![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
126 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an event occurring in the external environment or in the internal environment that cannot be detected by the body called? |
Stimulus
|
|
|
What are structures that detect stimuli?
|
Receptors
|
|
|
What are the three types of receptors?
|
Exteroceptor, interoceptors, proprioceptors.
|
|
|
What do Exteroceptors detect?
|
External stimuli
|
|
|
where are Exteroceptors located?
|
Near, or at the surface of the body.
|
|
|
What do Interoceptors detect?
|
Internal stimuli
|
|
|
Where are interoceptors located
|
Viscera,
blood vessels, nervous system. |
|
|
What do Proprioceptors detect?
|
Stimuli arising specifically from the musculoskeletal organs
|
|
|
Where are proprioceptors located
|
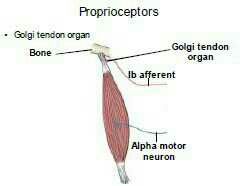
Skeletal muscles,
tendons, joints. |
|
|
What do you call a reaction to a specific stimulus
|
Response
|
|
|
What are the structures called that carry out responses
|
Effectors
|
|
|
What are action potentials
|
Muscle impulses, nerve impulses.
|
|
|
How many action potentials are there?
|
2.
(muscle impulses, nerve impulses) |
|
|
What is a muscle impulse
|
Action potential in muscle cells
|
|
|
What is a nerve impulse
|
Action potential in nerve cells
|
|
|
What are cells that conduct action potentials
|
Excitable cells
|
|
|
What cells do not conduct action potentials
|
Non excitable cells
|
|
|
How many divisions does the nervous system have
|
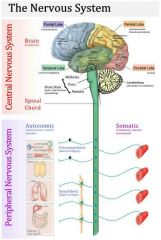
Two main divisions
(PNS and CNS) |
|
|
What are the two main divisions of the nervous system
|
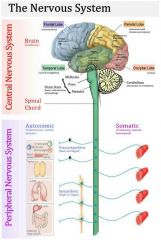
Peripheral nervous system, central nervous system.
|
|
|
What is the peripheral nervous system consist of
|
Nerves and ganglia.
|
|
|
What does the central nervous system consist of
|
Brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
What are nerves
|
Bundles of axons wrapped in connective tissue
|
|
|
What are ganglia
|
Clusters of cell bodies
|
|
|
What are bundles of axons in the CNS called
|
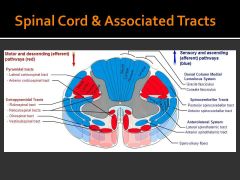
Tracts
|
|
|
What are tracts
|
Bundles of axons in central nervous system
|
|
|
what are clusters of cell bodies referred to as?
|
Nuclei
|
|
|
what does a nuclei consist of
|
Clusters of cell bodies
|
|
|
What is the master controlling and communicating system of the body
|
Nervous system
|
|
|
What is the nervous system
|
Master controlling and communicating system of the body
|
|
|
What are the three main functions of the nervous system
|
Sensory input, integration, motor output.
|
|
|
What is sensory input
|
Receptors send action potentials to the CNS via the PNS
|
|
|
what is integration
|
CNS processes the sensory information from receptors
|
|
|
What is motor output
|
The CNS sends action potentials via the PNS to effectors that carry out appropriate responses
|
|
|
Nervous tissue consists of how many cell types
|
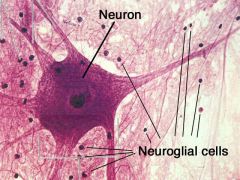
2.
(neuroglial cells, neurons) |
|
|
What are the two cell types that make up nervous tissue
|
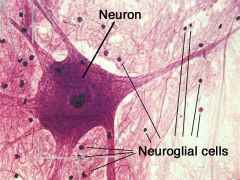
Neuroglial cells and neurons
|
|
|
What are neuroglial cells
|
Non excitable cells that serve various accessory functions in the nervous system
|
|
|
What are non excitable cells that serve various accessory functions in the nervous system
|
Neuroglial cells
|
|
|
What are neurons
|
Excitable cells that transmit nerve impulses
|
|
|
What excitable cells transmit nerve impulses
|
Neurons
|
|
|
What is the most abundant neuroglia in the CNS
|
Astrocytes
|
|
|
What are the functions of astrocytes
|
Support neurons,
maintain the blood brain barrier. |
|
|
What does the blood brain barrier do? |
Secretes chemicals that increases the selectivity of the capillary walls in the brain
|
|
|
True or false. brain tissue is replaceable
|
false
|
|
|
What is the blood brain barrier ineffective against
|
Fat soluble substances
|
|
|
What is microglia
|
Macrophages that develop from monocytes
|
|
|
What does microglia do
|
Performs complete checkups on CNS nervous tissue several times a day.
