![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
66 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
diaphragm
|
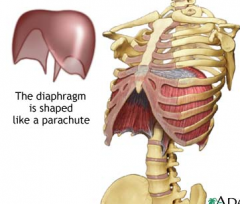
Origin- (where muscle begins) first 3-4 lumbar vertebrae, lower tip of sternum, cartalidge of ribs 7-12
(where muscle begins, attached to none moving object) Course – upward and toward middle Insertion – central tendon (top uppermost of the diaphragm is attached to this) (attached to bone that is moving) Function – contraction of muscles pulls central tendon downward toward the abdominal cavity |
|
|
Diaphragm
|
primary muscle of inhaliation
dome shaped quiet inhalation (80-90% of muscle activity) |
|
|
external intercoastals
|
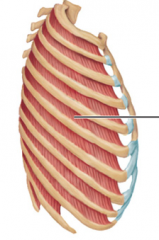
11 pairs
Origin – lower order of each rib (runs between each one of ribs) Course – down and forward Insertion – upper border of rib (top of the rib below) Function – if rib 1 is fixed then they pull ribs closer together and outward Rib one has to be held by the Clavical and scapula in order for these muscles to work |
|
|
pectoralis major
|
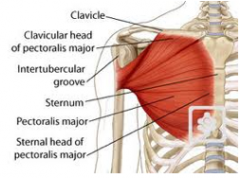
Origin – humerus (upper bone of the arm)
Course- fans out across thorax Insertion – clavicle and (inferior part connects to) sternum, cartilaginous portion of ribs Function – elevates ribs 2 - 5 |
|
|
pectoralis minor
|
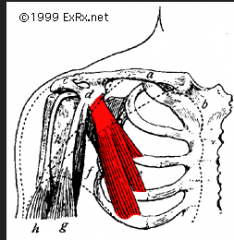
Origin – ant. Scapula
Course – downward and medially Insertion – ribs 2-5 Function – may act to raise ribs it attaches to, if pectoral girdle is fixed |
|
|
Serratus Anterior
|
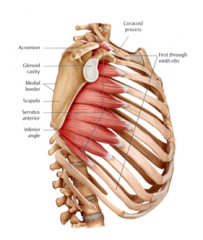
Origin – c3-c6
Course – downwards and forwards Insertion – upper 9 ribs Function – if scapula is fixed, it can raise first 9 ribs |
|
|
Subclavius (under clavical)
|
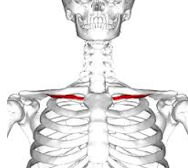
Origin – interior surface of clavicle
Course – downward and medially Insertion – anterior surface of 1st rib Function – fixator muscle – fixes the 1st rib so external intercostals can pull up on rib cage |
|
|
Levatores Costarum
|
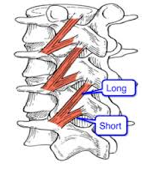
Origin – vertebral column
Course – downward and laternal Insertion – superior/posterior surface of ribs immediately below the vertebrae they originate from Function – assists in lifting the ribs |
|
|
Serratus posterior superior
|
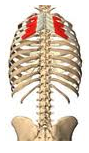
High back muscle
Origin – C7 –T3 Course – downward and lateral Insertion – lower spine and ribs Function – contraction of muscle elevates ribs 2-5 |
|
|
Latissimus Dorsi
|
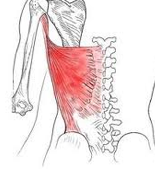
Origin – humerus
Course – downward and medial Insertion – lower spine and lower ribs Function – if arm is fixed, the costal fibers may pull up on rib cage |
|
|
Illiocostalis Cervicus
|
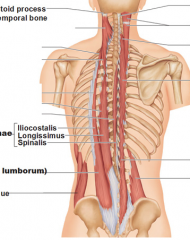
Origin – c4 -6
Course – downward Intersection – upper 6 ribs Function lifts up the upper 6 ribs |
|
|
Sternocleidomastoid (sternum clavical mastoid process)
|
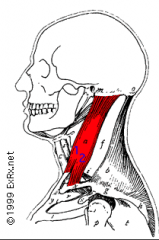
Origin – mastoid process of temporal lobe
Course – downward Insertion – 2 points Clavicular head – to superior surface of clavicle Sternal head – to manubrium of sternum (left and right) Function – main function is to rotate head, but if the head is fixed, then the thorax can be pulled up |
|
|
Scalenus
|
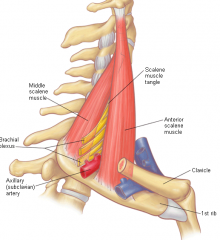
Origin - lower cervical vertebrae (C3-C6)
Course – downward Insertion – 1st and 2nd ribs (fixator muscle for fib one...holds it in place) Function – serves to fix upper ribs so intercostals can pull whole rib cage upward Contraction can lift 1st and 2nd ribs |
