs
2. White Blood Cells (leukocytes)
part of the immune system, defend againgst disease, virsus, bacteria etc
3. Platelets
responsible for blood clotting, seals cuts and wounds and forms scabs
4 Plasma
clear liquid that the other 3 travel in |
|
|
Pulse Points |
Carotid Pulse (neck)
Brachial Pulse (upper arm)
Radial Pulse (wrist)
Femoral Pulse ( femor)
popitical Pulse (behind knee)
Posterior tibal (inside ankle)
Dorsal pedial (down the middle of foot) |
|
|
label skull and head |
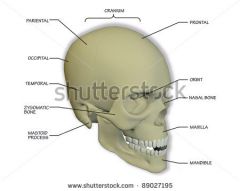
|
|
|
Heart Diagram |
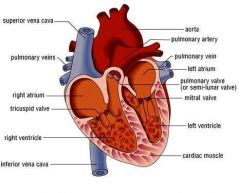
|
|
|
Stomach Diagram |
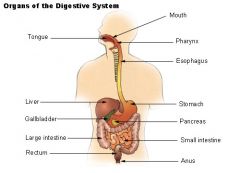
|