|
|
|
Where do microglia become concentrated
|
In areas damaged by infection, trauma, or stroke.
|
|
|
Where can Ependymal cells be found?
|
Lining the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord.
|
|
|
ependymal cells produce what?
|
Cerebrospinal fluid
|
|
|
What has processes that reach out to the axons of the neurons in the CNS
|
Oligodendrocytes
|
|
|
The processes of oligodendrocyte rap repeatedly around a portion of an axon to create what
|
Myelin sheath
|
|
|
True or false. oligodendrocyte slow down the conduction of action potentials.
|
false
|
|
|
What are the only glial cells in the PNS?
|
Schwann cells and satellite cells
|
|
|
What forms a myelin sheath around axons in nerves
|
Schwann cells
|
|
|
What is the function of the myelin sheath
|
Insulate axon, speed up the transmission of action potential along the axon
|
|
|
What is it called when the immune system attacks the myelin sheaths, reducing them to nonfunctional hardened lesions.
|
Multiple sclerosis
|
|
|
What are the common symptoms of multiple sclerosis
|
Visual disturbances and problems controlling muscles
|
|
|
Why can't axon repair occur in the central nervous system
|
no Schwann cells
|
|
|
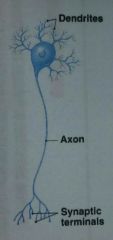
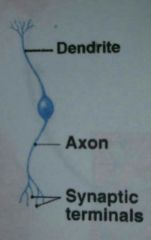
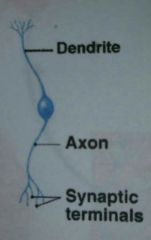
What are neuron processes?
|
Dendrites and axon
|
|
|
The term nerve fiber refers to what
|
Axon
|
|
|
What part of a neuron contains the nucleus
|
cell body (soma)
|
|
|
How are neurons classified
|
Structurally and functionally
|
|
|
How are neurons classified structurally
|
According to the number of processes(axons) directly connected to the cell body
|
|
|
How are neurons classified functionally
|
According to where they carry action potentials
|
|
|
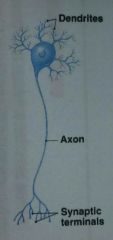
Multipolar neuron
|
|

|

Unipolar neuron
|
|
|
Bipolar neuron
|
|
|
What is the function of sensory neurons
|
Transmit action potentials to central nervous system from receptors
|
|
|
How many types of sensory neurons are there
|
2.
(somatic sensory neurons, and visceral sensory neurons) |
|
|
What are the two types of sensory neurons
|
Somatic sensory neurons and visceral sensory neurons
|
|
|
What is the function of somatic sensory neurons
|
Transmit action potentials to central nervous system from exteroceptors and proprioceptors.
|
|
|
What is the function of visceral sensory neurons
|
Transmit action potentials to central nervous system from interoceptors
|
|
|
What is the function of interneurons
|
Transmit action potentials within the central nervous system
|
|
|
What is the function of motor neurons
|
Transmit action potentials from the central nervous system to the effectors
|
|
|
How many types of motor neurons are there?
|
2.
(somatic motor neurons and visceral motor neurons) |
|
|
What are the two types of motor neurons
|
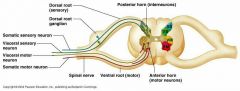
Somatic and visceral motor neurons
|
|
|
What is the function of somatic motor neurons
|
Transmit action potentials from central nervous system to skeletal muscles and skin
|
|
|
What is the function of visceral motor neurons
|
Transmits action potentials from central nervous system to viscera, blood vessels, and glands.
|
|
|
What does sensory neurons synapse with?