|
|
3 passive forces of exhalation (quiet breathing)
|
1. Elastic recoil of the lung tissue (Elasticity)
2. gravity (as the ribs come down they squeeze the lungs a little) 3. untwisting (untorquing) of the costal cartilage |
|
|
Internal intercoastal muscles
|
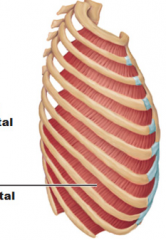
Origin – upper border of ribs 2 thru 12
Course – upwards and medially Insertion – inferior edge of rib abouve Function – (1) interosseous portion – contraction shortens distance between ribs and thereby decreases thoracic volume |
|
|
subcoastals
|
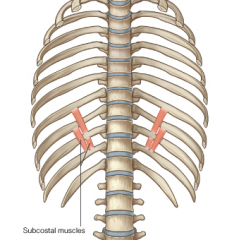
Origin – 2nd or 3rd rib below where it attaches to
Course – superior and lateral Insertion – inner surface of ribs – posterior wall Function – pulls ribs down – aids internal intercoastals |
|
|
transverse thoracis
|
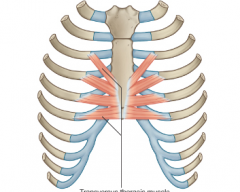
Origin- inner surface of lower sternum
Course – superior and lateral Insertion – ribs 2 – 6 Function – if sternum is fixed, they pull down and decrease thoracic volume |
|
|
rectus abdominis
|
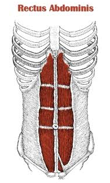
Origin – pubic bone
Course – upward Insertion – sternuma nd costal cartilages of ribs 5 thru 7 Function – (1) pulls downward on sternum (2) compresses abdomen |
|
|
transverse abdominis
(to cross; going across) |
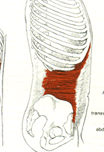
Origin – lower 6 ribs
Course – horizontal around abdomen Insertion – abdominal aporneurosis ( a tendenous sheath which covers the rectus abdominis) Functional – compress abdomen |
|
|
internal abdominal oblique
|
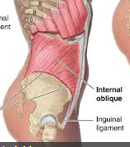
Origin – anterior half of iliac crest
Course – toward midline Insertion – abdominal apneurosis and coastal cartilages of lower 3 ribs Function – (1) compression of abdominal contents pushes up on diaphragm (2) may pull down on lower three ribs |
|
|
external abdominal oblique
|
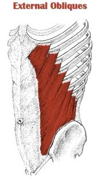
Origin – lower 8 ribs
Course – toward midline Insertion – iliac crest and abdominal aponeurosis Function – compress abdomen, draws lower ribs down |
|
|
serratus posterior inferior
|
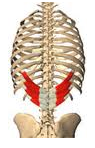
Origin – last 2 thoratic and first 2 lumbar vertebrae
Course – upward and lateral Insertion – posteror of bottom 4 ribs Function – (1) pulls down lower 4 ribs (2) for inhalation – may act as a fixator for ribs when the diaphragm contracts |
|
|
Quadratus lumborum
|
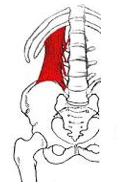
Origin – top of iliac crest
Course – upward Insertion – 12th rib and upper 4 lumbar vertebrae (L1- L4) Function – pulls rib 12 downward (underneath latissimus dorsi) |
|
|
back muscles
(exhalation) |
Latissimus dorsi
Serratus posterior inferior quadratus lumborum |
|
|
Abdominal muscles
(major in exhalation) |
Rectus Abdominis
Transvverse Abdominis Internal Abdominal Oblique External abdominal oblique |
|
|
Chest Muscles
(exhalation) |
Internal intercoastal muscles
Subcostals Transverse thoracis |
|
|
Neck Muscles
accessory muscles of inhalation |
Sternocleido Mastoid
Scalenus |
|
|
Back Muscles
(inhalation) accessory muscles |
Levatores Costarum
Serratus Posterior Superior Latissimus Dorsi Illiocostalis Cervicus |
|
|
Front Muscles
(inhalation) accessory muscles |
Pectoralis Major
Pectoralis Minor Serratus Anterior Subclavius (under clavical) |
|
|
Muscles of Inhalation
|
Diaphram
External Intercoastals |
|
|
Boyle's Law
|
volume and pressure are inversely related
|
|
|
Esohageal Hiatus
Foramen Vena Cava |
Holes in the diaphragm
|
|
|
Which muscles fixate rib 1?
