![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
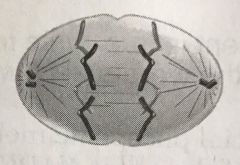
What stage of mitosis is illustrated in the figure? |
anaphase |
|
|
The skeleton of a cell is largely composed of these hollow, rodlike girders called ____.
|
microtubules
|
|
|
Clams, snails, octopuses, and nautiluses are ____.
|
mollusks
|
|
|
The type of endoplasmic reticulum that is involved in protein manufacture ____ ER.
|
rough
|
|
|
A ____ consists of stacks of flattened, membrane-enclosed compartments and is the shipping center of a cell.
|
Golgi apparatus
|
|
|
Microscopic multicellular invertebrates named for the rotating appearance of the cilia on their front ends are ____.
|
rotifers
|
|
|
Euglenas, amoebas, and paramecia are ____.
|
protozoa
|
|
|
Animals characterized by spiny skin and radial symmetry are ____.
|
echinoderms
|
|
|
Jellyfish, sea anemones, and hydra are ____.
|
coelenterates
|
|
|
Planarians, flukes, and tapeworms are ____.
|
flatworms
|
|
|
Earthworms, sea worms, and leeches are ____.
|
segmented worms
|
|
|
What sausage-shaped organelles are the "power plants" of a cell?
|
mitochondria
|
|
|
The ____ states that all living things are composed of cells and cell products and that all cells come from preexisting cells.
|
cell theory
|
|
|
A precious stone formed by an oyster in reaction to an irritating particle is a ____.
|
pearl
|
|
|
The fluid medium of a cell is the ____.
|
cytoplasm
|
|
|
The process by which old, worn-out cells self-destruct is called ____.
|
apoptosis
|
|
|
The coelenterates that live together in colonies and form vast reefs of limestone are the ____.
|
corals
|
|
|
The beltlike or file-like scraping organ in the mouth of a snail or slug is its ____.
|
radula
|
|
|
The outer skin like covering of a mollusk that secretes the shell is the ____.
|
mantle
|
|
|
The rigid, boxlike structure outside the cell membrane of plant cells that provides support and protection is the ____.
|
cell wall
|
|
|
only cephalopod with an external shell
|
nautilus
|
|
|
colorful marine slug with exposed gills
|
nudibranch
|
|
|
protozoan that uses pseudopods to move and engulf prey
|
amoeba
|
|
|
cephalopod with eight arms
|
octopus
|
|
|
protozoan that possesses a flagellum, chloroplasts, and an eyespot
|
euglena
|
|
|
ciliated protozoan that appears slipper-shaped under a microscope
|
paramecium
|
|
|
The stage of the cell cycle between cell divisions is ____.
|
interphase
|
|
|
The special phosphate molecule that serves as the energy carrier of the cell is____.
|
ATP
|
|
|
In what process where a cell engulf a solid particle by surrounding it with the cell membrane?
|
phagocytosis
|
|
|
Which group of invertebrates characterized by a muscular foot, a visceral hump, and a mantle?
|
mollusks
|
|
|
What are the bristles found on each body segment of an earthworm?
|
setae
|
|
|
What molecules that make up the cell membrane?
|
phospholipids
|
|
|
What group includes snails, slugs, conchs, and nudibranchs?
|
gastropods
|
|
|
What sessile animals characterized by spicules, incurrent pores, an osculum, and no nervous system?
|
sponges
|
|
|
What disease is NOT caused by a protozoa?
|
trichinosis
|
|
|
What are sessile protozoa called?
|
sporozoans
|
|
|
What are the only animals with a water-vascular system?
|
echinoderms
|
|
|
What stage of mitosis is illustrated in the figure below?
|
anaphase
|
|
|
Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that studies the structure and reactions of carbon-containing compounds. why would this branch of chemistry be described as "organic", which comes from the same Greek word as the word "organism"?
|
Most of the chemicals that make up living things contain carbon.
|
|
|
What BEST explains why serious infections by parasitic worms are rare in industrialized nations?
|
Proper sanitation prevents the spread of parasitic worms.
|
|
|
Octopuses, squid, and nautiluses are ____.
|
cephalopods |
|
|
The free-swimming, umbrella-shaped form of a coelenterate is a ____.
|
medusa
|
|
|
Facilitated diffusion is a form of ____ transport.
|
passive |
|
|
The process through which living cells produce energy by combining food with oxygen is ____.
|
cellular respiration
|
|
|
The master program of a cell is encoded in the molecules of ____.
|
DNA
|
|
|
The distinct region within the nucleus that manufactures ribosomes is the _____.
|
nucleolus |
|
|
A large, moveable, whiplike tail that extends from a cell and allows it to swim is a _____.
|
flagellum
|
|
|
Clams, oysters, and scallops are ____.
|
bivalves
|
|
|
ESSAY: Contrast cellular respiration and fermentation and explain which process is more efficient. Why do your body's cells use fermentation during intense exercise? |
In cellular respiration, glucose reacts with oxygen to produce ATP. Glycolysis, the first step of cellular respiration, takes place in the cytoplasm and produces the chemical pyruvate and a small amount of ATP. Glycolysis can take place in the absence of oxygen. The remainder of cellular respiration takes place in the mitochondria, where the pyruvate from glycolysis is reacted with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and more ATP.
In fermentation, glucose reacts in the absence of oxygen to produce ATP. Fermentation involves glycolysis (the first step of cellular respiration) but converts the pyruvate into alcohol or lactic acid instead of reacting it with oxygen. Fermentation takes place entirely in the cytoplasm. Cellular respiration is the more efficient process because it produces much more ATP from each glucose molecule than does fermentation. The body's cells use fermentation during intense exercise because their oxygen supply is limited. Because there is not enough oxygen available to produce the large amounts of ATP required through cellular respiration, the cells will make up the difference by producing ATP through fermentation. |