|
Interneurons
|
|
|
True or false. dendrites soma and axon of the interner on are all located in the CNS
|
True
|
|
|
Where are the dendrites and Soma of a motor neuron located
|
Central nervous system
|
|
|
The dendrites of a neuron function as what
|
The receptive region of a neuron
|
|
|
What part of a neuron along with dendrites serve as a receptive region
|
Cell body
|
|
|
What is the axon hillock
|
Where the axon attaches to the cell body
|
|
|
What is another name for the cell body
|
Soma
|
|
|
What is the function of an axon
|
To generate in conduct action potentials
|
|
|
What is the portion of the axon immediately distal to the axon hillock called
|
Initial segment
|
|
|
What is the plasma membrane of an axon called
|
Axolemma
|
|
|
the section of the neuron that form synapses with other neurons and effector cells is called what?
|
Axon terminals
|
|
|
What is a synapse
|
The junction between two neurons or between a neuron and an effector cell
|
|
|
The junction between two neurons or between a neuron and effector cell is called what
|
Synapse
|
|
|
What is a presynaptic neuron
|
Neuron before a given synapse
|
|
|
What do you call a neuron before a given synapse
|
Presynaptic neuron
|
|
|
What is a postsynaptic neuron
|
Neuron after a given synapse
|
|
|
What is a neuron after a given synapse
|
Postsynaptic neuron
|
|
|
How are neurotransmitters effects terminated
|
Reuptake through transport proteins, enzymatic degradation, or diffusion away from the synapse.
|
|
|
How are nerves classified
|
Functionally and structurally
|
|
|
How are nerves classified functionally
|
according to the direction their axons transmit action potentials
|
|
|
How are nerves classified structurally
|
According to whether they arise from the brain or the spinal cord
|
|
|
What is the direction of impulse for motor nerves
|
Central nervous system to effectors
|
|
|
What type of nerve fibers are in motor nerves
|
Motor axons
|
|
|
What is direction of impulse in sensory nerves
|
Receptors to central nervous system
|
|
|
What type of nerve fibers are in sensory nerves
|
Sensory axons
|
|
|
What is the direction of impulse in mixed nerves
|
To and from central nervous system
|
|
|
What type of nerve fibers are in mixed nerves
|
Motor and sensory axons
|
|
|
what nerves arise from the brain
|
Cranial nerves
|
|
|
how many nerves make up cranial nerves
|
12 pairs
|
|
|
cranial nerves serve what area of the body
|
Cephalic, cervical regions and viscera
|
|
|
What are the functions of cranial nerves
|
Sensory, mixed, and motor.
|
|
|
What nerves arise from the spinal cord via the fusion of the dorsal and ventral roots
|
Spinal nerves
|
|
|
How many spinal nerves are there
|
31 pairs
|
|
|
What body areas do the spinal nerves serve
|
All regions of the body
|
|
|
What is the function of spinal nerves
|
All mixed
|
|
|
Name the cranial nerves
|
Olfactory, Optic, Oculomotor, Trochlear, Trigeminal, Abducens, Facial, Vestibulocochlear, Glossopharyngeal, Vargus, Accessory, and Hypoglossal Nerves
|
|
|
How many motor nerves are in the brain
|
5.
(Oculomotor, Trochlear, Abducens, Accessory, Hypoglossal) |
|
|
How many sensory nerves are in the brain
|
3.
(Olfactory, Optic, Vestibulocochlear) |
|
|
How many mixed nerves does the brain have
|
3.
(Trigeminal, Facial, Glossopharyngeal) |
|
|
What are the motor nerves of the brain
|
Oculomotor, trochlear, abducens, accessory, hypoglossal.
|
|
|
What are the sensory nerves of the brain
|
Olfactory, Optic, Vestibulocochlear nerves
|
|
|
What nerves of the brain are mixed nerves
|
Trigeminal, Facial, Glossopharyngeal nerves.
|
|
|
Dorsal roots contain what type of axons
|
Sensory axons
|
|
|
Ventral roots contain what type of axons
|
Motor axons
|
|
|
Spinal nerves contain what type of axons
|
sensory and motor axons
|
|
|
How do spinal nerves penetrate the vertebral column
|
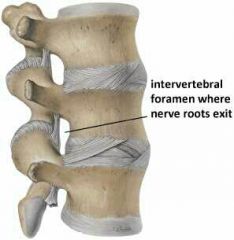
Through intervertebral foramina
|
|
|
What type of axons do Rami have
|
Motor and sensory axons
|
|
|
which Remi serves the skin and musculature of the posterior trunk at their proximal level of emergence
|
Dorsal Rami
|