|
Scalenus
Subclavius |
|
|
Egressive air flow
Ingressive air flow |
exhalation/expiration
inhalation/inspiration |
|
|
Respiratory system consists of
|
chest wall
thorax abdomen pulmanary system |
|
|
Thoracic vertebrae
|
12
post. Margin |
|
|
Sternum
|
(breast bone)
Manubraiaum Corpus Xiphoid process |
|
|
Manubraiaum
|
the point of attachment for the clavical
|
|
|
Corpus
|
Main part of the sternum
|
|
|
Xiphoid process
|
little part of bone on the bottom of the sternum
|
|
|
Ribs
|
12 pair
true ribs (1 - 7) false ribs (8 - 10) floating ribs (11 & 12) |
|
|
Pectoral Girdle
|
Scapula
Sternum Clavicle |
|
|
True Ribs
|
1 - 7
attach to the sternum thru cartalidge |
|
|
False Ribs
|
8 - 10
connect to sternum throu |
|
|
Floating ribs
|
11 & 12
do not attach to sternum |
|
|
Anything in front of _______ is considered abdomen
|
Lumbar Vertibrae
|
|
|
Pulmonary system
|
Tubes in the lungs, lunges and all tubes that connect the lungs to the outside air
|
|
|
Trachea
|
(windpipe)
runs below larynx and into chest cavity horseshoe shaped cartalidge rings...open in back..elastic cartalidge in between |
|
|
Trachea splits into two other tubes called ________
|
Bronchi
|
|
|
Bronchi
|
Two primary -- left and right main bronchi
left lung divides out into two secondary right branches into 3 secondary |
|
|
Mainstream Bronchi
|
Left and right secondary bronchi
feed each one of the five indipendant lobes in the lungs |
|
|
plural lining
|
pulmonary pleura
costal pleura plural linkage |
|
|
pulmonary pleura
|
smooth lines
|
|
|
costal pleura
|
line the inside of the rib cage
|
|
|
Plural Linkage
|
two pleura are stuck together ny the negitive pressure between them
|
|
|
Basic components of ribs
|
head (attaches to spine)
neck tubercle angle shaft of rib |
|
|
patent airway
|
open airway
most open if you tip your head back a little |
|
|
Respiratory cycle
|
One full inhalation
|
|
|
Forced respiration
Quiet resperation |
40% - 60% balance
|
|
|
Resting expiratory level
|
Point where all of the muscles are relaxed...when forces of expiration are all done
|
|
|
Vital Capacity
|
all of the air you could breathe in and out
male 4 -5 liters female 3 - 4 liters |
|
|
Tidal Volume
|
Volume of air actually used
|
|
|
Inspiratory reserve
|
amount of air you could breathe in beyond a given peak tidal volume...up to the max of your vital capacity
|
|
|
Expiratory reserve
|
the amount of air exhaled at the lower peak or tidal volume
|
|
|
Residual volume
|
volume of air remaining in lungs after maximum exhalation
20% of vital capacity |
|
|
Total lung volume
|
vital capacity plus the residual volume
4 liters + 20% |

